Capacity control valve for variable displacement compressor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
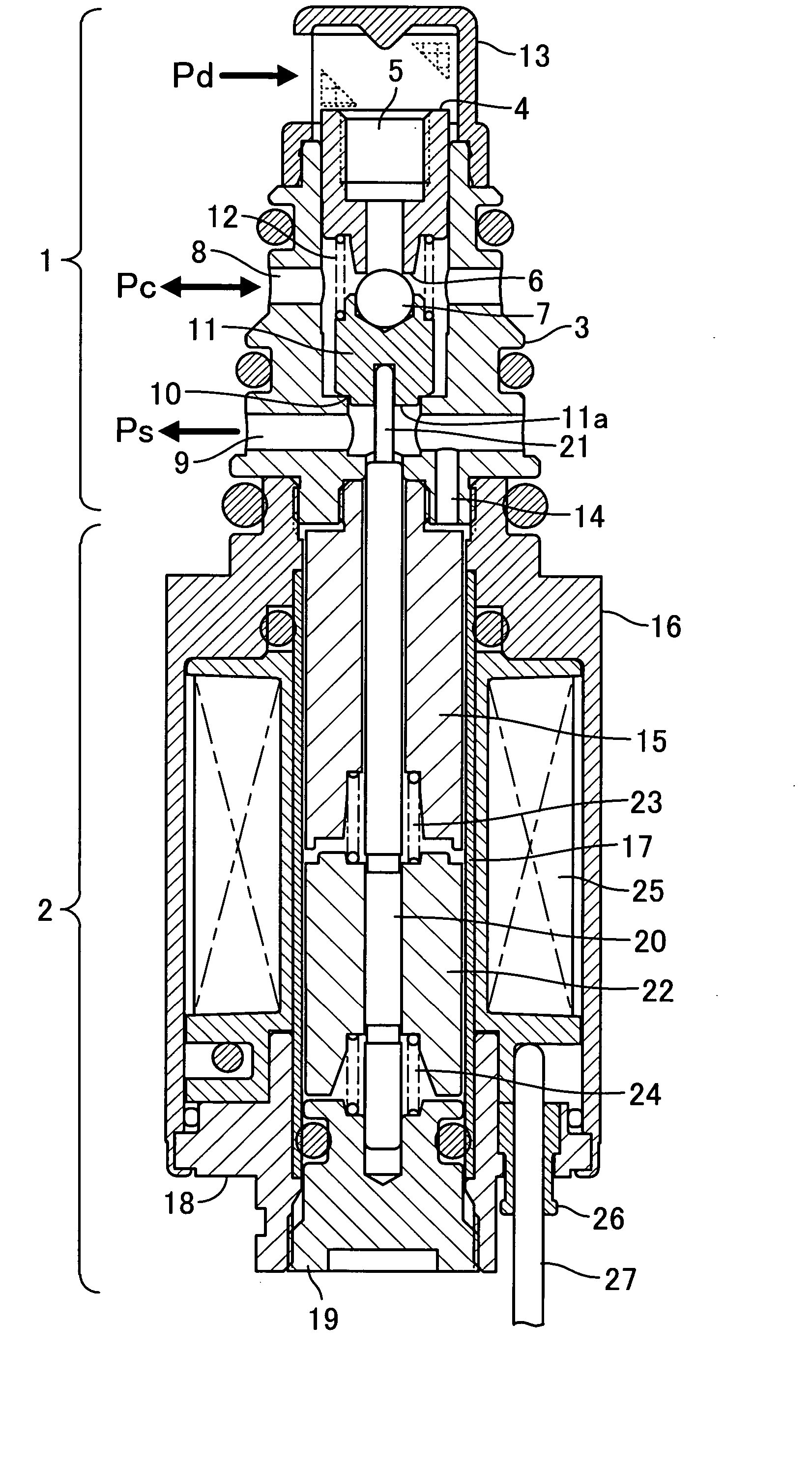
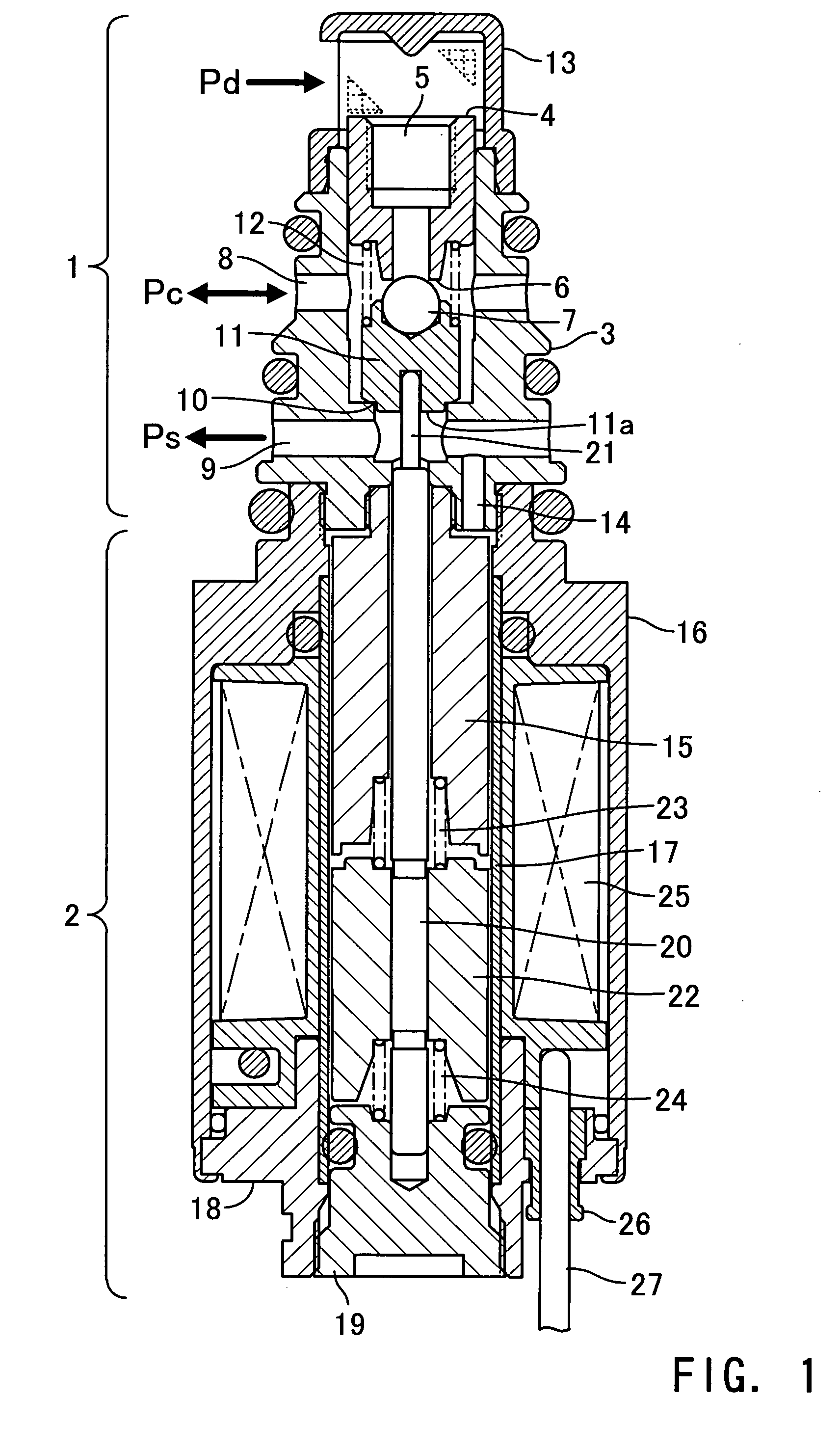
[0041]FIG. 4 is a central longitudinal cross-sectional view showing a capacity control valve according to the invention. In FIG. 4, component elements identical to those in FIG. 1 are designated by identical reference numerals, and detailed description thereof is omitted.
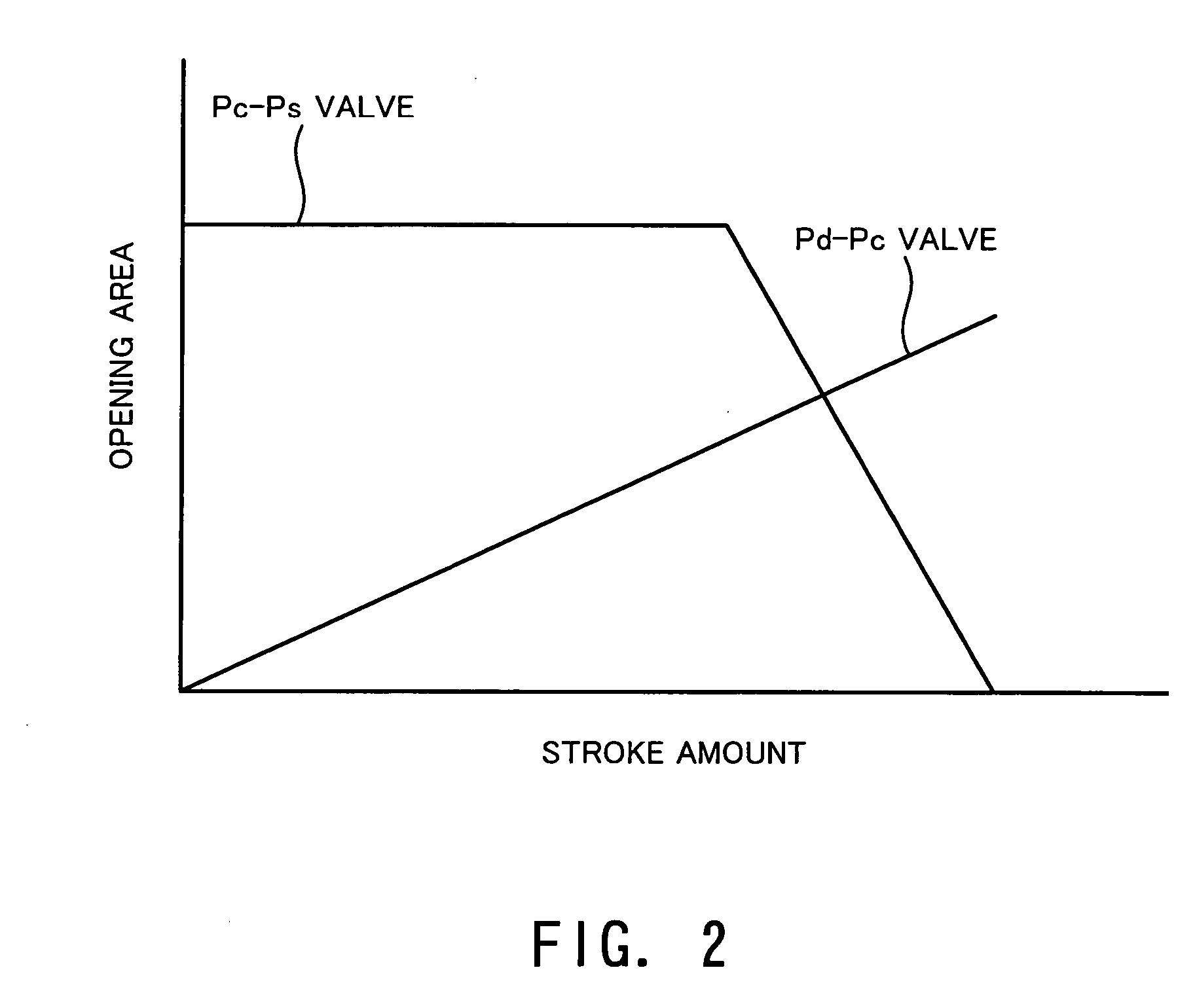
[0042] Although the capacity control valve according to the first embodiment attains the flat characteristic of the Pc-Ps valve by the spool valve structure, the capacity control valve according to the second embodiment attains the same by providing an orifice 28 as flow rate-restricting means whose opening area does not change.
[0043] That is, the Pc-Ps valve has a valve element 11 whose surface opposed to the valve seat 10 is formed to have a tapered shape, and the orifice 28 is provided between the downstream side of the valve element 11, and the port 9 and the passage 14. The orifice 28 is disposed in series with the Pc-Ps valve, and therefore, when the opening area of the Pc-Ps valve becomes larger than the ope...
third embodiment
[0044]FIG. 5 is a central longitudinal cross-sectional view showing a capacity control valve according to the invention. In FIG. 5, component elements identical to those in FIG. 1 are designated by identical reference numerals, and detailed description thereof is omitted.
[0045] Compared with the capacity control valve according to the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1, the capacity control valve according to the third embodiment is configured such that the operation of the Pc-Ps valve is not adversely affected by the pressure Pc in the crankcase.
[0046] More specifically, the capacity control valve is provided with a passage 14 which causes a space between the Pd-Pc valve and the Pc-Ps valve, which is connected to the crankcase via the port 8, to communicate with the inside of the solenoid section, whereby the pressure Pc in the crankcase is transmitted to the inside of the solenoid section 2. This causes the valve element 11 of the Pc-Ps valve to receive the pressure Pc in the crank...
fourth embodiment
[0049]FIG. 6 is a central longitudinal cross-sectional view showing a capacity control valve according to the invention. In FIG. 6, component elements identical to those in FIG. 4 are designated by identical reference numerals, and detailed description thereof is omitted.
[0050] Compared with the capacity control valve according to the second embodiment shown in FIG. 4, the capacity control valve according to the fourth embodiment is configured such that the operation of the Pc-Ps valve thereof is not adversely affected by the pressure Pc in the crankcase.
[0051] More specifically, the capacity control valve is provided with a passage 14 which causes space between the Pd-Pc valve and the Pc-Ps valve connected to the crankcase via the port 8 to communicate with the inside of the solenoid section, whereby similarly to the capacity control valve according to the third embodiment, the pressure Pc in the crankcase is transmitted to the inside of the solenoid section 2. This causes the pre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com