Apparatus for thermal treatment of substrates
a substrate and apparatus technology, applied in the direction of chemically reactive gases, coatings, crystal growth processes, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of integrated circuit manufacturers, wafer handlers, and more vulnerable to physical damage, so as to facilitate conductive cooling of substrates and reduce the time of cooling. time, the effect of significantly faster cooling of substrates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
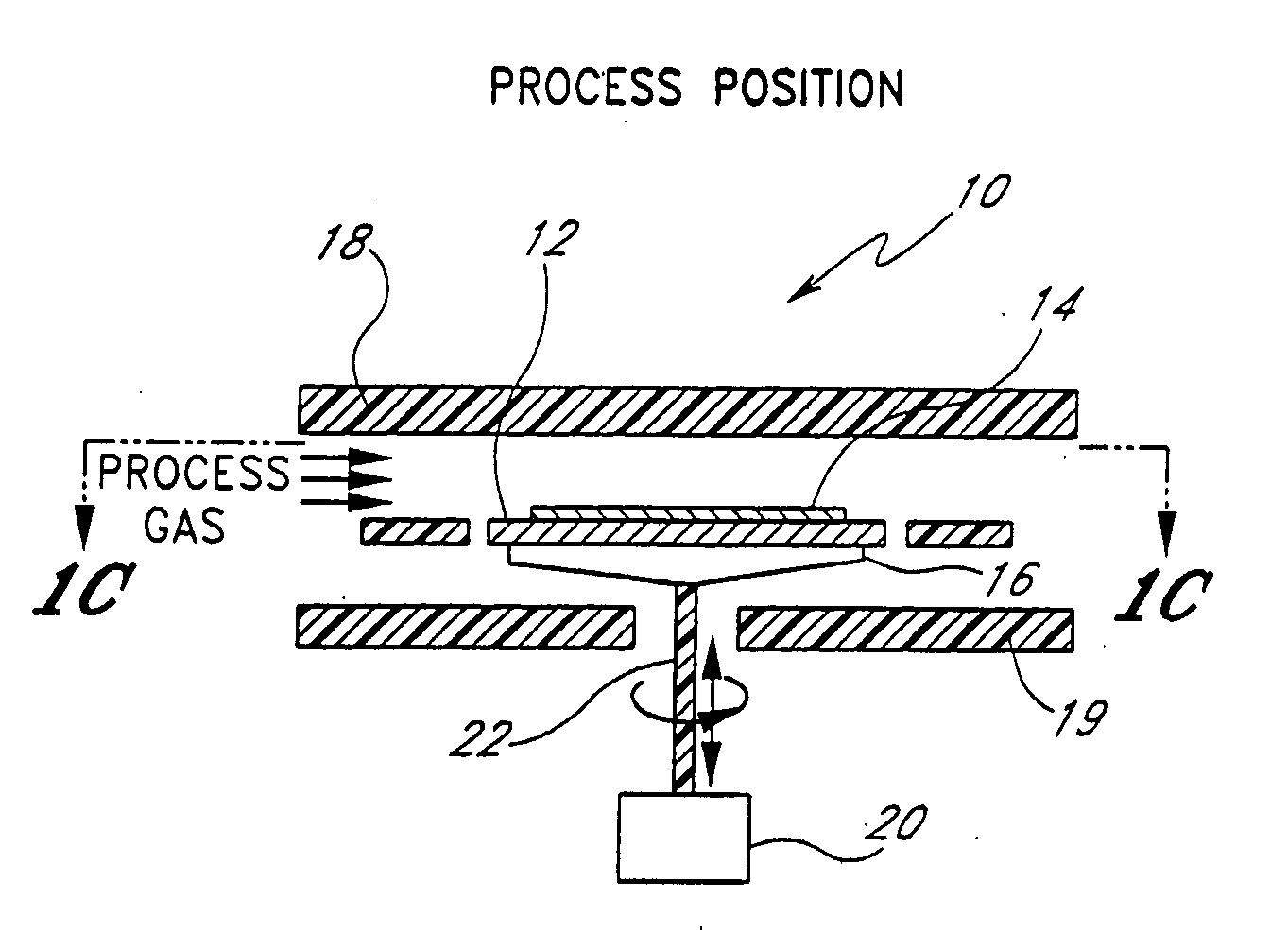
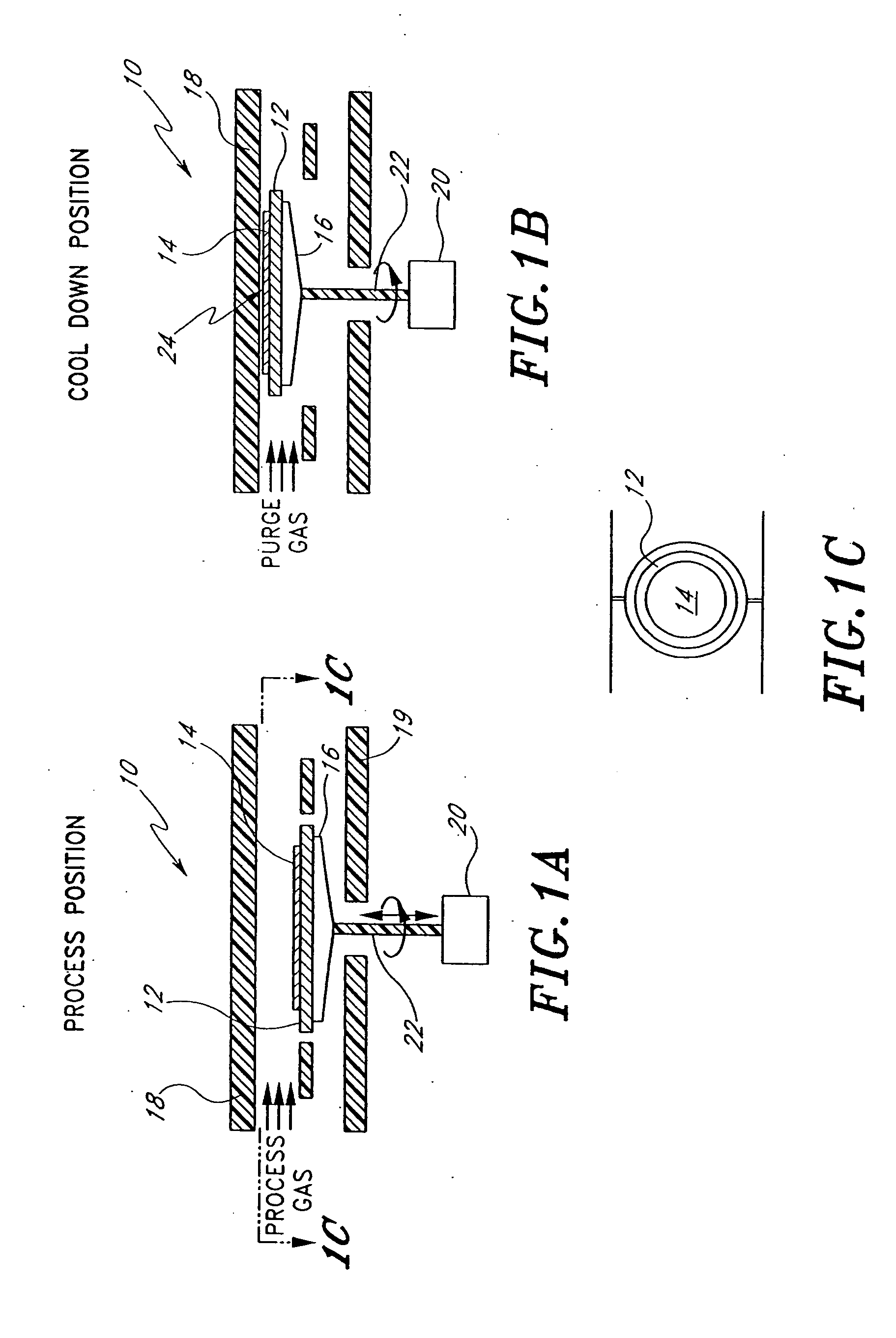
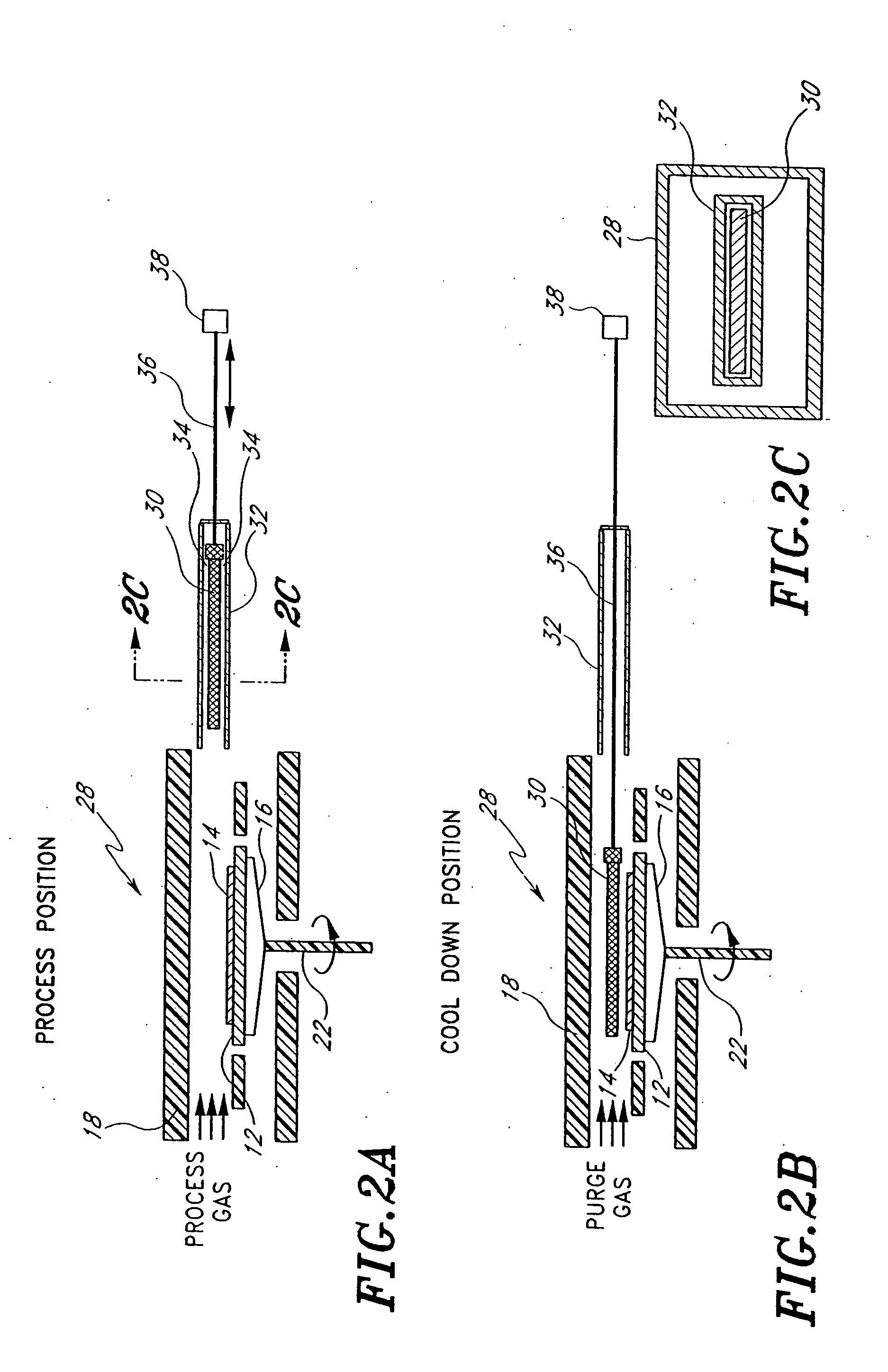
[0025] While the invention is illustrated in the context of a single-wafer, horizontal gas flow reactor, it will be understood by one of ordinary skill in the art that the cooling mechanism of the present invention is not limited to any specific type of reactors or processing chambers. Rather, the skilled artisan will find application for the principles disclosed herein in connection with a number of different types of processing chambers or reactors, including cluster tools, batch processing systems, vertical gas flow or showerhead systems, etc. Furthermore, while the applications have particular utility for cooling down wafers before handling and removing the wafer from the process chamber, the principles disclosed herein have application whenever it is desirable to cool a workpiece prior to handling or storage.
[0026]FIGS. 1A, 1B and 1C illustrate a processing chamber which incorporates a cooling system constructed in accordance with a first preferred embodiment of the present in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com