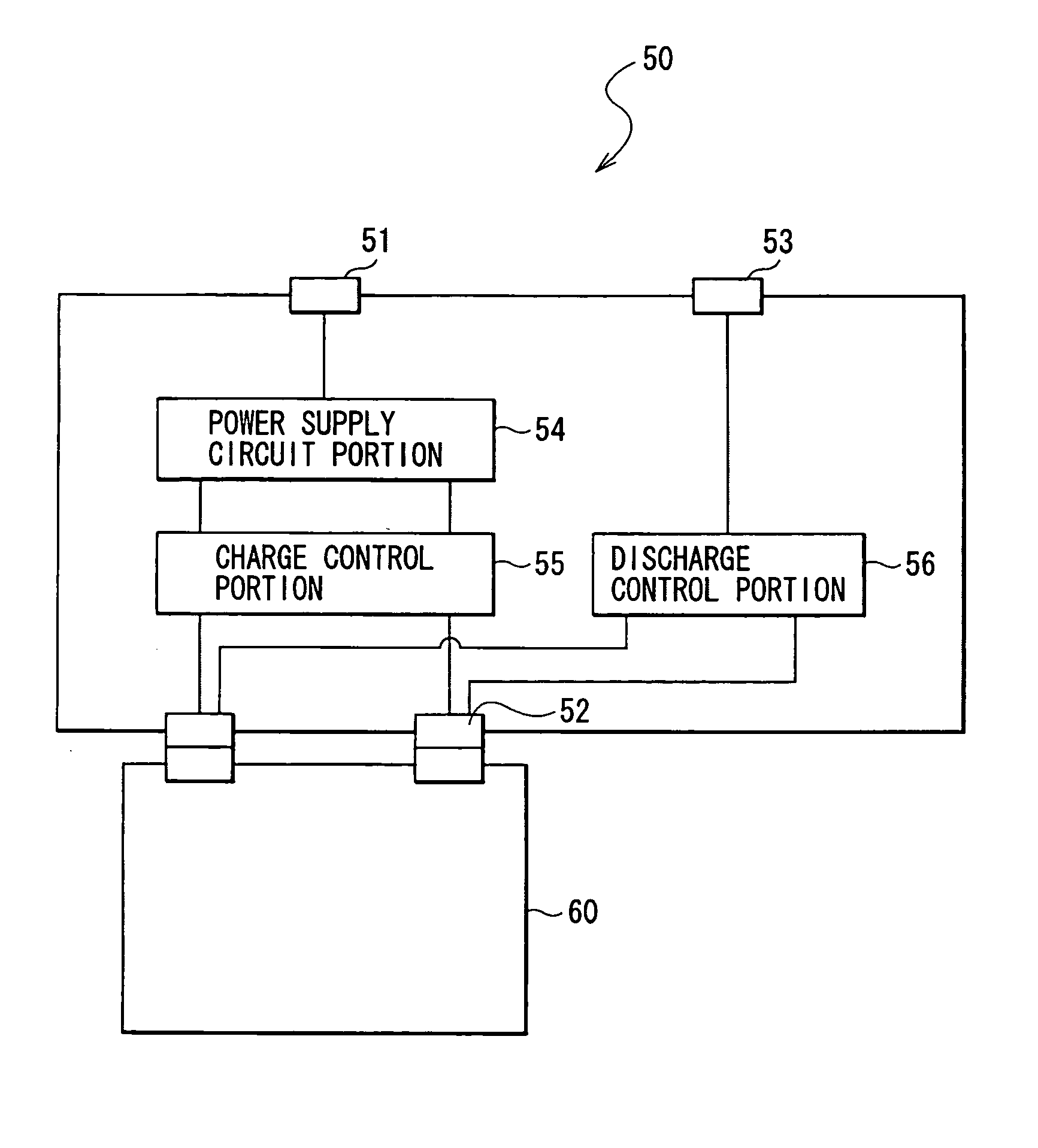
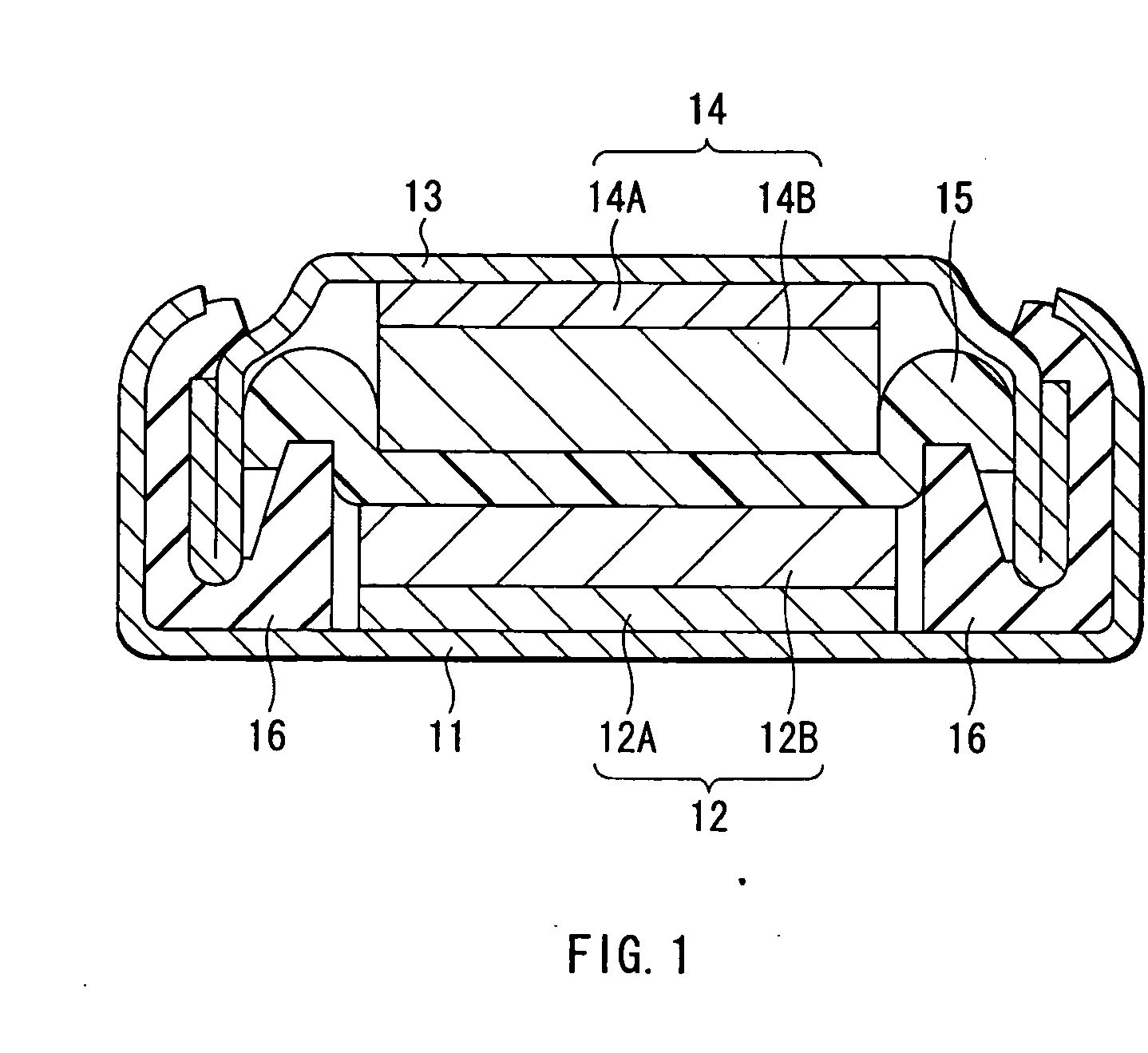
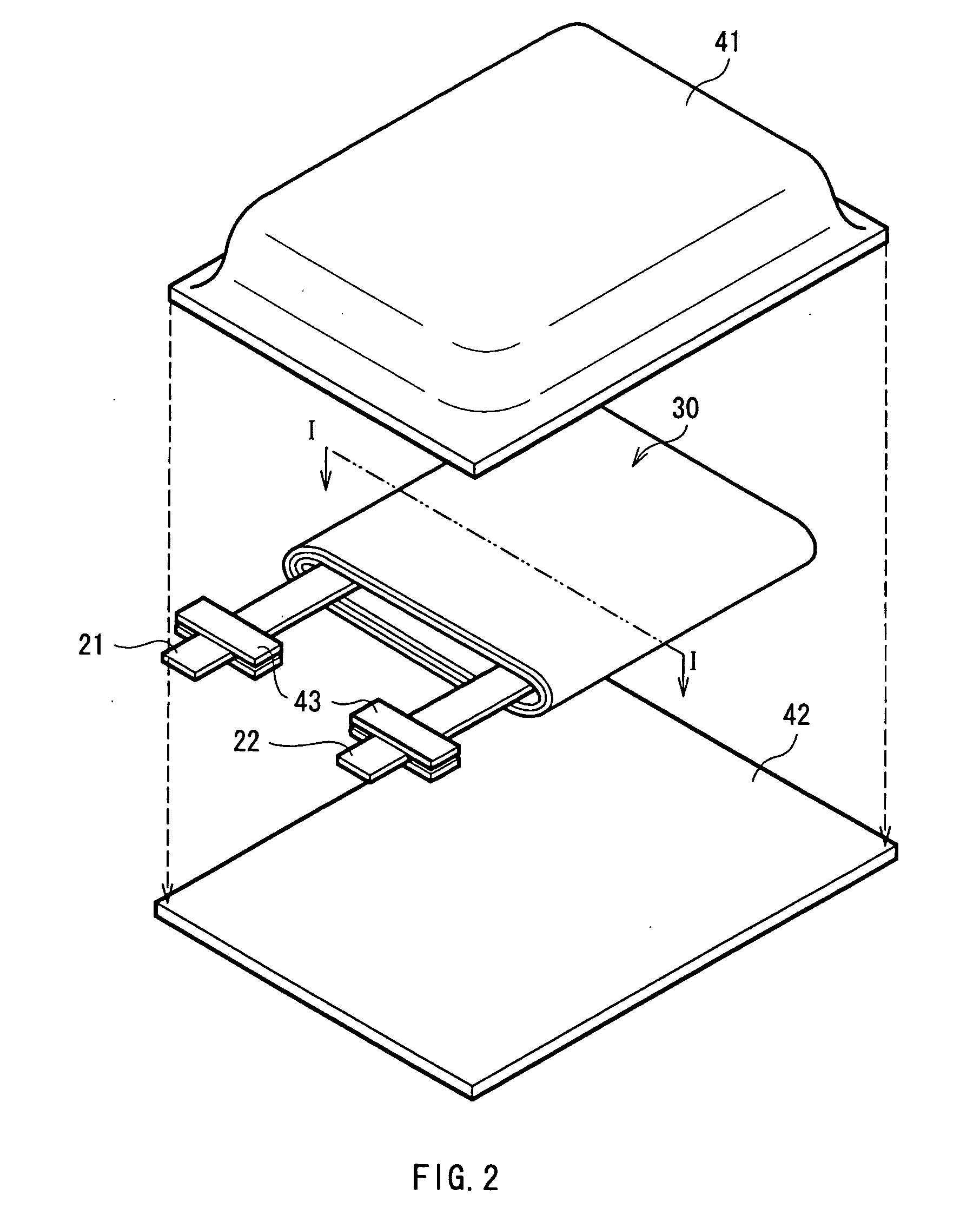
Battery, method of charging and discharging the battery and charge-discharge control device for the battery
a technology of battery and control device, which is applied in the direction of secondary cell servicing/maintenance, non-aqueous electrolyte cells, cell components, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the capacity of the battery, accelerating the electrolyte solution, and reducing the collection property of current, so as to reduce the structural fracture of the anode and improve the cycle characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0077] Examples of the invention will be described in detail below referring to the drawings. In the following examples, like components are donated by like numerals as of the above embodiment.
examples 1-1 through 1-6
[0078] Coin-type secondary batteries with a diameter of 20 mm and a thickness of 16 mm shown in FIG. 1 were formed. The cathode 12 was formed through the following steps. At first, lithium carbonate (LiCO3) and cobalt carbonate (CoCO3) were mixed at a molar ratio of LiCO3:CoCO3=0.5:1 to form a mixture, and the mixture was fired for 5 hours at 900° C. in air to obtain lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) as a cathode active material. Next, the lithium cobalt oxide, graphite as an electrical conductor and polyvinylidene fluoride as a binder were mixed at a mass ratio of lithium cobalt oxide:graphite:polyvinylidene fluoride=91:6:3 to form a mixture. Next, the mixture was dispersed in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone as a dispersion medium to form mixture slurry, and the mixture slurry was applied to the cathode current collector 12A made of aluminum foil with a thickness of 20 μm, and dried, the mixture slurry was pressurized to form the cathode active material layer 12B, and then the cathode current c...
examples 2-1 through 2-3
[0088] Secondary batteries were formed as in the case of Example 1-5 or Example 1-6, except that the composition of the electrolyte solution was changed. As the electrolyte solution, an electrolyte solution formed through adding 1,3-dioxol-2-one (VC) or 4-vinyl-1,3-dioxolane-2-one (VEC) to the electrolyte solution used in Examples 1-1 through 1-6, that is, the electrolyte solution including the solvent which included ethylene carbonate and dimethyl carbonate at a mass ratio of 1:1 and LiPF6 which was dissolved in the solvent at a concentration of 1 mol / l was used. At that time, the contents of VC and VEC in the electrolyte solution were changed as shown in Tables 2 and 3 in Examples 2-1 through 2-3.
[0089] A charge-discharge test was carried out on the secondary batteries of Examples 2-1 through 2-3 as in the case of Examples 1-5 and 1-6 to determine their capacity retention ratios in the 100th cycle and measure the Li / Si ratio in the anode 14 and the potential of the anode 14 vs. L...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com