Method for making chemically cross-linked cellulosic fiber in the sheet form
a cellulosic fiber and sheet form technology, applied in papermaking, non-fibrous pulp addition, bandages, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitable applications, time-consuming process, and high cost, and achieve enhanced bulking characteristics, long shelf life, and high stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0090] This example illustrates a method for making mercerized fibers and a method for forming handsheets from a blend of mercerized and Rayfloc®-J-LD fibers.
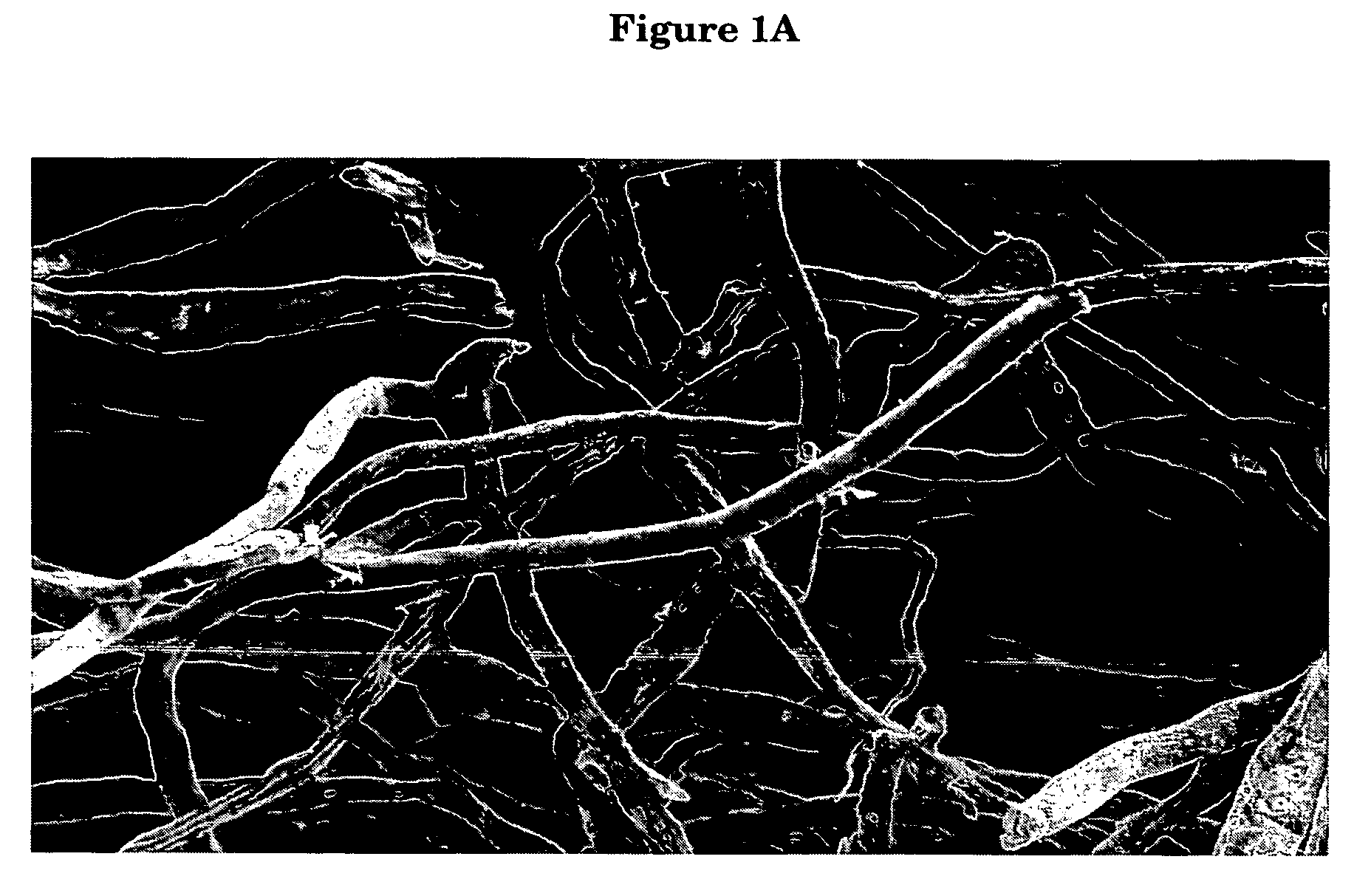
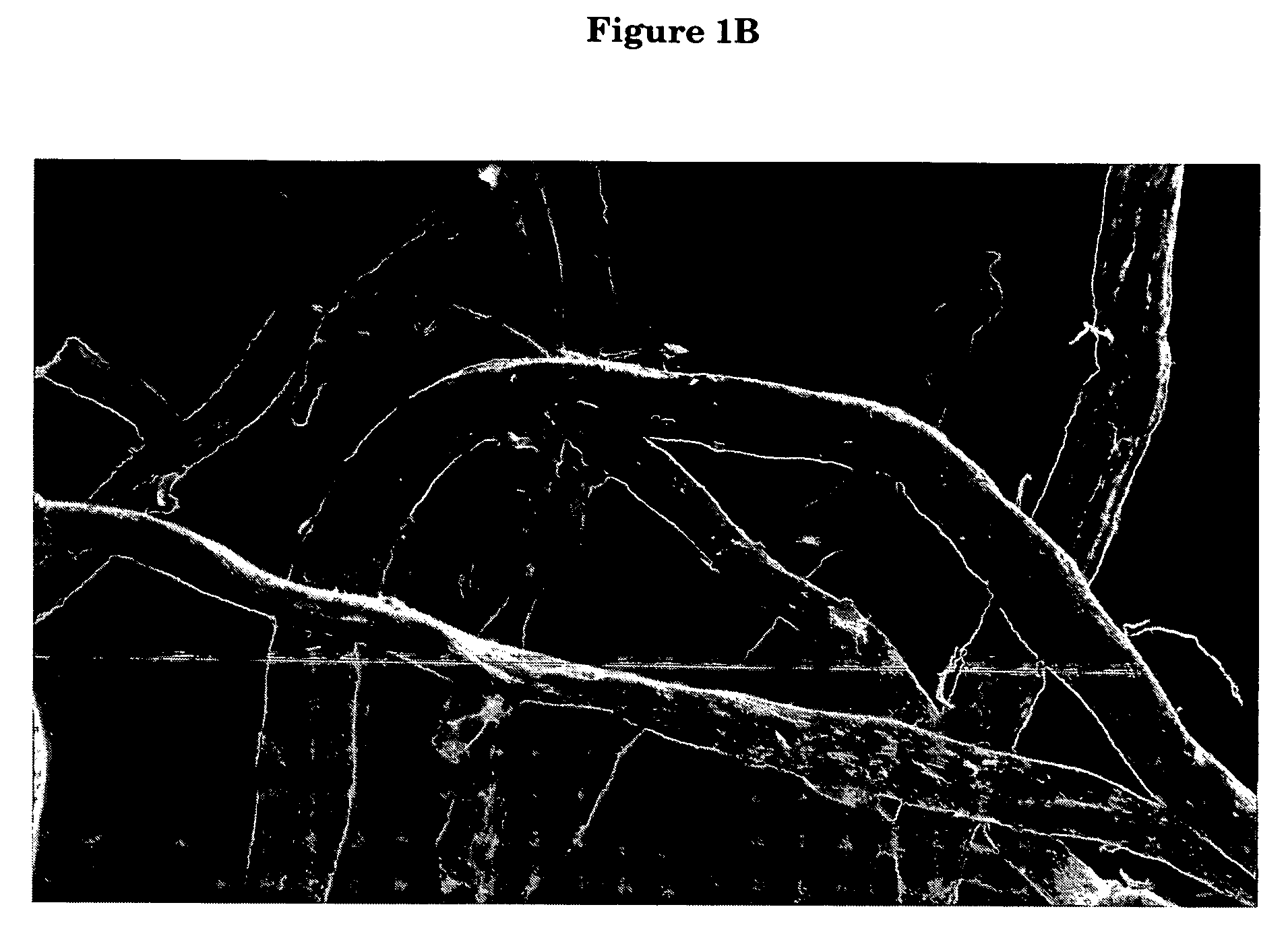
[0091] Fiber mercerization was carried out as follows: A sample of Rayfloc®-J-LD (never dried) was obtained as a 33.7% solid wet lap from the Rayonier mill at Jesup, Ga. Rayfloc®-J-LD is an untreated southern pine Kraft pulp commercially available from Rayonier Performance Fibers Division, Jesup, Ga. A 70.0 g (dry weight base) sample of Rayfloc®-J-LD was treated with an aqueous solution of 16% (w / w) sodium hydroxide at room temperature at a consistency of about 3.5%. The mixture was agitated for about 10 min; then excess NaOH was removed by suction filtration or centrifuge. The resulting mercerized pulp then was washed with excess water, neutralized to a pH of 6.4 with acetic acid solution (0.01 M) at a consistency of about 3.5%, and optionally sheeted and dried.
[0092] Handsheets of blends of fibers then were formed by thorou...
example 2
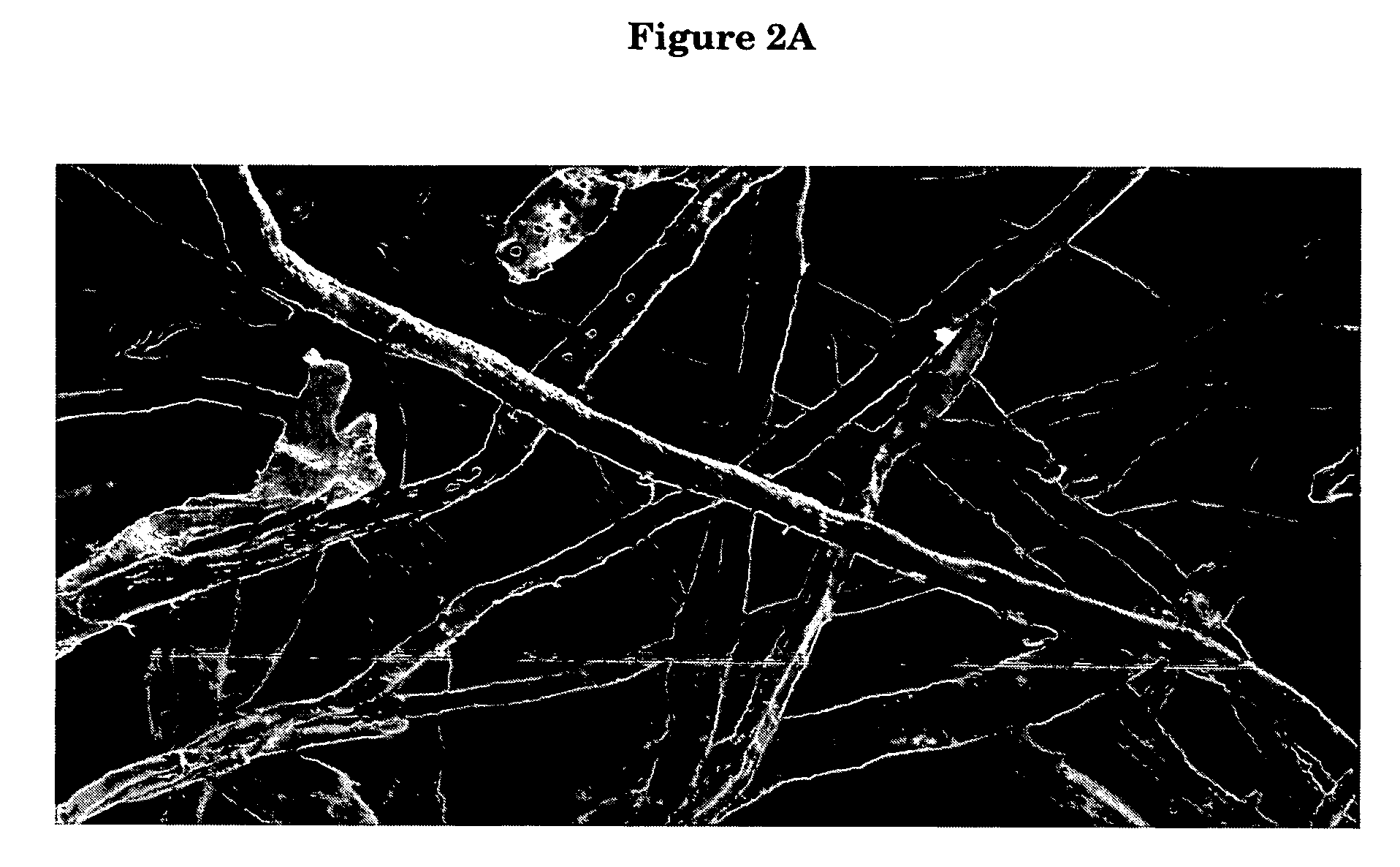
[0094] This example illustrates a method for cross-linking a blend of fibers in the sheet form prepared in the manner described above in example 1. In order to determine the effect of increasing the amount of conventional fiber on absorbent properties of fibers cross-linked in the sheet form, sheets with various proportions of Rayfloc®-J-LD and mercerized fibers were prepared as described in example 1 and used in this example. Sheets were soaked in a bath of 2% solution of glyoxylic acid (obtained as 50% solution in water commercially available from Clarinet Corporation, Charlotte, N.C.) for about 1 to 2 min and then pressed to a pick-up that affords about 2% of glyoxylic acid on fiber. Sheets then were dried and cured in one step process at 190° C. for 15 min.
[0095] The absorbent capacity, absorbency under load, centrifuge retention, knots and fine contents of the cross-linked sheets were determined. The results are summarized below in Table 1.
TABLE 1Fiber BlendMer-AbsorbencyAbs...
example 3
[0096] This example illustrates a method for cross-linking a blend of fibers in sheet form using DP-60 as a cross-linking agent (Belclene® DP-60 is a mixture of polymaleic acid terpolymer with the maleic acid monomeric unit of dominating (molecular weight of about 1000) and citric acid commercially available from BioLab Industrial Water Additives Division). Sheets with various proportions of Rayfloc®-J-LD and mercerized fibers were prepared as described above in Example 1, and then were soaked in a bath of DP-60 solution (5%) for about 1 to 2 min and then pressed to a pick-up that affords about 5% of DP-60 on fibers. Sheets were then dried and cured in a one step process at 190° C. for about 15 min.
[0097] The absorbent capacity, absorbency under load, centrifuge retention, knots and fine contents of cross-linked sheets were determined. The results are summarized in Table 2.
TABLE 2Fiber BlendAbsorbencyAbsor-KnotsMer-Under LoadbentCentrifugeandRayfloc ®-cerized(0.3 psi)Capac-Retent...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com