Burner, gas turbine combustor, burner cooling method, and burner modifying method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
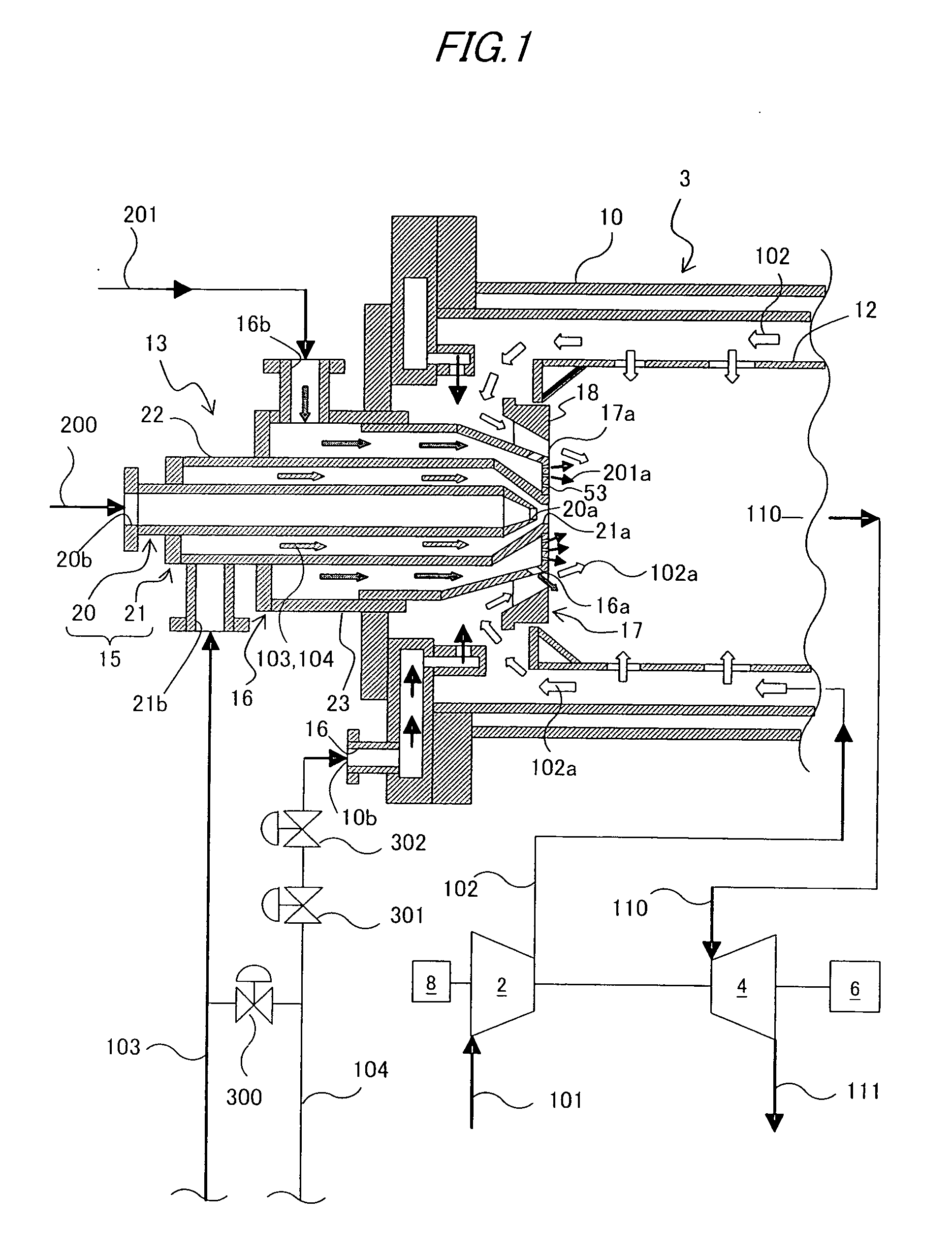
[0033]FIG. 1 is a schematic view of a gas turbine plant equipped with a burner related to the present invention.
[0034] The gas turbine plant equipped with the burner related to this first embodiment comprises an air compressor 2, a combustor 3, a turbine 4, a generator 6, a startup motor 8 for driving a gas turbine, and so on. Inlet air 101 is compressed in the air compressor 2, and compressed air 102 from the air compressor 2 is burned in the combustor 3 together with fuel 200 and 201. When burned gas 110 from the combustor 3 is supplied to the turbine 4, the turbine 4 produces torque with the burned gas 110, and the torque produced by the turbine 4 is transmitted to both the air compressor 2 and the generator 6. The torque transmitted to the air compressor 2 is used as power for compressing air, and the torque transmitted to the generator 6 is converted to electrical energy.
[0035] While the generator 6 is shown as being load equipment in FIG. 1, a pump, etc. may also be used as t...
second embodiment
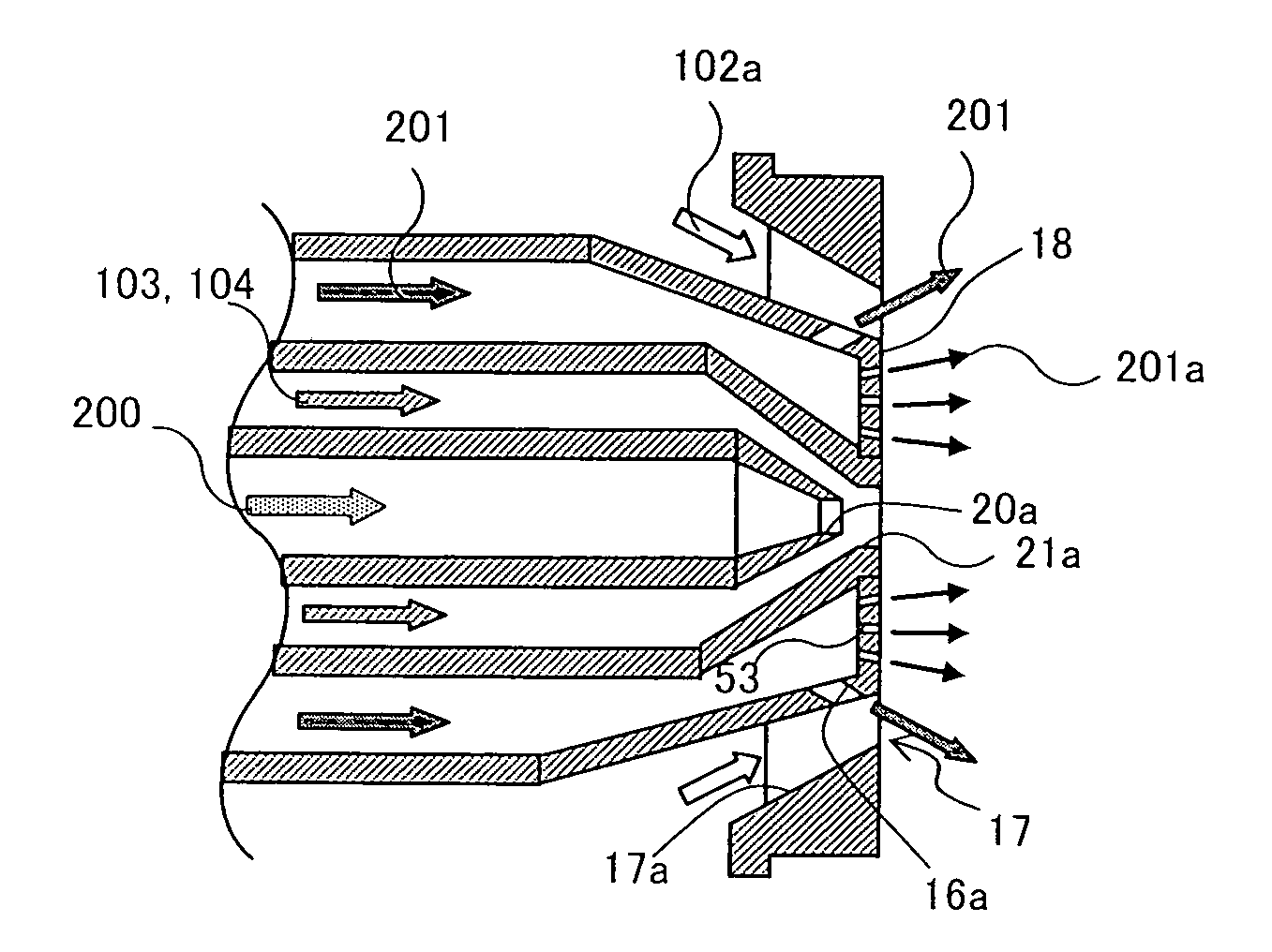
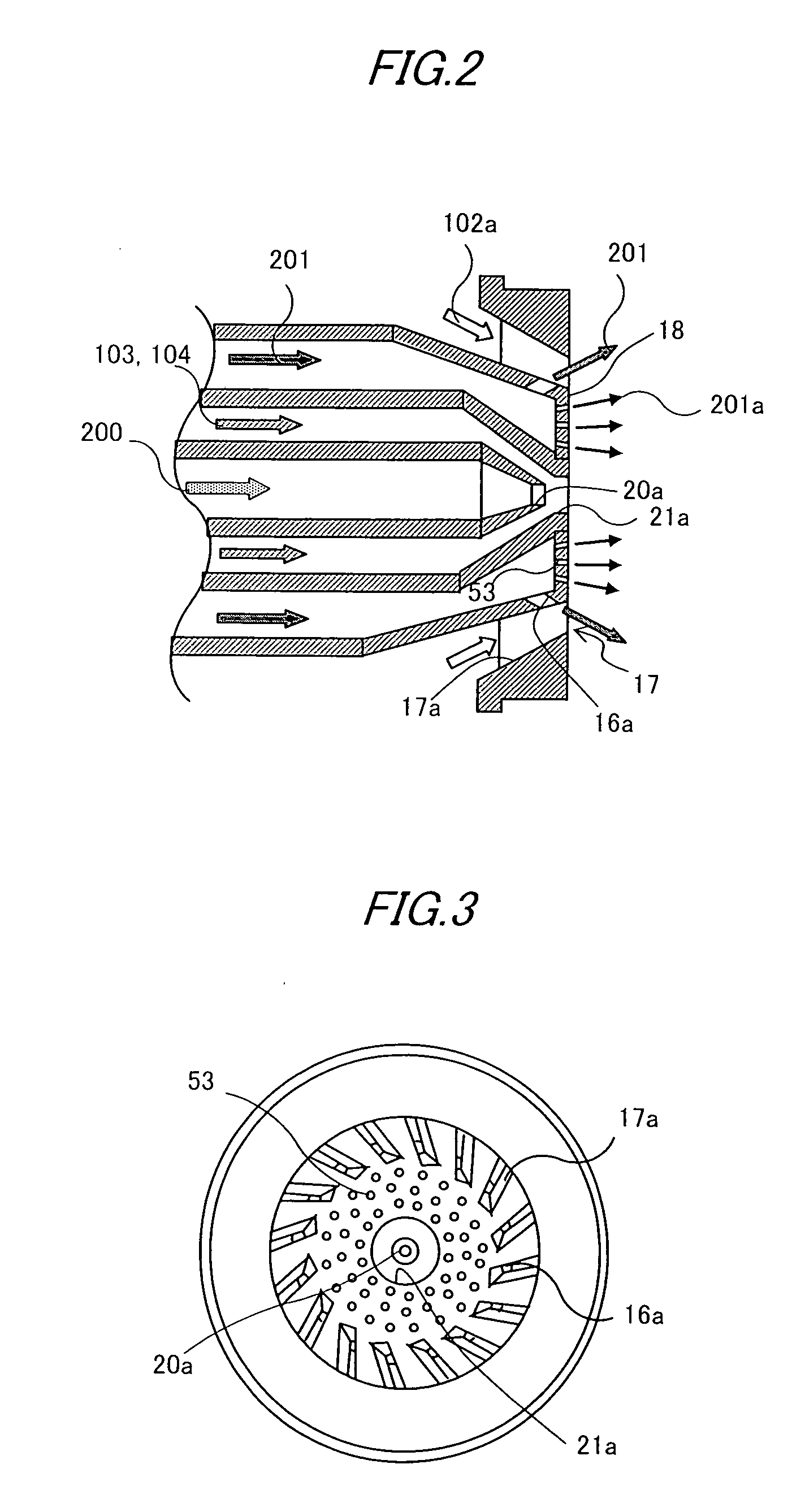
[0065] In the burner shown in FIGS. 4 and 5, the injection ports 16a are formed at the inner peripheral side of the flow passages 17a of the air swirler 17, and the fuel nozzle 15 for startup is disposed at the center of the air swirler 17 in the radial direction. Stated another way, the burner has the same structure as that shown in FIGS. 2 and 3 except for that the cooling holes 53 are omitted. A rise of the metal temperature at the nozzle surface 18 can also be suppressed even with the burner having the structure that the cooling holes 53 are not formed and the fuel concentration in the area near the nozzle surface 18 cannot be enriched with the absence of the cooling holes 53 for introducing a part of the gas fuel.
[0066]FIG. 6 is a schematic view of a gas turbine plant equipped with the burner, shown in FIGS. 4 and 5, according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0067] As in the gas turbine plant shown in FIG. 1, the gas turbine plant shown in FIG. 6 employs the...
third embodiment
[0070]FIG. 9 is a schematic view of a gas turbine plant equipped with a burner according to the present invention, the plant including a system for purging liquid fuel residing in a nozzle for startup.
[0071] In the first and second embodiments, the liquid fuel 200 is used for the startup of the gas turbine, and the supply of the liquid fuel 200 is stopped after the operating mode is shifted to the gas combustion mode using only the mixed fuel in a certain load condition. In such a process, if the liquid fuel 200 resides in the liquid fuel nozzle 20, there occurs a phenomenon (coking) that the liquid fuel nozzle 20 is heated by heat from the flame and the residing liquid fuel 200 is solidified in the nozzle. To avoid such a phenomenon, after completion of the shift to the gas combustion mode using only the mixed fuel, gas such as nitrogen is supplied to the liquid fuel nozzle 20 to purge the residing liquid fuel 200 into the combustion chamber, to thereby prevent the flow passage of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com