Method for manufacturing a magnetic memory device, and a magnetic memory device
a technology of magnetic memory and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of digital storage, semiconductor devices, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of efficient introduction, efficient introduction of memory elements, and reduction of the number of steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
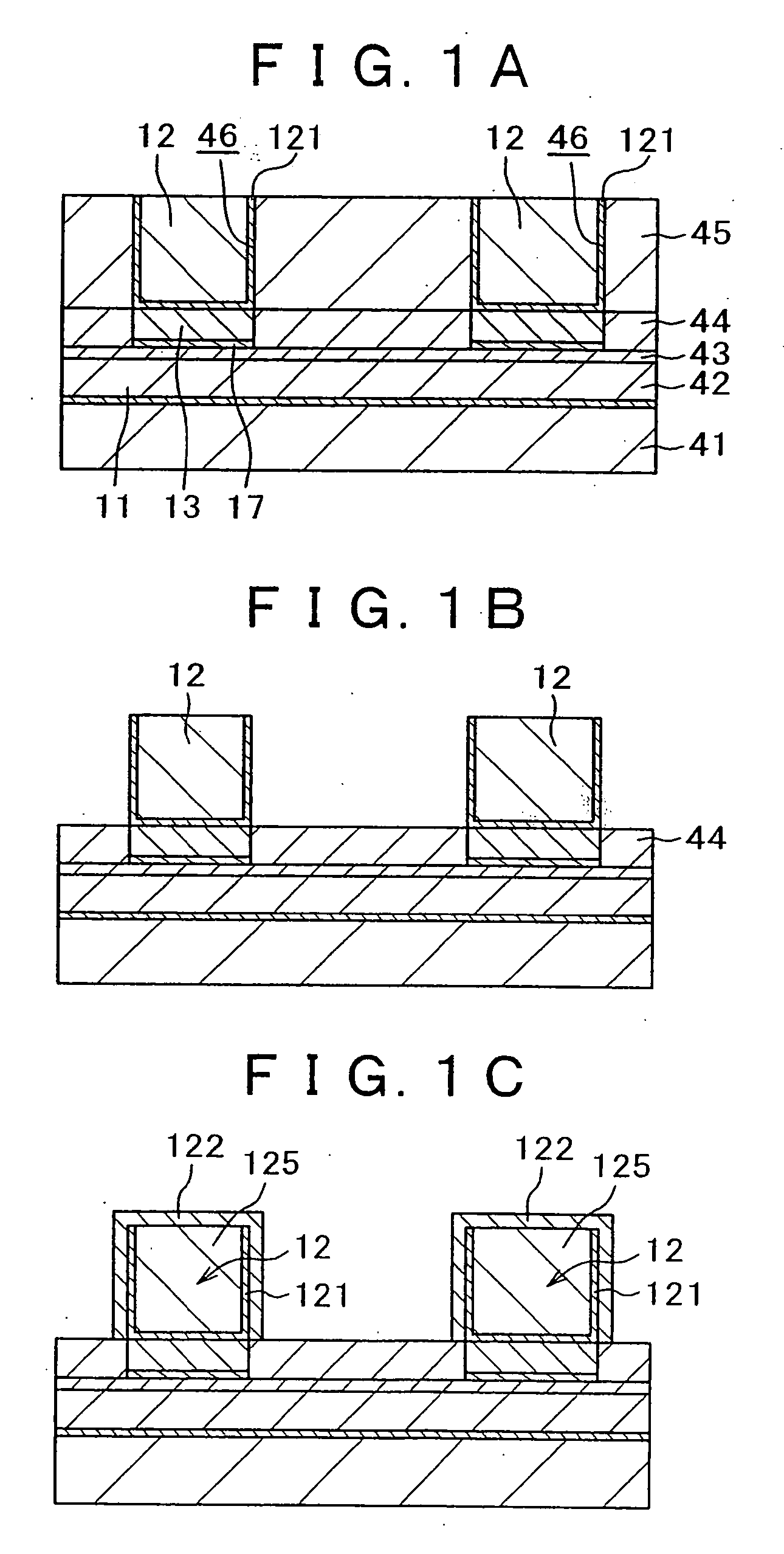
[0054] The method for manufacturing a magnetic memory device and the magnetic memory device according to the present invention will be described with reference to the diagrammatic cross-sectional views of steps of FIGS. 1A to 1C. The cross-sectional views for the embodiments below are those taken along the line in the width direction of a bit line, namely, cross-sectional views taken along the line in the direction of a word line.
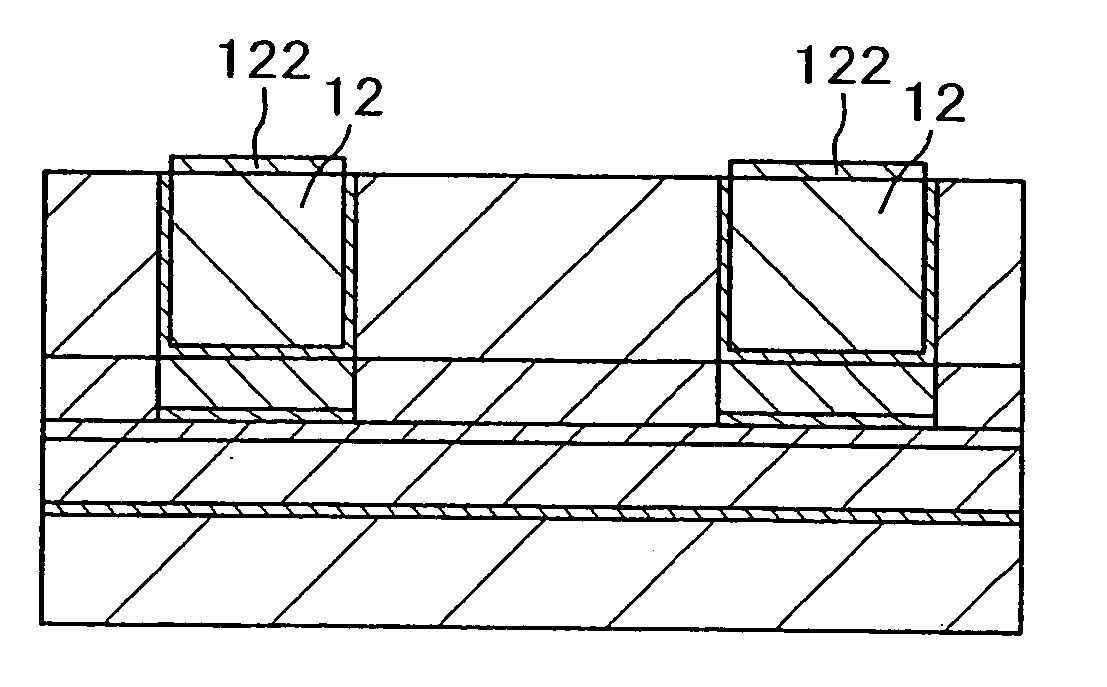
[0055] As shown in FIG. 1A, an element for selection (not shown), a sense line (not shown), and the like are formed on a substrate (not shown), and a first insulating film 41 is formed so as to cover them. On the first insulating film 41 is formed a second insulating film 42 in which a word line and the like are formed, and in the second insulating film 42 are formed a word line (first wiring) 11 having a trench wiring structure, an electrode (not shown) connected to the element for selection (not shown), and the like. On the second insulating film 42, a me...
second embodiment
[0084] Next, the method for manufacturing a magnetic memory device and the magnetic memory device according to the present invention will be described with reference to the diagrammatic cross-sectional views of steps of FIGS. 4A to 4D.
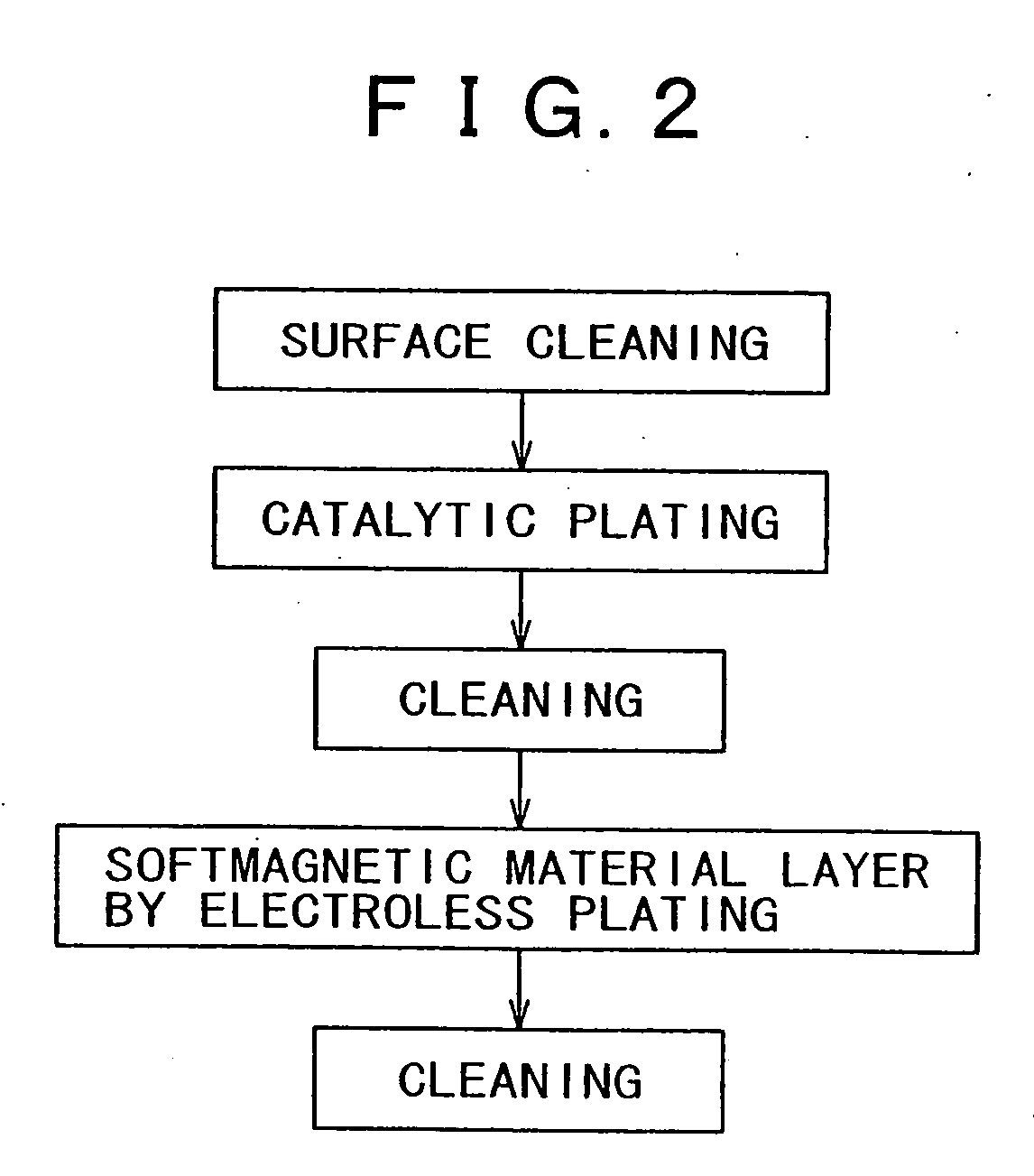
[0085] The second embodiment is a method having an effect to further improve the selectivity for the soft magnetic material layer in the first embodiment. A difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment resides in that, after removal of the fifth insulating film, a process for removing the barrier metal layer on the bit line is introduced. By removing the barrier metal layer, the entire surface of the bit line is comprised of copper, facilitating selective growth of the soft magnetic material layer. This attributes to deposition of palladium by catalytic plating. A high melting point metal is used in the barrier metal layer, and hence it is not easy to deposit a catalyst metal layer on the barrier metal layer. On the other hand, the...
third embodiment
[0091] Next, the method for manufacturing a magnetic memory device and the magnetic memory device according to the present invention will be described with reference to the diagrammatic cross-sectional views of steps FIGS. 5A to 5E.
[0092] For achieving selective complete coverage for the bit line by electroless plating in the first and second embodiments, in the third embodiment, a so-called lift-off method is used in which a mask is formed on a portion on which a soft magnetic material layer is not deposited and a soft magnetic material layer is deposited by selective electroless plating, followed by removal of the mask. The third embodiment is described below.
[0093] As shown in FIG. 5A, the bit line 12 having a trench wiring structure is formed in the fifth insulating film 45 in the same manner as that described above with reference to FIG. 1A.
[0094] Then, as shown in FIG. 5B, the fifth insulating film 45 {see FIG. 5A} is removed in the same manner as that described above with r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com