Non-volatile memory and method of manufacturing floating gate
a floating gate, non-volatile technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical equipment, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to obtain desirable lower operating voltage, easy to occur electrical leakage, and affect device reliability, etc., to achieve the effect of improving the reliability of memory devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
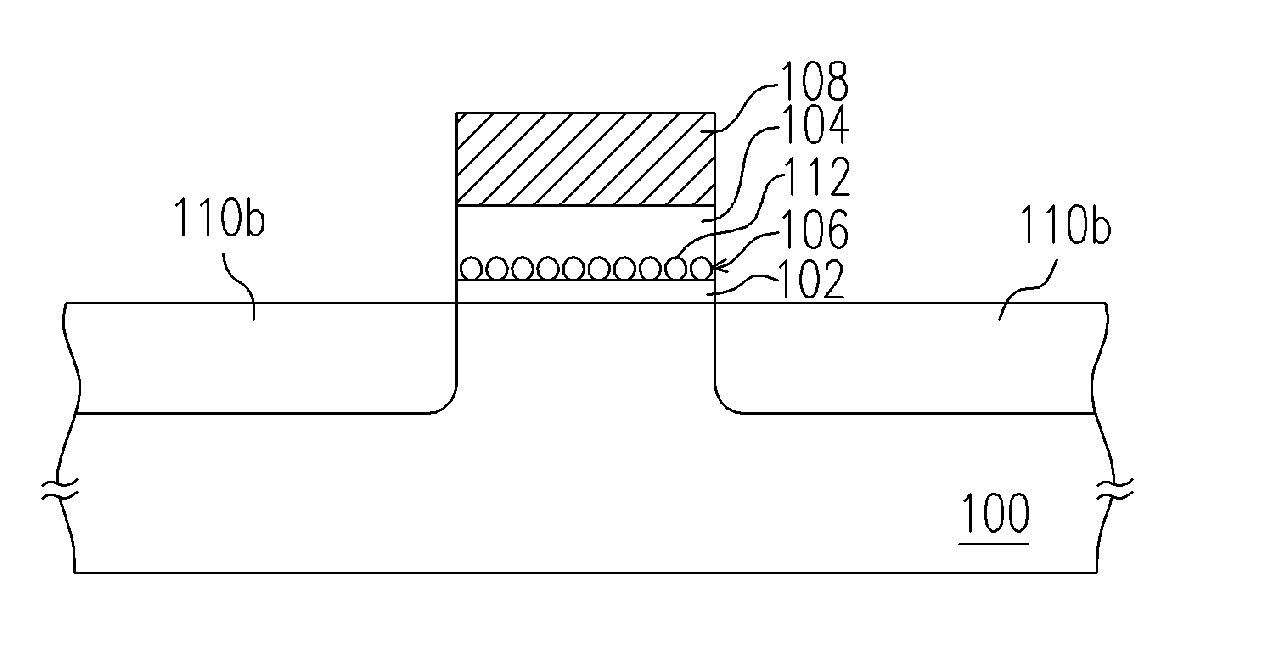
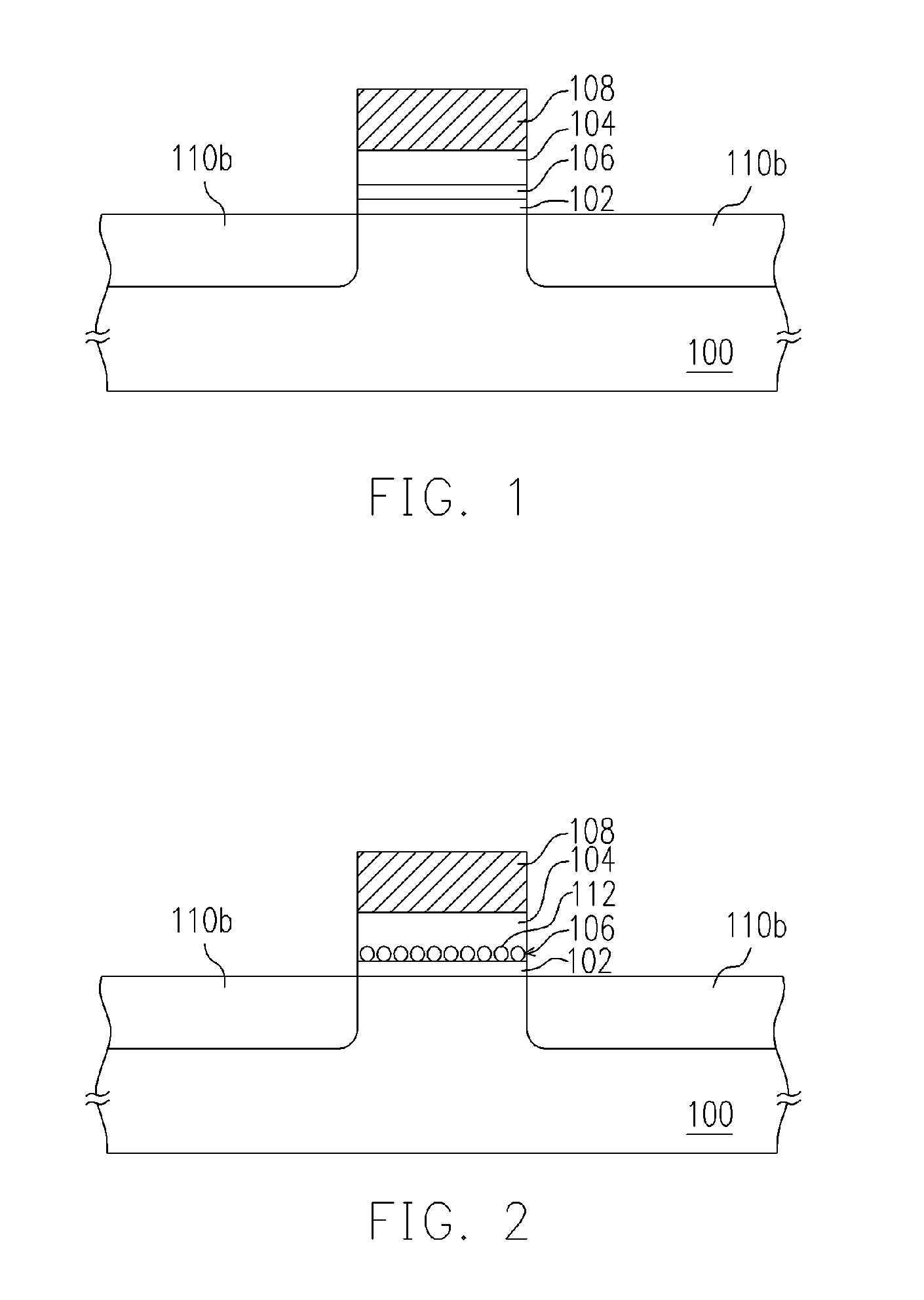
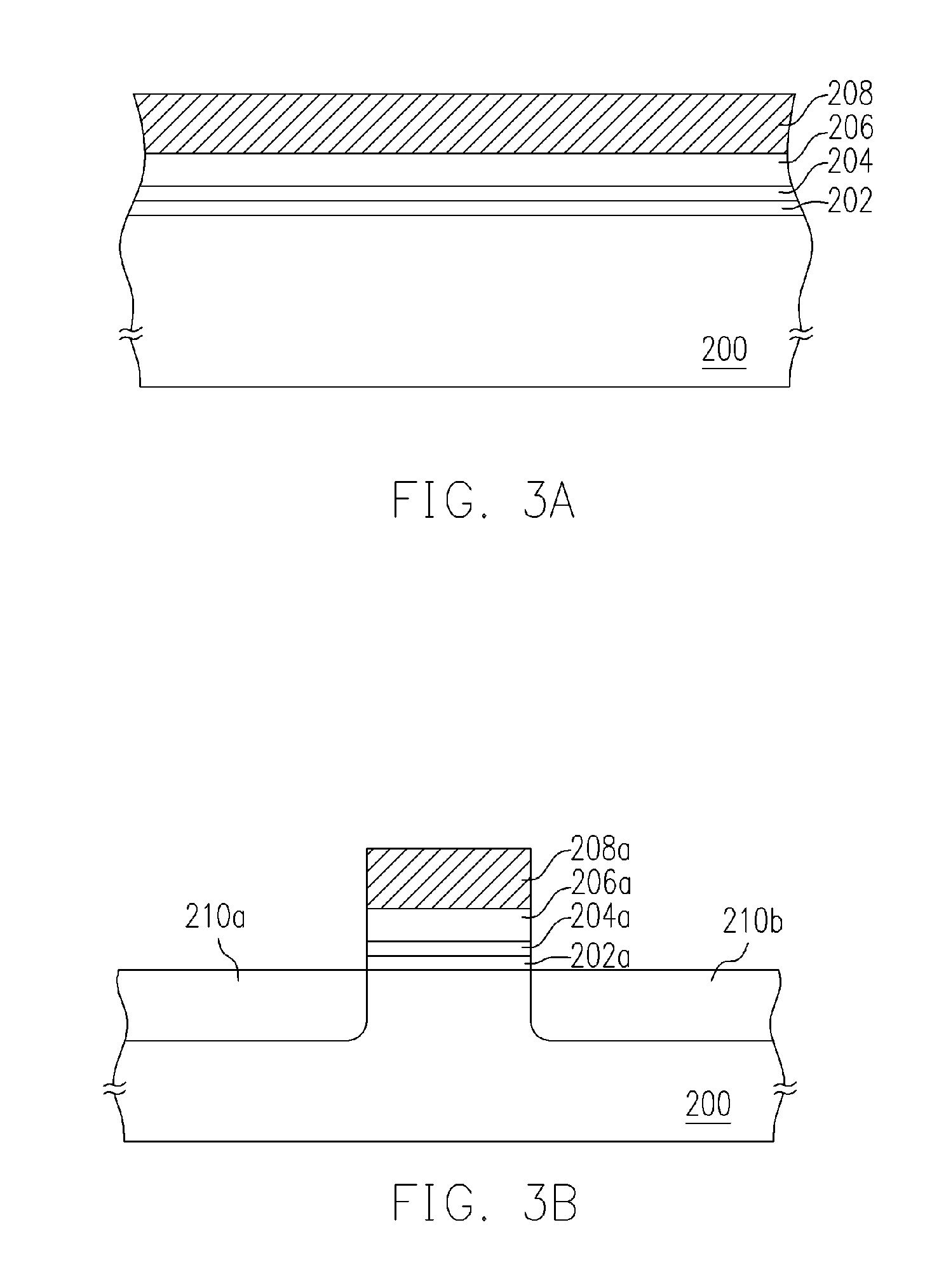
[0039] A first preferred embodiment of method of manufacturing the non-volatile memory of this invention is illustrated in FIGS. 3A and 3B.
[0040] Referring to FIG. 3A, a tunneling layer 202 is formed on a substrate 200. The substrate 200 is a silicon substrate for example, while the tunneling layer 202 is made of silicon oxide or other kind of dielectric, and is formed via a process such as thermal oxidation or chemical vapor deposition. In this embodiment, the tunneling layer 202 of silicon oxide is formed, for example, via dry oxidative deposition of a film of about 5 nm in a chemical vapor deposition chamber at 925° C. under normal pressure.
[0041] A semiconductor oxide layer 204 is then formed on the tunneling layer 202. The semiconductor oxide layer 204 is a film used as a floating gate. Here, the semiconductor oxide refers to element semiconductor or compound semiconductor. The semiconductor oxide layer 204 contains semiconductor components, which include Group II elements, G...
second embodiment
[0045] A second preferred embodiment of method of manufacturing the non-volatile memory of this invention is illustrated in FIGS. 5A to 5D.
[0046] Referring first to FIG. 5A, a substrate 200 is provided and a tunneling layer 202 is formed thereon. A semiconductor silicide layer 400 is then formed on the tunneling layer 202, wherein the semiconductor silicide refers to silicide of element semiconductor or compound semiconductor. The semiconductor silicide layer 400 contains semiconductor components, for example, as described in the first preferred embodiment. The semiconductor silicide layer 400, when made of Si1-xGex (0400 is formed via a process of, for example, low-pressure chemical vapor deposition, while a layer of Si1-xGex in a thickness of, for example, 20 nm is formed on the tunneling layer 202. The low-pressure chemical vapor deposition is carried out at about 550° C. and under about 460 mTorr, while the process gases are SiH4 and GeH4.
[0047] Referring to FIG. 5B, an oxidat...
third embodiment
[0052] A third preferred embodiment of method of manufacturing the non-volatile memory of this invention is illustrated in FIGS. 6A to 6C.
[0053] Referring first to FIG. 6A, a substrate 200 is provided, and a tunneling layer 202 is formed thereon. A semiconductor layer 500, a thin film, is then formed on the tunneling layer 202, while the semiconductor layer 500 is made of, for example, the components as mentioned in the first embodiment. In this embodiment, the semiconductor layer 500 is made of, for example, germanium (Ge) in a thickness of 1 to 10 nm, and is formed, for example, via a process of physical vapor deposition or chemical vapor deposition. The process is carried out at a temperature of, for example, between 100 to 1000° C., and under a pressure of, for example, between 1 to 500 mTorr. The process of chemical vapor deposition can be, for example, low-pressure chemical vapor deposition, plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition, high-density plasma chemical vapor deposit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com