Material compositions for reinforcing ionic polymer composites
a technology of ionic polymer and composites, which is applied in the field of preparation of ionic polymer compositions, can solve the problems of not teaching the use of soy protein and soy carbohydrate in ionic, patent also fails to teach the formation of intimate ionic complexes in aqueous phase with neutralized carboxylic acid functional groups, and achieves improved functional properties and high elastic modulus.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of 10% Soy Spent Flakes Composite.
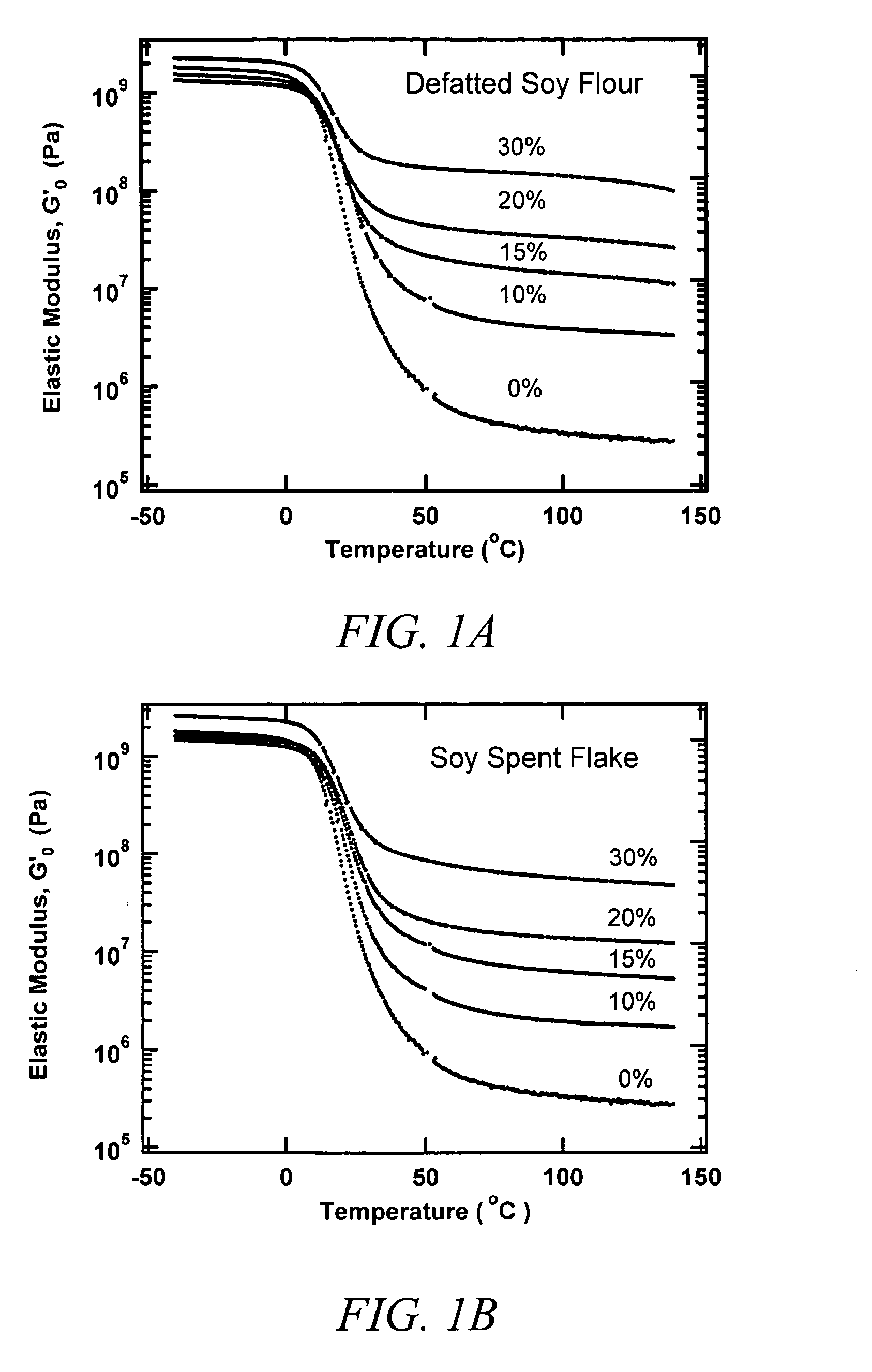
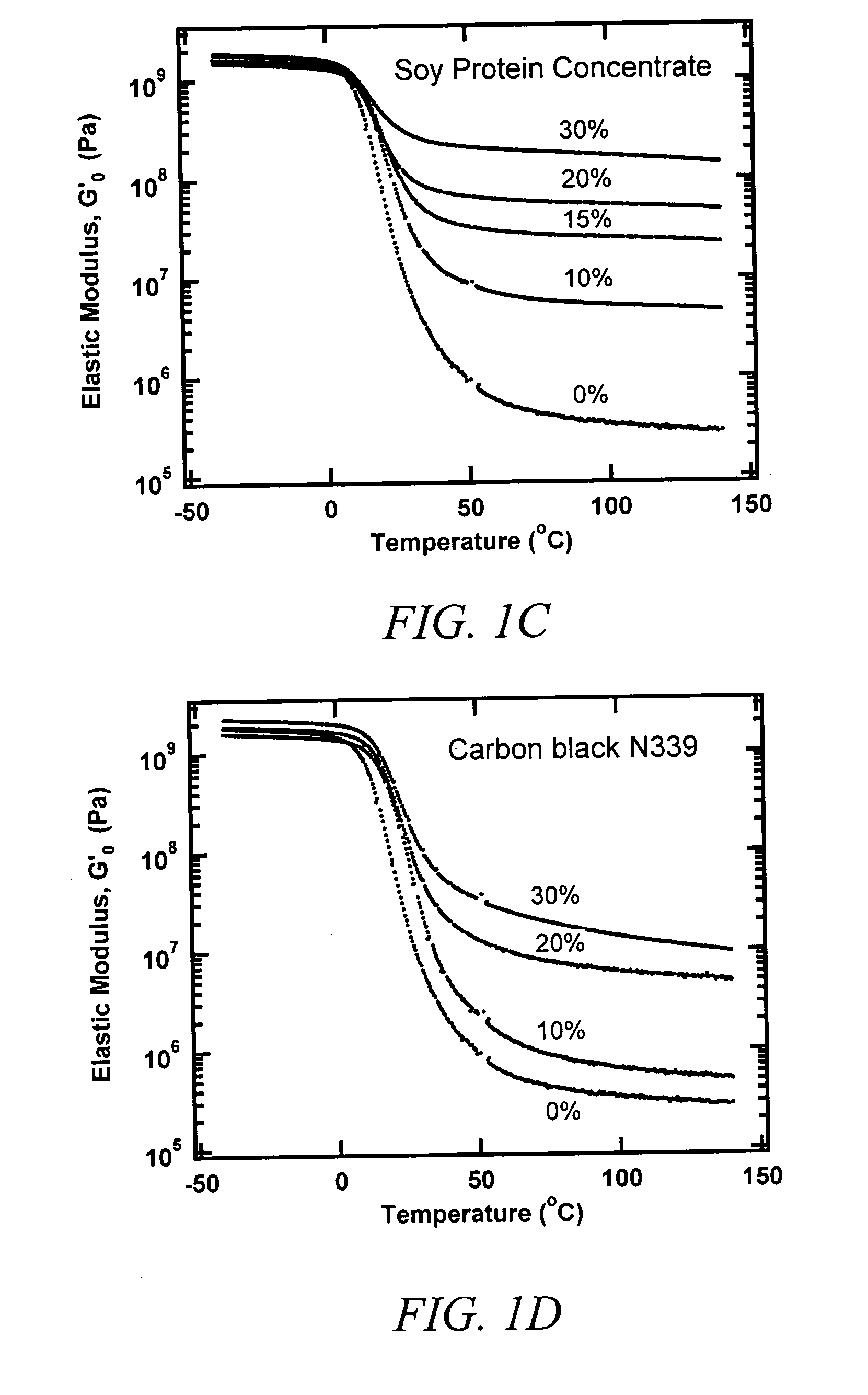
[0051] Soy spent flakes were obtained by dispersing 154 gm of defatted soy flour (Nutrisoy 7B, ADM) in 810 gm of water and cooking at pH 10 and 45° C. for 1 hour. The resulting dispersion was then centrifuged at 3000 rpm and 15° C. for 10 minutes. Soy protein dispersion was removed and the spent flakes were washed with water and centrifuged again to obtain spent flakes with a solids content of 12.2%. A 131.1 gm sample of a 7.6% aqueous dispersion of spent flakes was mixed with 177.3 gm of 50.7% carboxylated styrene-butadiene latex (CP620NA, Dow), and the pH was adjusted to 9. The dispersion was first dried at 75° C. to a moisture content of 3-4% and then dried at 140° C. to a moisture content of less than 1%. After drying, the shear elastic moduli from −40° C. to 140° C. were measured by a dynamic mechanical method at 1 rad / s and 0.05% strain (Rheometric ARES). The effect of dynamic strain is measured at 1 Hz. The stress-strain propert...
example 2
Preparation of 15% Soy Spent Flakes Composite.
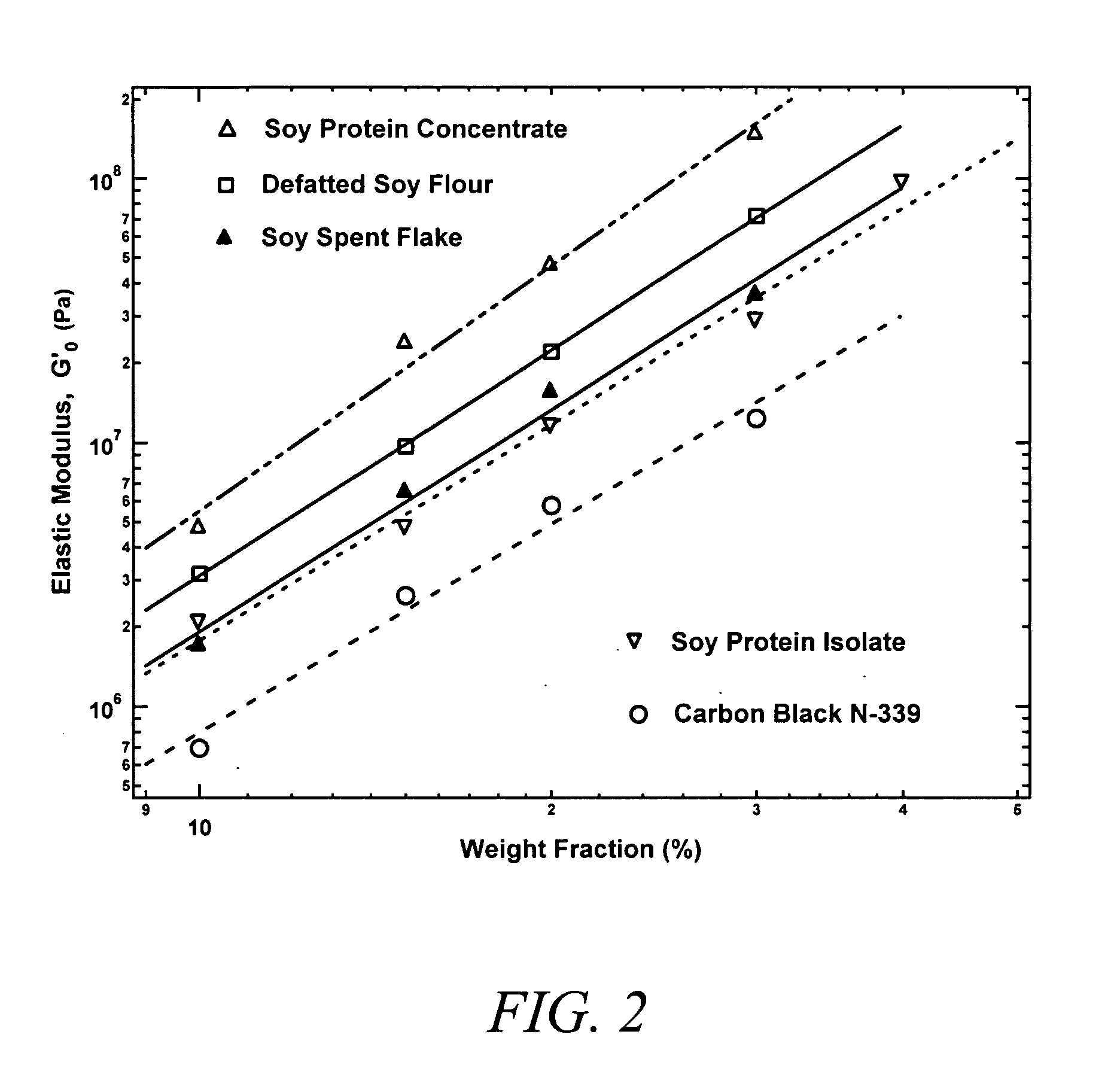
[0052] Soy spent flakes were obtained by dispersing 250 gm of defatted soy flour (Nutrisoy 7B, ADM) in 1300 gm of water and cooking at pH 10 and 45° C. for 1 hour. The resulting dispersion was then centrifuged at 3000 rpm and 15° C. for 10 minutes. Soy protein dispersion was removed and the spent flakes were washed with water and centrifuged again to obtain spent flakes with a solids content of 9.4%. A 209.7 gm sample of a 7.2% aqueous dispersion of spent flakes was mixed with 167.5 gm of 50.7% carboxylated styrene-butadiene latex (CP620NA, Dow) and the pH adjusted to 9. The dispersion was dried in the same manner as that in Example 1. After drying, the mechanical properties were measured as described in Example 1. The mechanical properties of this composite are shown in FIG. 1B, FIG. 2, and FIG. 5B.
example 3
Preparation of 20% Soy Spent Flakes Composite.
[0053] Soy spent flakes were obtained by dispersing 154 gm of defatted soy flour (Nutrisoy® 7B, ADM) in 810 gm of water and cooked at pH 10 and 45° C. for 1 hour. The resulting dispersion was then centrifuged at 3000 rpm and 15° C. for 10 minutes. Soy protein dispersion was removed and the spent flakes were washed with water and centrifuged again to obtain spent flakes with a solids content of 12.2%. A 382.5 gm sample of a 5.2% aqueous dispersion of spent flakes was mixed with 157.51 gm of 50.7% carboxylated styrene-butadiene latex (CP620NA, Dow) and the pH adjusted to 9. The dispersion was dried in the same manner as that in Example 1. After drying, the mechanical properties were measured as described in Example 1. The mechanical properties of this composite are shown in FIG. 1B, FIG. 2, FIG. 3B, and FIG. 5B.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com