Piezoelectric substrate, piezoelectric element, liquid discharge head and liquid discharge apparatus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
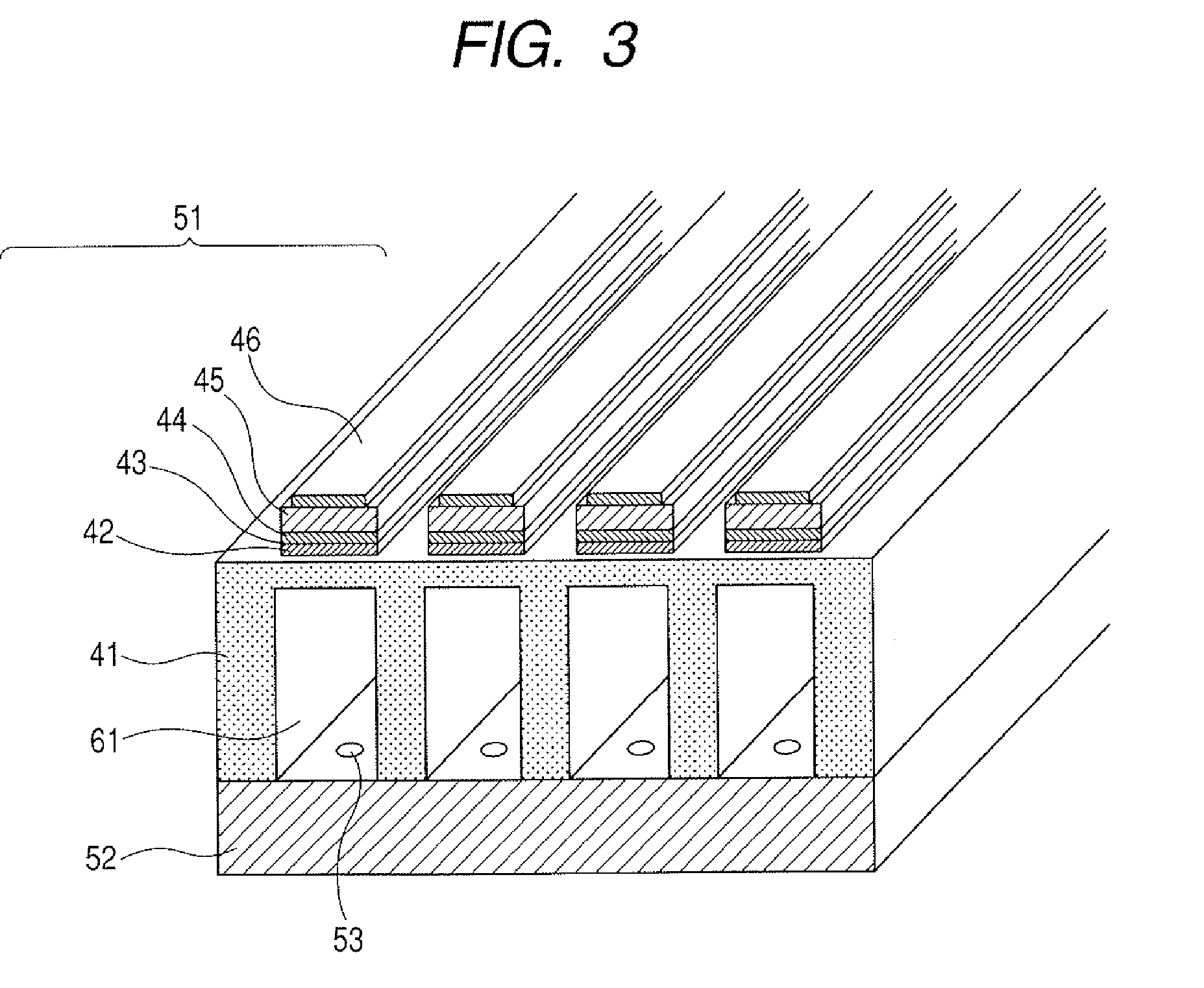
[0072] Firstly, a vibration plate was prepared by forming a film of stabilized zirconia YSZ (Y2O3—ZrO2) on an open section of an Si substrate by means of a sputtering system (L-210-FH (available from ANELVA)). In this process, the Si substrate was heated to 800° C. and Ar and O2 were used as gas to be ionized. Electric power of 100 W was applied between the Si substrate and the target and the internal pressure of the system was held to 1.0 Pa. As a result, a 200 nm thick uniaxial vibration plate was obtained.
[0073] Then, a process same as that of preparing the vibration plate was used to prepare a lower electrode. In this process, Pt was used as target and the substrate was heated to 600° C., while Ar was used as gas to be ionized. Electric power of 100 W was applied between the vibration plate and the target and the internal pressure of the system was held to 0.5 Pa. As a result, a 400 nm thick highly uniaxial Pt film was obtained.
[0074] Subsequently, films of two different oxide...
example 2
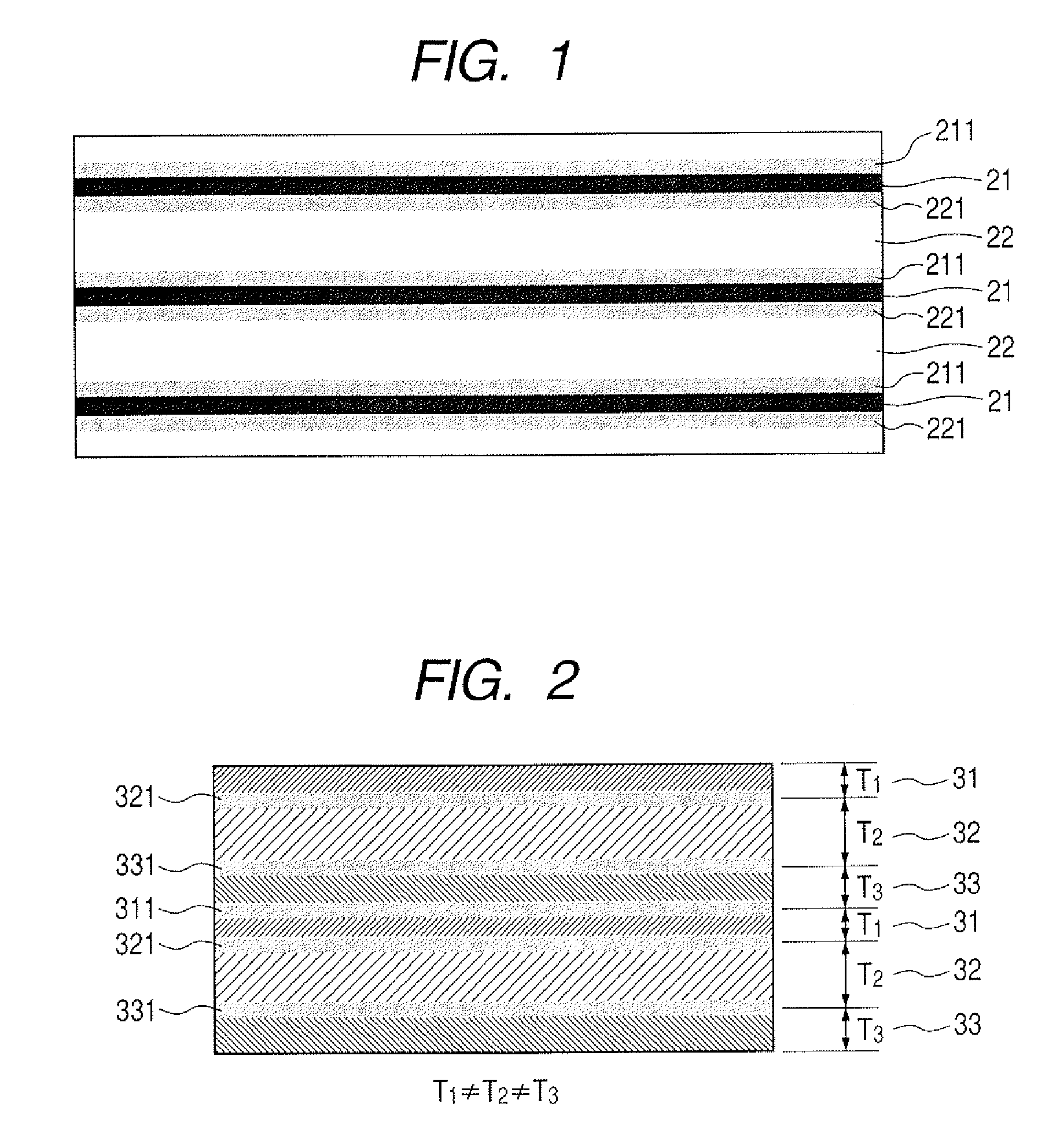
[0079] A liquid discharge head was prepared by following the process of Examples 1 and 2 except that the target compositions as listed below were used for preparing the piezoelectric substrate and a target as illustrated in FIG. 6 was used. As shown in FIG. 6, the target compositions (1) through (3) were arranged in the respective target regions formed by dividing the target by three as materials of the piezoelectric substrate. The sputtering time was 15 minutes, 13 minutes and 11 minutes for the three regions of the different compositions and 4 minutes were spent to form a boundary layer, while moving the aperture of the shutter from one of the compositions to the other. As a result, a piezoelectric substrate comprising 20 layers of the tetragonal structure and 20 layers of the rhombohedral structure and 20 MPB layers that were mixed layers of the two structures was obtained. Thus, it is possible to form a piezoelectric boy having different film thicknesses for layers of different ...
example 3
[0082] A liquid discharge head was prepared by following the process of Examples 1 and 2 except that the target compositions (1) through (4) as listed below were used for preparing the piezoelectric substrate and a target where the materials of the piezoelectric substrate were arranged in the respective target regions formed by dividing the target by four. The sputtering time was 24 minutes, 24 minutes, 24 minutes, 30 minutes, 24 minutes and 36 minutes for the regions of the different compositions and 6 minutes were spent to form a boundary layer, while moving the aperture of the shutter from one of the compositions to the other. As a result, a piezoelectric substrate comprising 10 layers of each of the six structures including the tetragonal structure, the rhombohedral structure, the tetragonal structure, the pseudocubic structure, the tetragonal structure and the monoclinic structure was obtained. Thus, it is possible to form a piezoelectric substrate having desired film thickness...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com