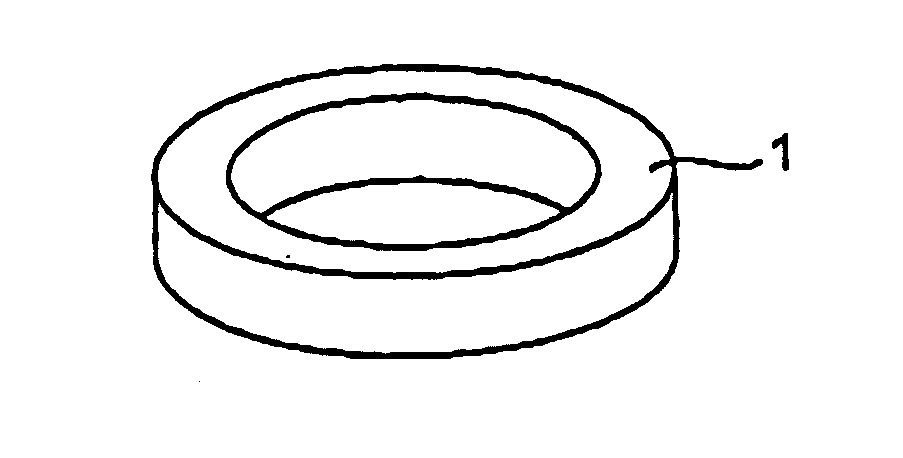
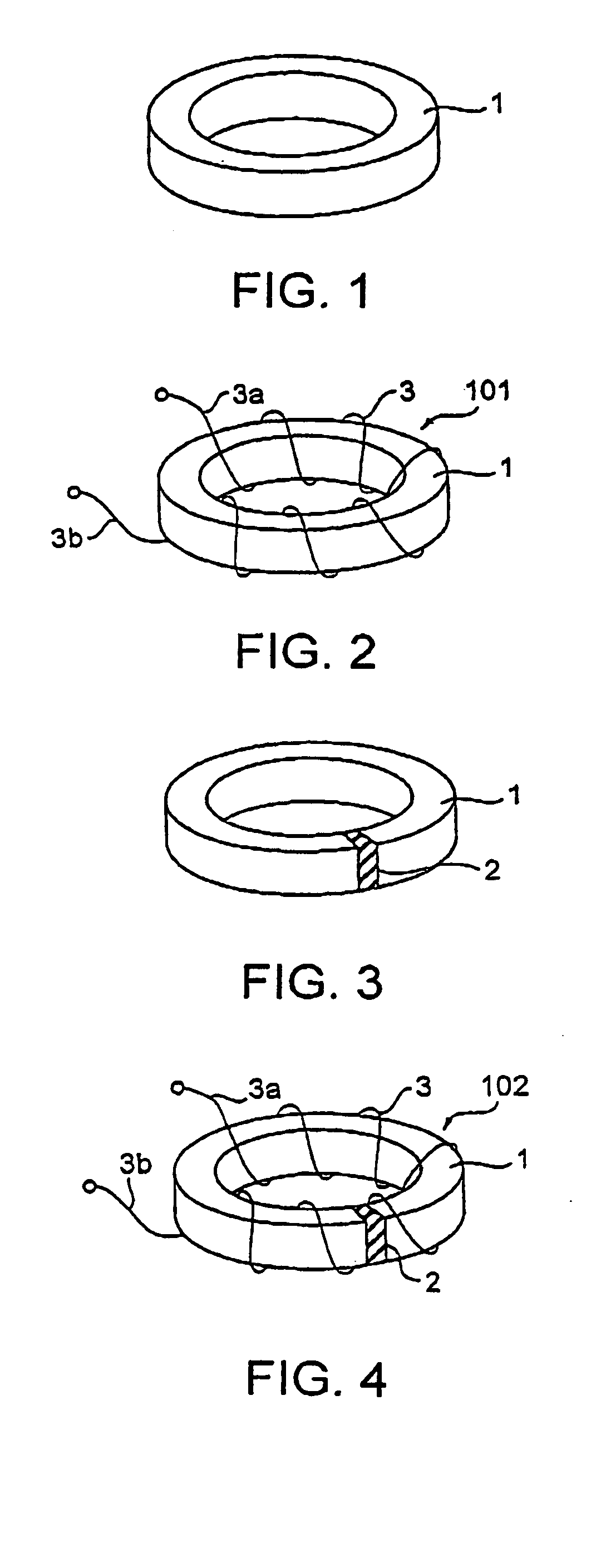
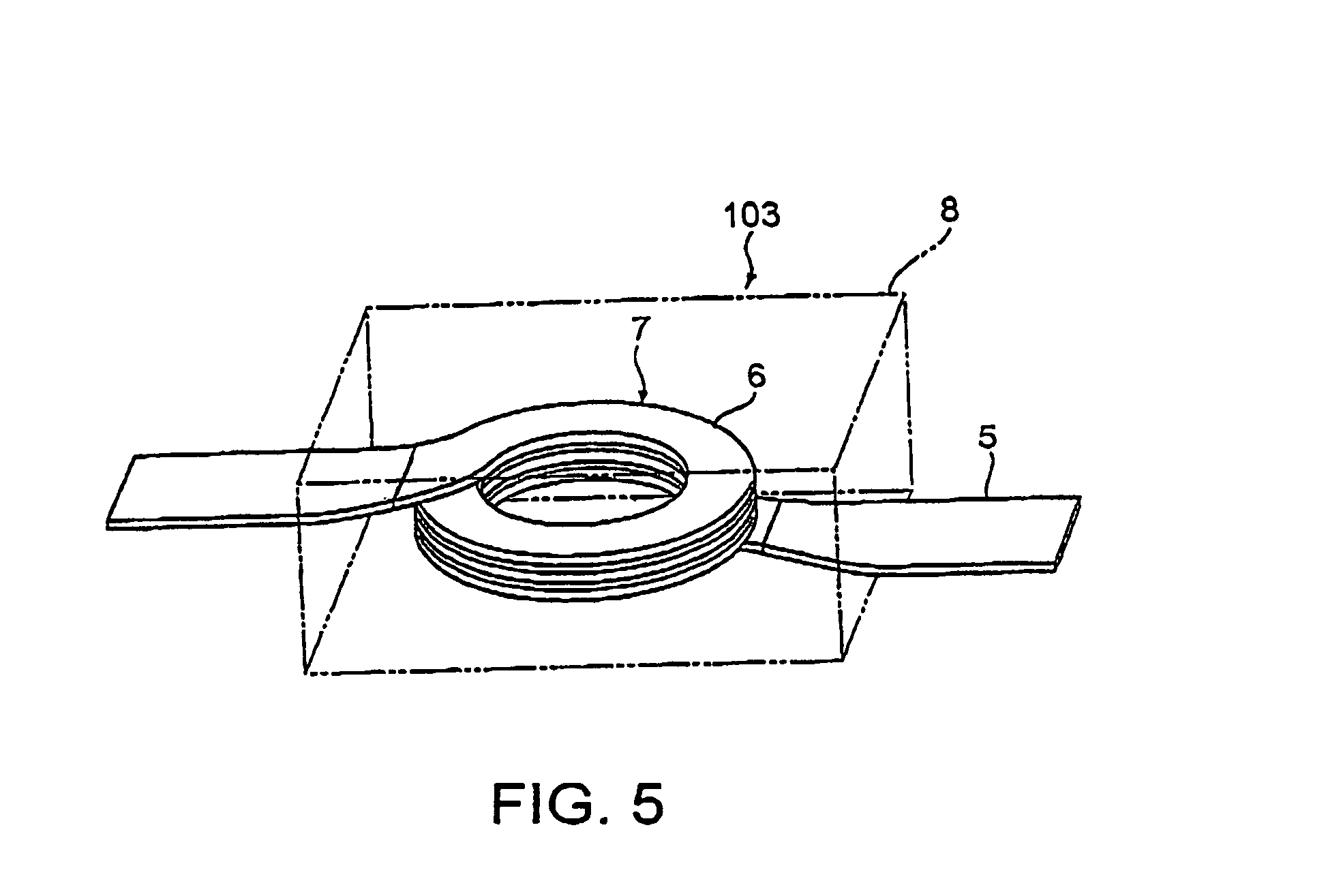
High-frequency core and inductance component using the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-26
, COMPARATIVE EXAMPLES 1-11
[0054] At first, as a powder preparing step, pure metal element materials including Fe, Si, B. Nb, Al, C, and substitute elements therefor or, if desired, various mother alloys were weighed so as to obtain predetermined compositions. By the use of these materials, various kinds of soft magnetic alloy powders were produced by water atomization generally used. It is noted here that a misch metal is a mixture of rare earth metals. Herein, a mixture of 30% La, 50% Ce, 15% Nd, and the balance other rare earth element or elements was used.
[0055] Next, as a molded body preparing step, each of the alloy powders was classified into those having a powder size of 45 μm or less. Thereafter, a silicone resin as a binder was mixed in an amount of 4% in mass ratio. Then, by the use of a die with a groove having an outer diameter of hope φOUT=27 mm×an inner diameter φIN=14 mm, various kinds of molded bodies were formed by applying a pressure of 1.18 GPa (about 12 t / cm2) ...
example 27
[0067] An alloy powder having a composition of (Fe0.8Co0.2)73Si9B14.5Nb2Al1.0C0.5 was prepared by water atomization. The powder thus obtained was classified into those having a size of 75 μm or less. XRD measurement was carried out to confirm a broad peak specific to a glass phase.
[0068] Next, thermal analysis by DSC was carried out to measure a glass transition temperature and a crystallization temperature to find out that ΔTx was 35K. Then, the powder was heat treated at 450° C. lower than the glass transition temperature for 0.5 hour in atmospheric air to form oxide on the surface of the powder. Next, the powder was mixed with 10%, 5%, 2.5%, 1%, and 0.5% silicone resin. By the use of a die of φ27×φ14, these powders were molded under three conditions at a room temperature, at 150° C. higher than a softening temperature of the resin, and at 550° C. in a supercooled liquid temperature range of this metallic glass powder. The powder filling rate, the magnetic flux density by d.c. ma...
example 28
[0070] In an example 28, an alloy powder having a composition of Fe72Si9B14.5Nb3Al1.0C0.5 was prepared by water atomization. Thereafter, the powder thus obtained was classified into those having a particle size of 75 μm or less. Then, XRD measurement was carried out to confirm a broad peak specific to a glass phase.
[0071] Further, thermal analysis by DSC was carried out to measure a glass transition temperature and a crystallization temperature to confirm that a vitrification start temperature range or a supercooled liquid temperature range ΔTx was 35K. Then, the powder was kept at a temperature condition of 450° C. lower than the glass transition temperature and heat treated for 0.5 hour in atmospheric air to form oxide on the surface of the powder.
[0072] Next, the powder with oxide formed thereon was mixed with, in mass ratio, 10%, 5%, 2.5%, 1%, and 0.5% silicone resin as a binder. By the use of a die with a groove having an outer diameter φOUT=27 mm×an inner diameter φIN=14 mm,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com