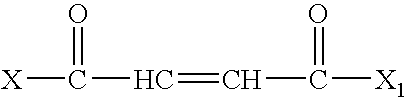
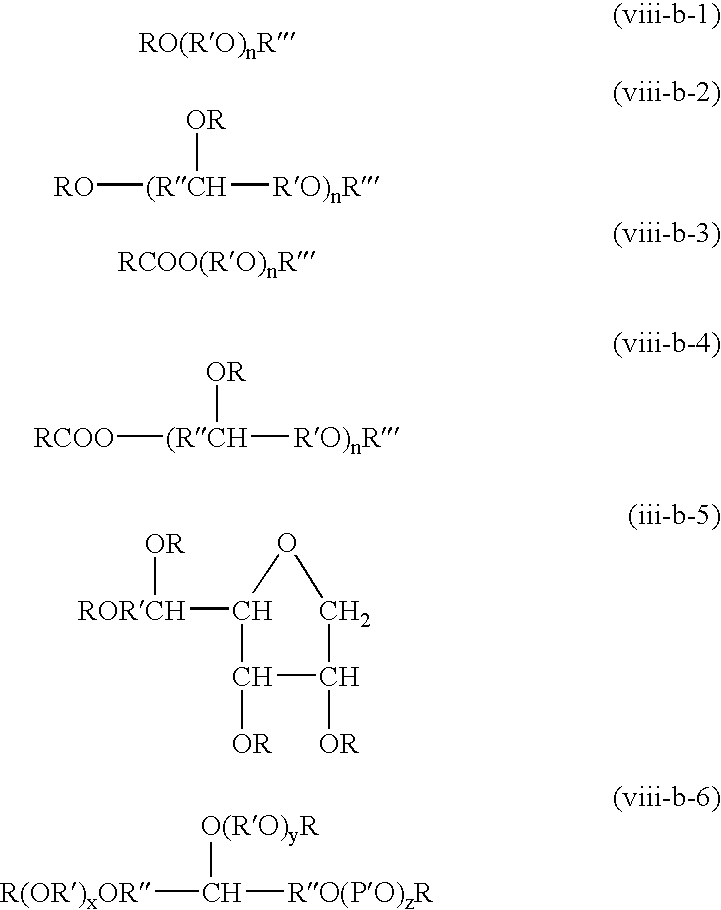
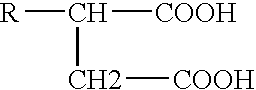Fuel composition having a fuel, water, a high molecular weight emulsifier, and a surfactant including natural fats, non-ionic and ionic surfactants, co-surfactants, fatty acids and their amine salts, or combinations thereof
a fuel and water technology, applied in the direction of fuels, mixing, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to reach and maintain stable water in fuel emulsions of a small particle size, high cost or complicated to be readily commercially available, etc., and achieve low molecular weight and low interfacial tension. , the effect of low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0048] About 0.3 parts by weight of glycerol monooleate and about 2.3 parts by weight of a concentrate mixture containing about 23% wt 2300 MW PIB succinic acid / diethyl ethanolamine salt plus about 31% wt oleic acid / diethyl ethanol amine salt plus about 9.7% of about a 50% ammonium nitrate solution and about 4.7% propylene glycol is mixed into about 77.0 parts by weight of diesel fuel. This organic mixture is then co-fed with about 20 parts by weight water through an 8.0 mm diameter Sulzer SMX static mixer unit consisting of about 48 mixing elements at a total volumetric flow rate of about 470 millilitres per minute. The final white emulsion was placed in storage bottles. After standing for one month at room temperature, about 99% of the material was still an emulsion. No banding or water was observed and only about 1% of the diesel fuel had separated. Particle size, oil separation, and sedimentation were found to be comparable to emulsifiers made using high shear mixing. The partic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mean diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mean diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mean diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com