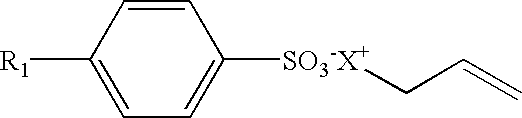
Process for improving water-whitening resistance of pressure sensitive adhesives
a technology water-whitening resistance, which is applied in the direction of adhesive types, coatings, emulsion paints, etc., can solve the problems that none of the above patents/publications disclose the preparation of pressure sensitive adhesives, and achieve enhanced resistance to water-whitening and water-whitening. the effect o
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0083] In a 2 L jacketed glass reactor equipped with a reflux condenser, thermocouple and twin blade agitator, 701.5 g of polyacrylate latex was prepared. Monomer pre-emulsion was prepared by mixing 110 g water, 192.4 g 2-EHA, 64 g BA, 45 g MA, 6.25 g MAA, and 9.75 g AA with 9.27 g Polystep NMS-7. The reactor was charged with 140 g of water and 3 g of Polystep NMS-7. Separately, 117 g of PPS stock solution (0.94 wt. % concentration) was prepared in water. The reactor was heated with water. When the temperature reached 79° C., 0.75 g PPS was added followed by continuous addition of the monomer pre-emulsion at a 2.1-2.2 g / min rate for 3.5 hr. The temperature was maintained at 83° C. and the polymerization charge agitated continuously at 240 rpm. Every 20 min, 10 g of the PPS stock solution was added to the reactor. After the pre-emulsion addition was complete, the reactor temperature was raised to 85° C. and agitated for an additional 40 min after which 1.5 g VeoVa 5 was added to the ...
example 2
Control
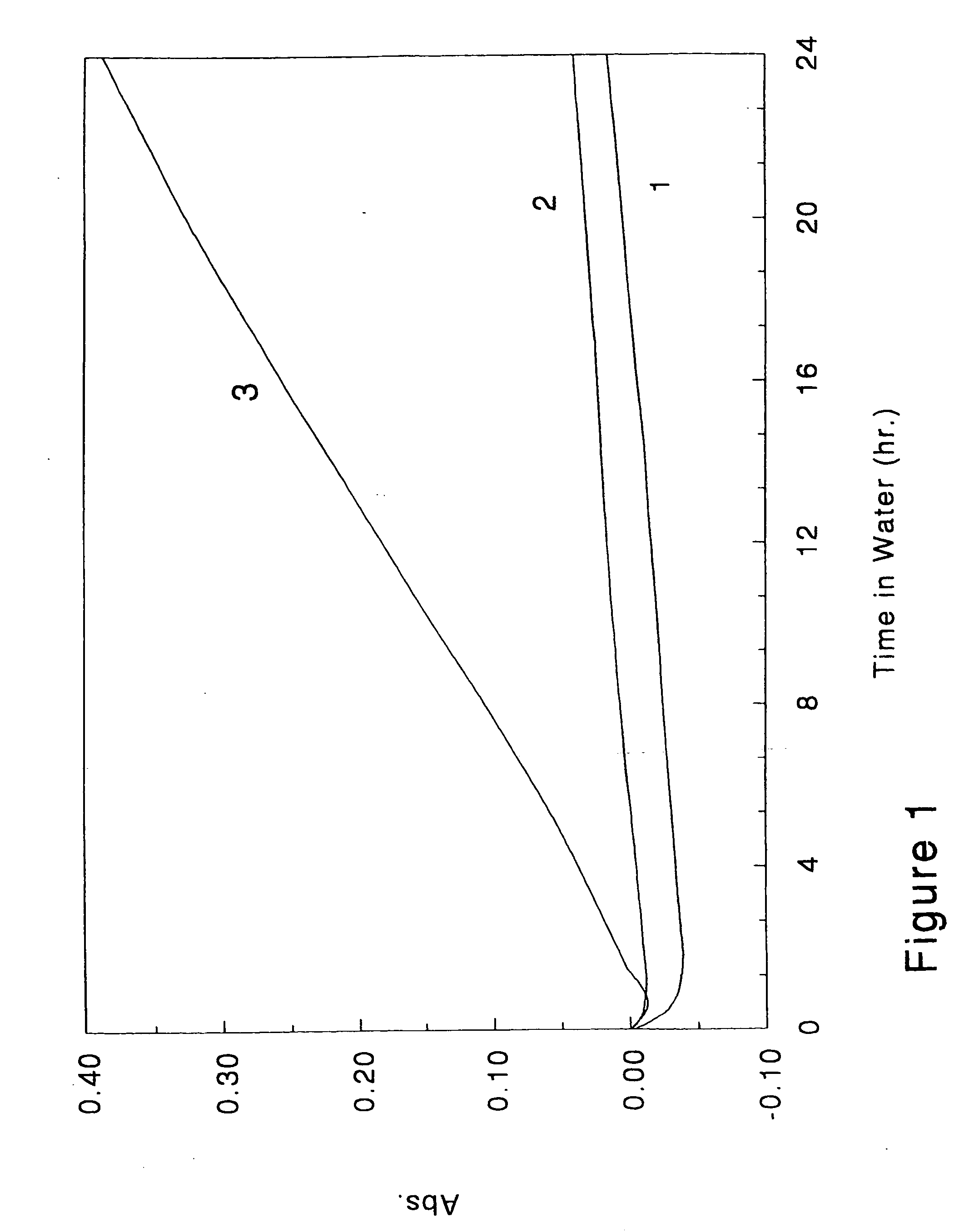
[0087] In a control experiment, latex was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 except conventional surfactants were used in place of the Polystep NMS-7. Thus, 5.3 g Abex EP-120 (30% solids) was used in the initial reactor charge, and 3.2 g Abex EP-120, 0.78 g AOT 75, and 3.88 g Igepal Co-630 was used to stabilize the pre-emulsion. The final latex had an average particle size of 87 nm, 46.9% solids, pH=2.24, and Brookfield viscosity of 546. The latex was neutralized to pH 7.84. The latex film was direct coated as described in Example 1, and the UV / VIS absorbance was measured in room temperature water during a 24 hr immersion test. The final absorbance was 0.388 (curve # 3 in FIG. 1).
[0088] The results of Examples 1 and 2 demonstrate that the PSAs of the invention have significantly improved resistance to water-whitening compared to a similar polymer prepared using conventional surfactants.
example 3
[0089] A polymerization was carried out according to the procedure described in Experiment 1 except instead of 2-EHA, 192 grams of iOA was emulsified with BA, MA, AA, and MAA.
[0090] The latex had 47.5% solids. The average particle size was 98 nm and pH=2.23. Brookfield viscosity was 740 cp. The latex was neutralized to a pH of 7.98 with NH4OH.
[0091] Latex film was prepared by direct coating on Mylar at 1 mil coat weight. The change of absorbance after 24 hr room temperature immersion was 0.039.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt. % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt. % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com