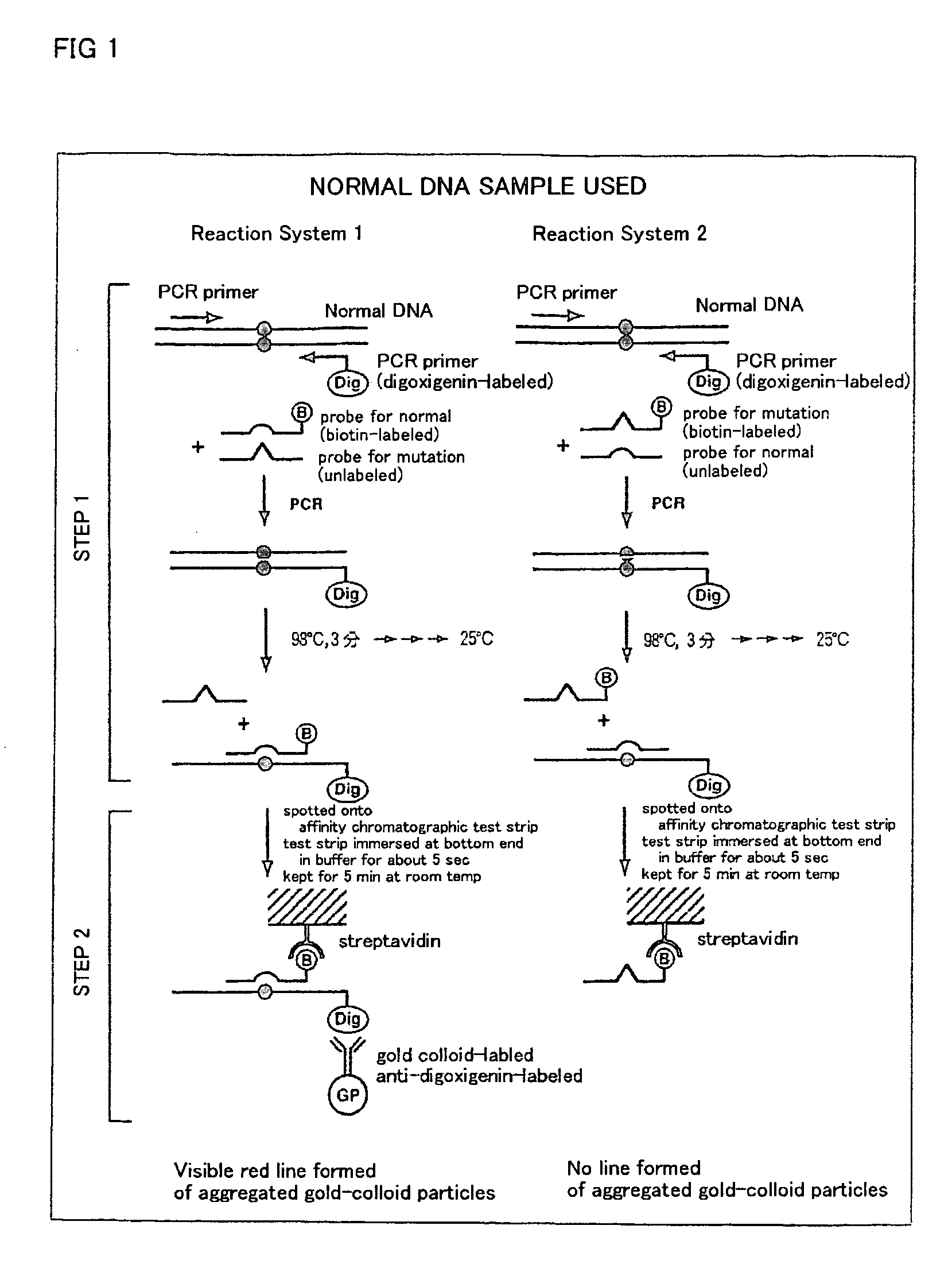
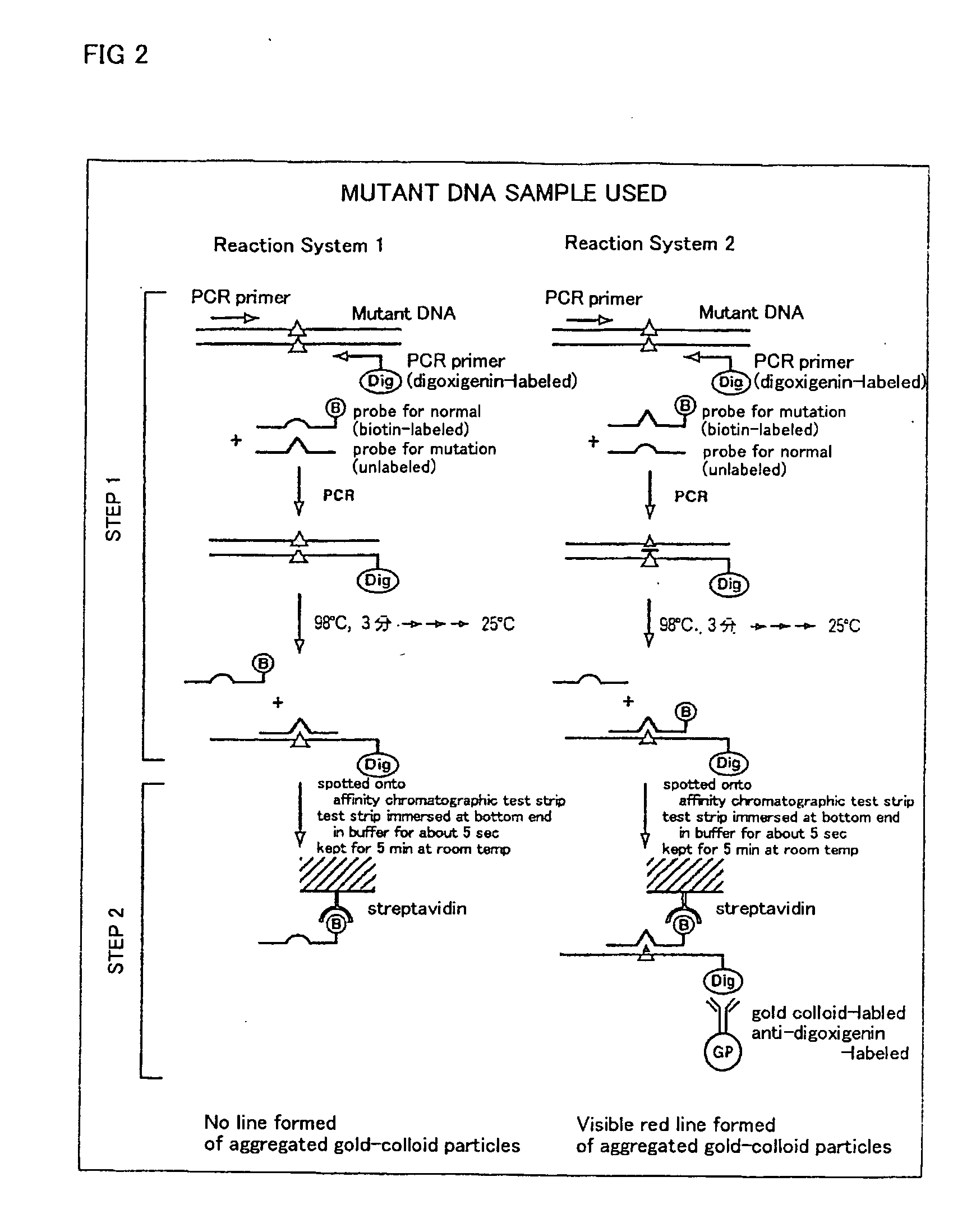
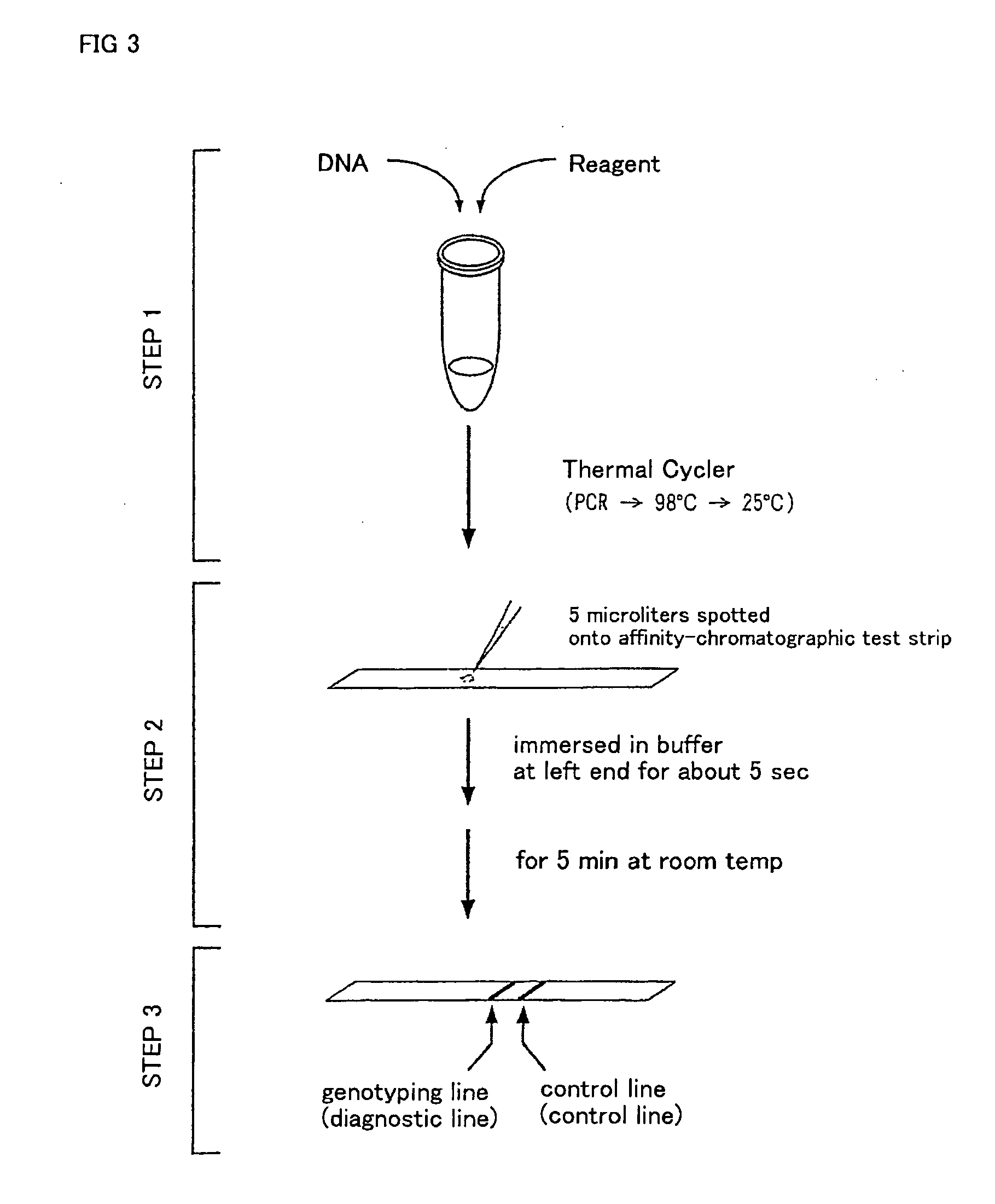
Method of detecting gene mutation
a gene mutation and gene technology, applied in the field of gene mutation detection methods, can solve the problems of complex procedures, high price, specialized instruments, and cannot be easily performed in clinical laboratories, and achieve the effect of simple and rapid detection of gene mutations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Detection of Mutation g727t in Glycogenosis Type Ia
(1) Reaction System and Experimental Procedure
[0076] For detecting g727t mutation in glycogenosis Type Ia, primers listed in Table 1 were prepared on the basis of known base sequences around the mutation site.
TABLE 1Primers and probes for detection of g727t mutationin glycogenosis type IaPCR forward primer (G6P-E5-1F-Dig):5′-Dig-CCCAAATCCTTCCTATCTCTCACAG-3′(SEQ ID NO: 1)PCR reverse primer (G6P-E5-1R(20)):5′-TGCTGGAGTTGAGAGCCAGC-3′(SEQ ID NO: 2)
[0077] For examining the effect of chain lengths of probes, oligonucleotides listed in Table 2 were prepared as hybridization probes and competing probes.
TABLE 2(I) Biotin-labeled oligonucleotide for detectionof normal base sequence:17 mer:5′-AAGCTGAACAGGAAGAA-Biotin-3′(SEQ ID NO: 3)15 mer:5′-AGCTGAACAGGAAGA-Biotin-3′(SEQ ID NO: 4)13 mer:5′-GCTGAACAGGAAG-Biotin-3′(SEQ ID NO: 5)11 mer:5′-CTGAACAGGAA-Biotin-3′(SEQ ID NO: 6)(II) Unlabeled competing oligonucleotide for de-tection of normal...
example 2
[0088] Detection of Mutation a985g of Medium-Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency, Mutation g1691t of GLDC Gene in Hyperglycinemia, Mutation g681a of Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme Gene CYP2C19, and Point Mutation of Glu487Lys of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 Polymorphism
[0089] The detection method of the present invention was carried out to detect a point mutation, including mutation a985g of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, mutation g1691t of GLDC gene in hyperglycinemia, mutation g681a of drug-metabolizing enzyme gene CYP2C19, and point mutation of Glu487Lys of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 polymorphism.
[0090] The PCR primers for amplifying base sequences containing the respective point mutation sites were adjusted in chain length so as to carry out PCR reactions with setting of an annealing temperature of 55° C. In addition, the hybridization probes were designed to have Tm values in the range of 35 to 40° C. As a result, the chain lengths thereof were 10 mers to 15 mers. Th...
example 3
[0095] Detection of Delta F508 Deletion Mutation in Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Regulator Protein Gene, 1277insTATC Insertion Mutation in HEXA Gene of Tay-Sachs Disease, 5382insC Insertion Mutation in BRCA1 Gene of Breast Cancer, 6174delT Deletion Mutation in BRCA2 Gene of Breast Cancer, and G1691A Point Mutation in Blood Coagulation Factor V Gene of Thrombosis
[0096] The detection method of the present invention was carried out to detect a mutation, including deltaF508 deletion mutation in the gene of cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator protein; 1277insTATC insertion mutation in HEXA gene of Tay-Sachs disease; 5382insC insertion mutation in BRCA1 gene of breast cancer; 6174delT deletion mutation in BRCA2 gene of breast cancer; and G1691A point mutation in Blood Coagulation Factor V gene of thrombosis.
[0097] The PCR primers for amplifying base sequences containing the respective mutation sites were adjusted in chain length so as to carry out PCR reactions with setting of an a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com