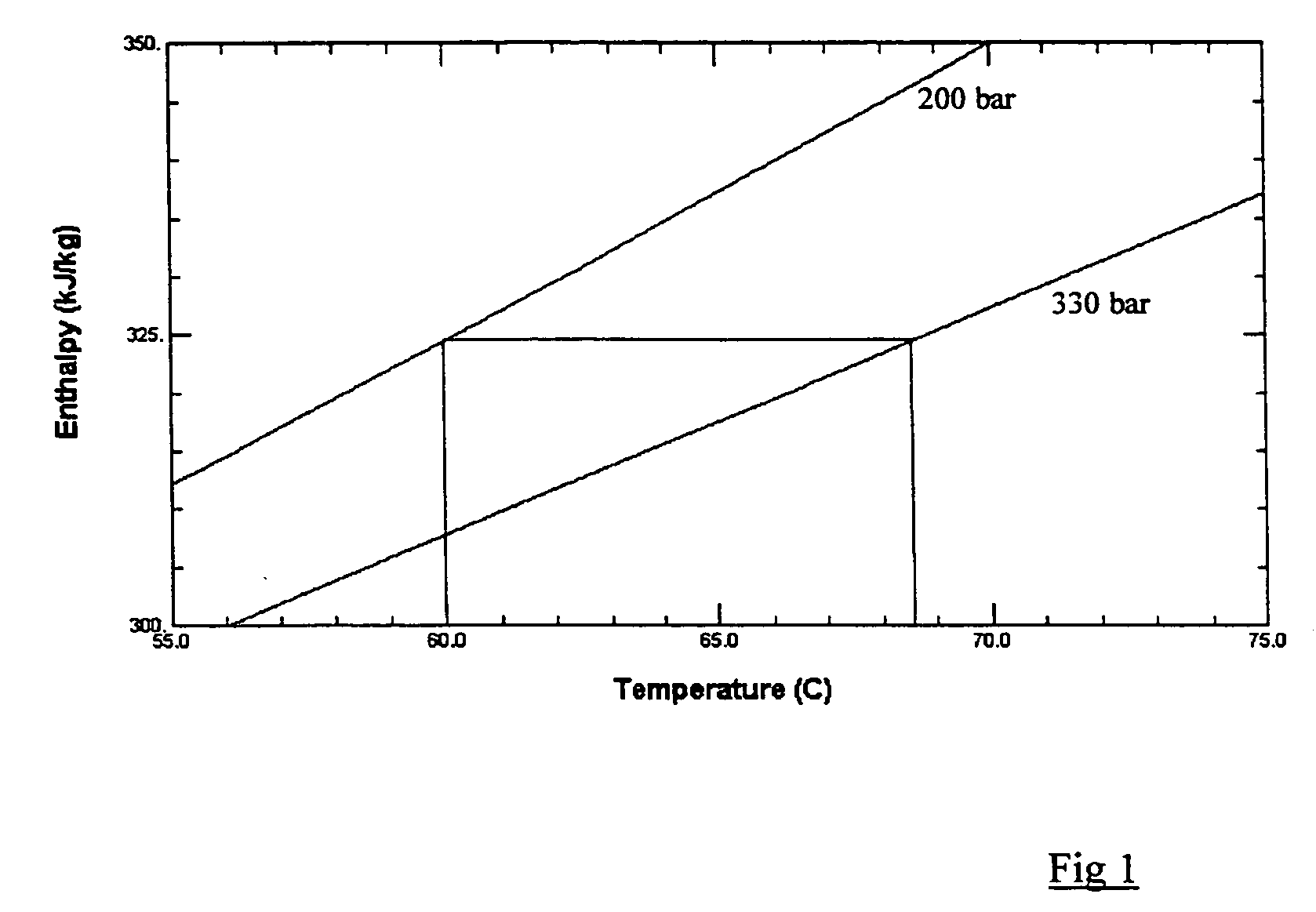
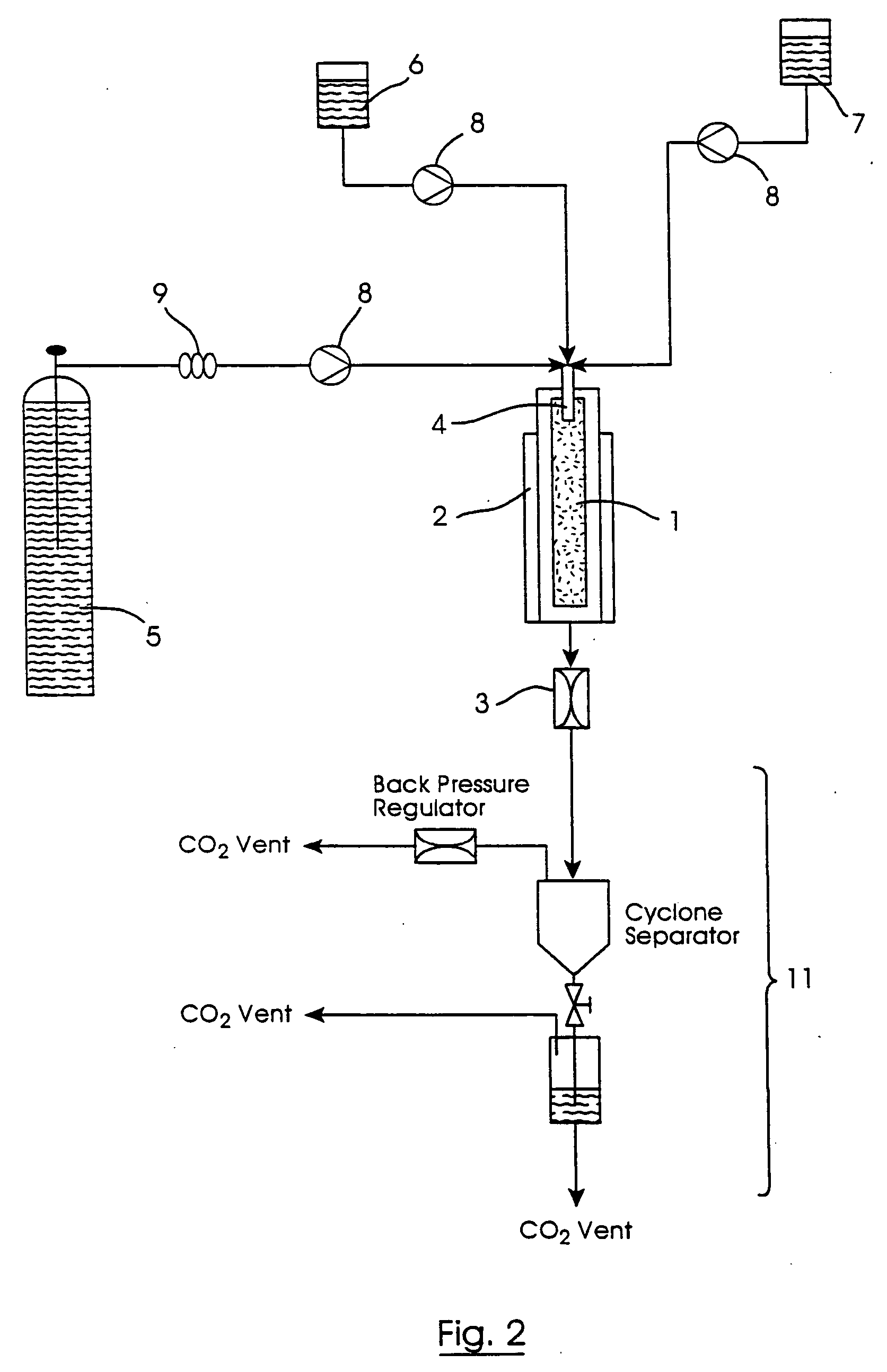
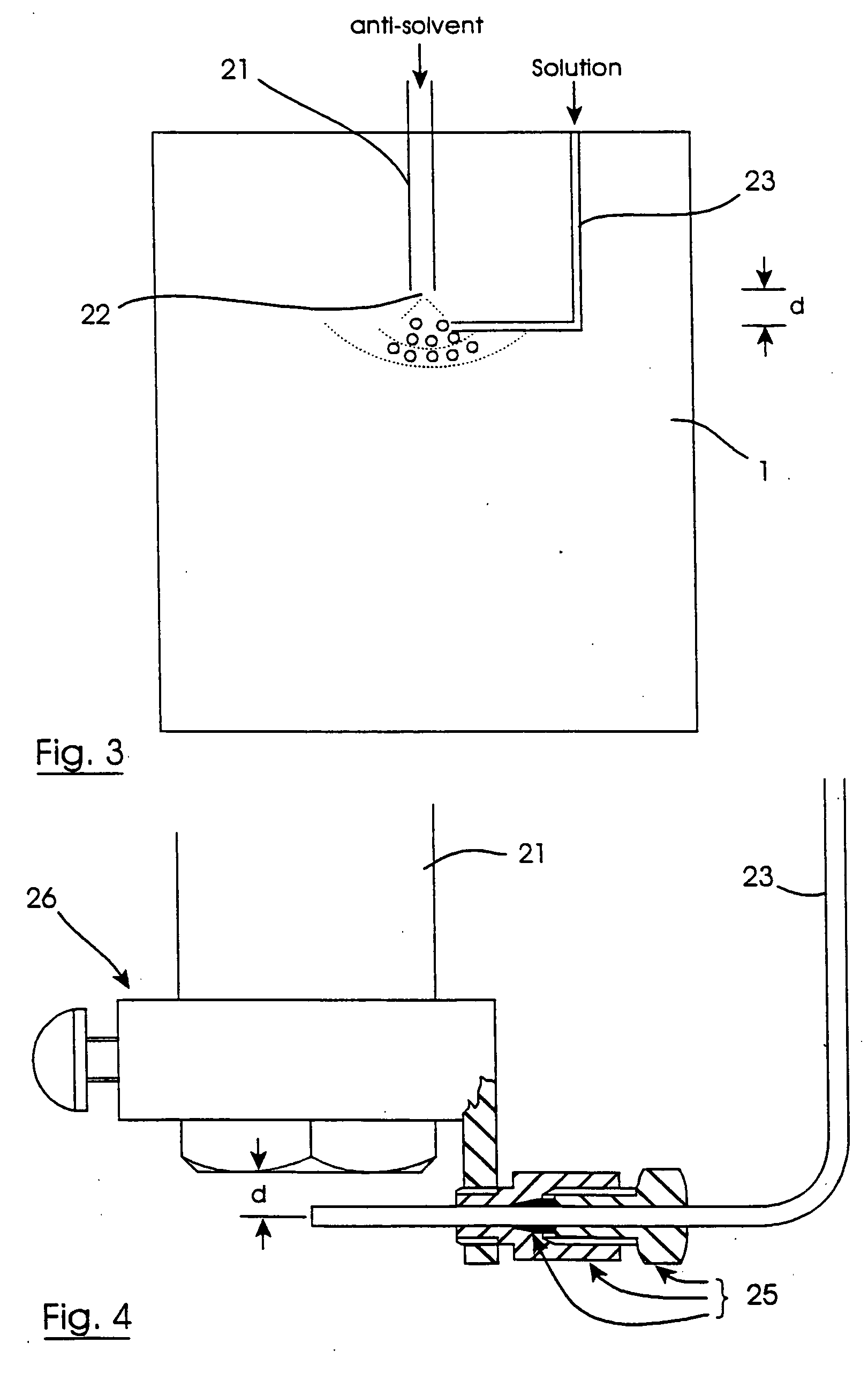
Particle formation
a particle and particle technology, applied in the field of particle formation, can solve the problem that authors have not appeared to have achieved such high velocities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples a
[0115] Apparatus as shown in FIG. 2, incorporating a fluid inlet assembly as shown in FIGS. 3 to 5, was used to carry out particle formation methods in accordance with the invention.
[0116] The nozzle 21 comprised a fluid inlet tube of internal diameter 0.75 mm, a convergent tip with a 60° half angle taper (with respect to the central longitudinal nozzle axis) and an outlet of diameter 0.2 mm. According to theory, this generates a fluid jet with a cone angle of approximately 20°.
[0117] The internal bore at the end of the inlet tube 23 was 0.125 mm.
[0118] The experiments investigated the effect of varying both (a) the horizontal distance x between the solution line outlet and the central axis of anti-solvent flow, and (b) the vertical distance y between the nozzle outlet 22 and the solution line outlet (y being measured, for convenience, from the top external wall of the solution inlet tube 23).
[0119] Supercritical carbon dioxide, pre-heated to 70° C., was used as the anti-solvent...
examples b
[0127] Apparatus as shown in FIG. 2, incorporating a fluid inlet assembly as shown in FIGS. 6 and 7, was used to carry out a further particle formation method in accordance with the invention. The nozzle 21 was the same as used in Examples A.
[0128] The target solution inlet comprised a fused silica capillary of length 20 mm and internal diameter 50 μm, glued into a standard 1.59 mm ({fraction (1 / 16)}″) internal diameter stainless steel tube. Its outlet, into the particle formation vessel 1, was therefore 50 μm in diameter, and its cross sectional area only 6% of that of the outlet of nozzle 21. A two-component epoxy resin was used to secure the capillary in place, under elevated temperatures (180° C.) to enhance the mechanical strength of the bond. Due to the viscous flow of the uncured resin, it was not possible to centre the capillary within the stainless steel tube.
[0129] The vertical separation “y” was ˜0.5-1 mm.
[0130] Again supercritical carbon dioxide was used as the anti-s...
examples d
[0140] Examples A were repeated, using the same nozzle 21 but with a 0.4 mm diameter outlet.
[0141] The vertical distance y between the nozzle outlet 22 and the solution tube outlet was varied between 4 and 8 mm. The solution tube outlet was positioned in line with the nozzle outlet (ie, x=0 mm).
[0142] The supercritical carbon dioxide anti-solvent was pumped at a flow rate of 200 ml / min. The salmeterol solution flow rate was 4 ml / min. The vessel temperature and pressure were as in Examples A, and the CO2 velocity at the nozzle outlet 22 was sub-sonic throughout the experiments. The run time for each experiment was approximately one hour.
[0143] Product particle sizes were measured using a Sympatec™ apparatus at 2 bar shear pressure.
[0144] The results are shown in Table 4.
TABLE 4YieldParticleParticleExpt.(%sizesizeno.y (mm)w / w)(μm)*spread**D144911.75 ± 0.05 2.25D2649 8.6 ± 0.032D38498.65 ± 0.012.04
*Volume mean diameter, representing the average of two analyses.
**Particle size sp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com