Mobile communication system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
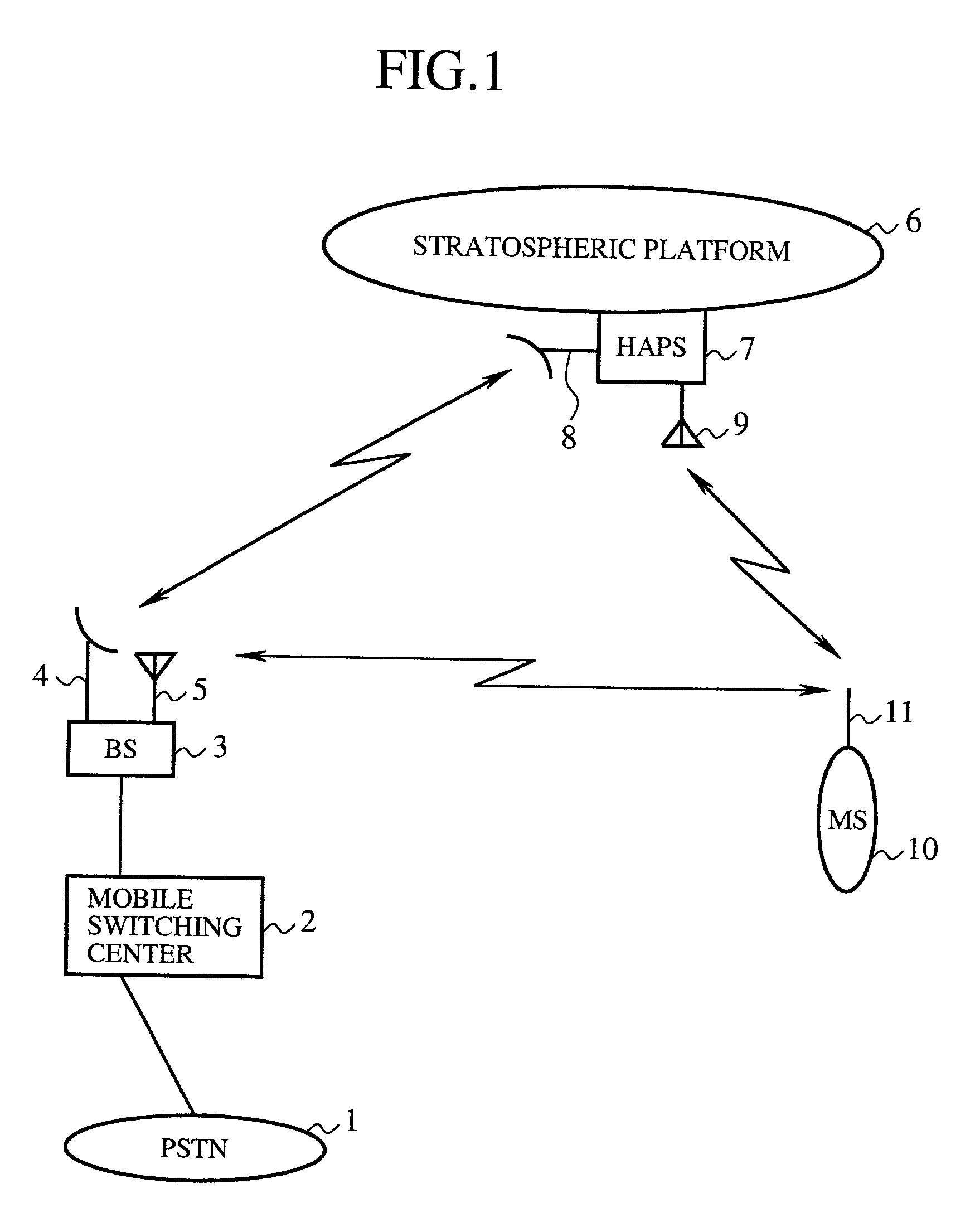
[0053] FIG. 1 is a constitutional diagram showing a mobile communication system according to the present invention. In FIG. 1, 1 indicates a public switching telephone network (PSTN). 2 indicates a mobile switching center, wire-connected with the PSTN 1, for controlling a ground radio base station 3. 3 indicates the ground radio base station (BS), arranged on the ground, for performing a two-way communication of information with a stratospheric platform base station 7 and performing a two-way communication of information with a subscriber station 10. 4 indicates a directional antenna for performing a radio communication with the stratospheric platform base station 7. 5 indicates an antenna for performing a radio communication with the subscriber station 10.
[0054] 6 indicates a stratospheric platform which is halted at an elevation of about 20 km from the ground (automatically halted at a prescribed position while using a power of propellers against a wind which is a low-density air ...
embodiment 2
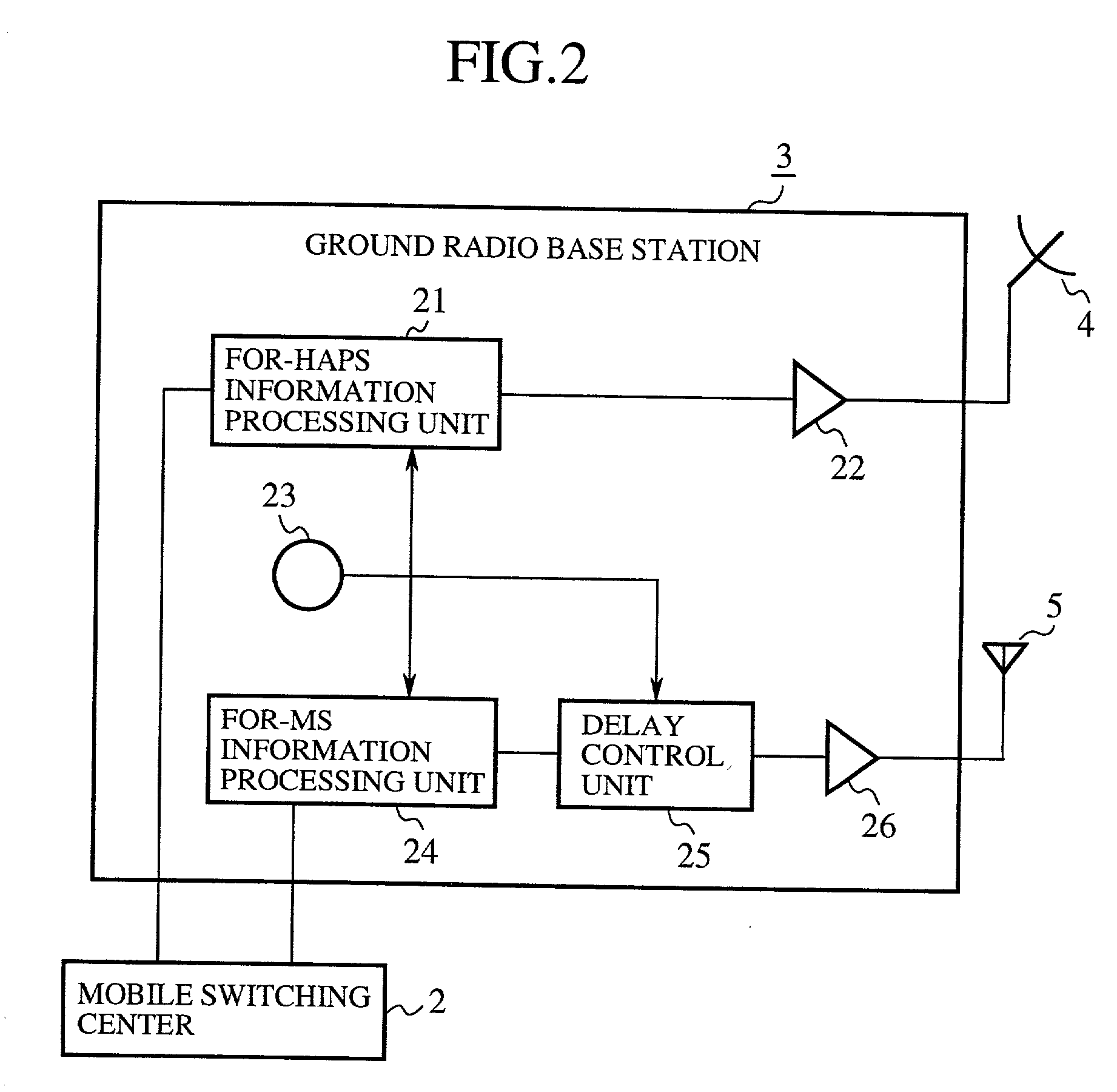
[0089] FIG. 5 is a constitutional diagram showing a main portion of the subscriber station 10 of a mobile communication system according to a second embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 5, 31 indicates an amplifier for amplifying the radio wave received in the antenna 11. 32 to 34 indicate a plurality of time slot detectors for respectively detecting time slots from the radio wave amplified in the amplifier 31. In the example shown in FIG. 5, a plurality of time slot detectors, of which the number is n, are prepared. 35 to 37 indicate a plurality of information detectors for respectively detecting information from the time slots detected in the corresponding time slot detector 32, 33 or 34, 38 indicates a delay time measuring unit for detecting a time difference (or a phase difference) between the time slots detected in the time slot detectors 32 to 34 and transmitting information of the phase difference to the delay control unit 25 of the ground radio base station 3.
[0090] ...
embodiment 3
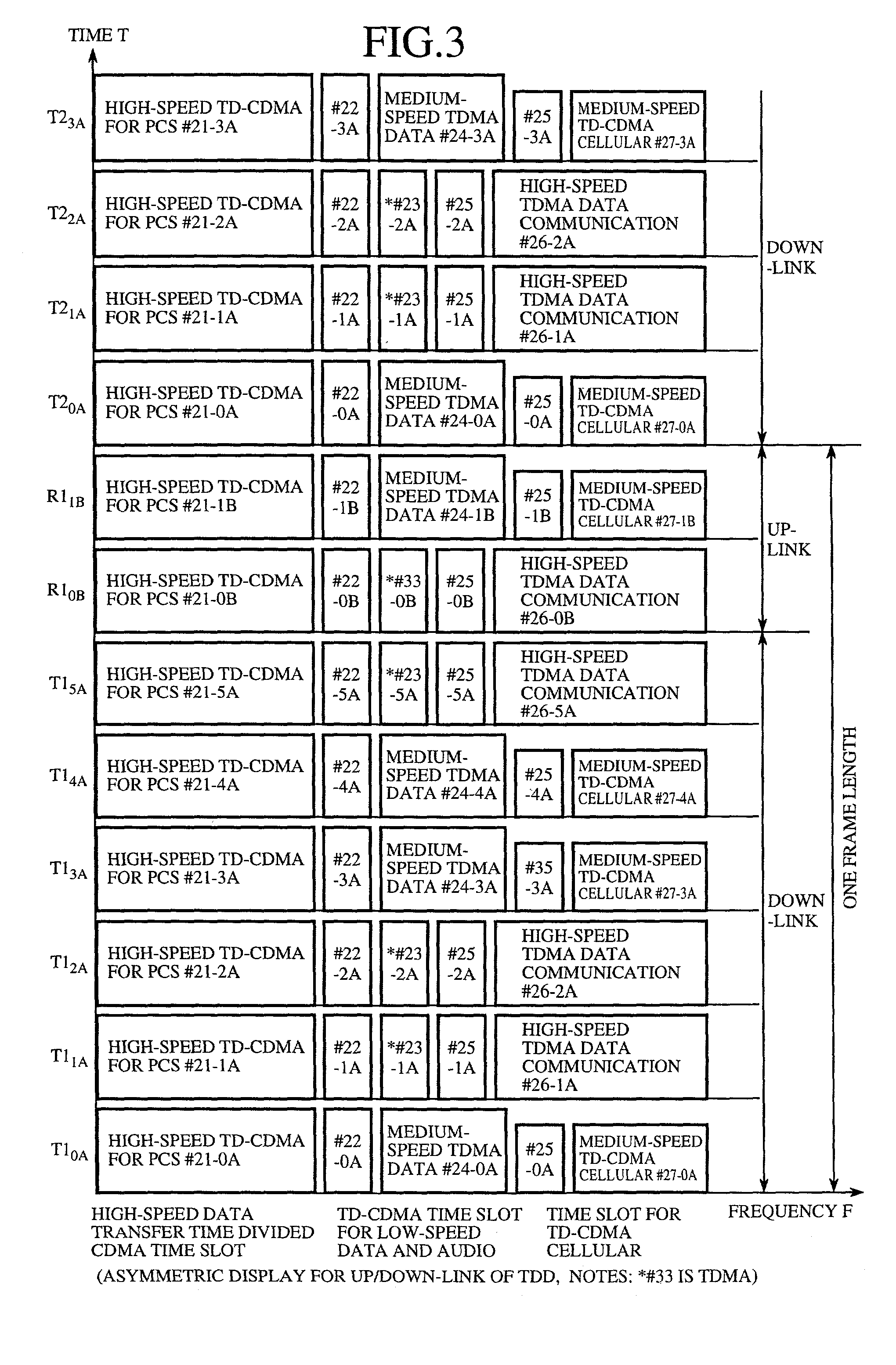
[0100] In the second embodiment, the subscriber station 10 has one delay time measuring unit 38 (or one phase detecting unit), and the phase difference information is transmitted to the ground radio base station 3. However, in cases where a subscriber station can perform an information communication not only with one set of the ground radio base station 3 and the stratospheric platform base station 7 but also with a set of a plurality of ground radio base stations 3 and the stratospheric platform base station 7, it is applicable that a plurality of delay time measuring units 38 be arranged in the subscriber station 10 to transmit pieces of phase difference information to the plurality of ground radio base stations 3.
[0101] Therefore, even though the subscriber station 10 moves to a zone of an adjacent ground radio base station 3 during the communication, communication turbulence can be suppressed. That is, the subscriber station 10 can hand over phase difference information to anoth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com