Method for cloning and expressing target gene by homologous recombination
a technology of homologous recombination and target genes, which is applied in the field of cloning and expressing target genes by homologous recombination, can solve the problems of high cost and expensive enzymes, and achieve the effect of easy cloning of target genes and high speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Transformed Cells Containing Expression Vectors pRMT, and pRMT & pKD46
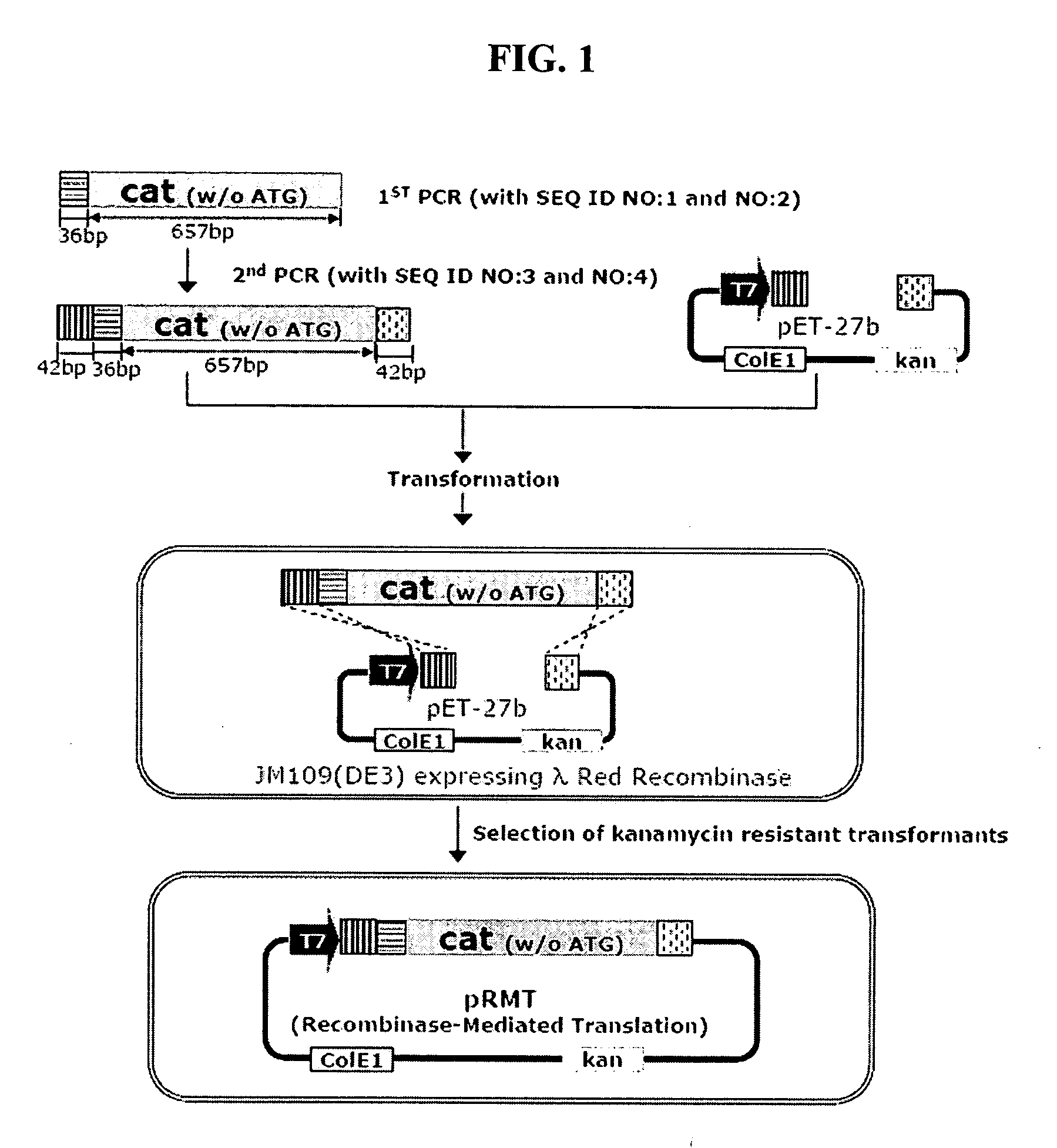
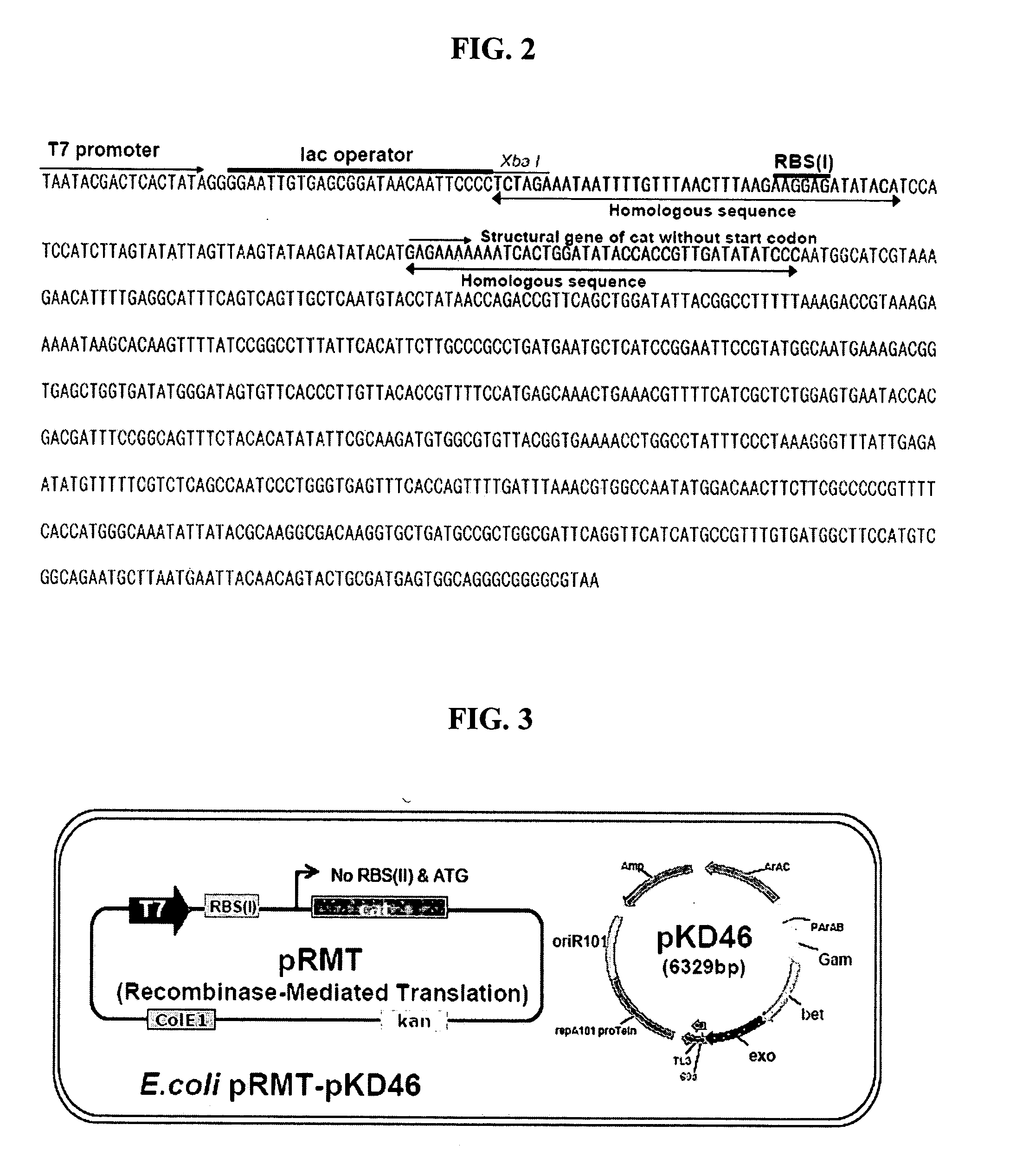
[0084] To construct recombinant vector pRMT comprising a chloramphenicol-resistant gene (cat) having deletions of a ribosome recognition sequence and start codon required for the expression thereof as a first selection marker gene, and a kanamycin-resistant gene (kan) as a second selection marker gene, a homologous recombination technique was used, wherein a DNA fragment containing a PCR-amplified cat gene having deletion of a start codon was linked to a plasmid vector linearized with restriction enzymes (FIG. 1).
[0085] Specifically, in the homologous recombination technique, the linear vector and the linear DNA fragment containing sites homologous to each other, were introduced into recombinant E. coli (arabinose-induced pKD46 / E. coli JM109(DE3)) by electroporation to clon. This method has advantages over a conventional restriction enzyme-ligase technique, in that it has no restriction in selecti...
example 2
[0099] As a target gene for application to the recombinant vector pRMT constructed in Example 1, a red fluorescent protein gene (DsRed2) was used. The DsRed2 gene can be visually observed for the expression of protein by UV irradiation.
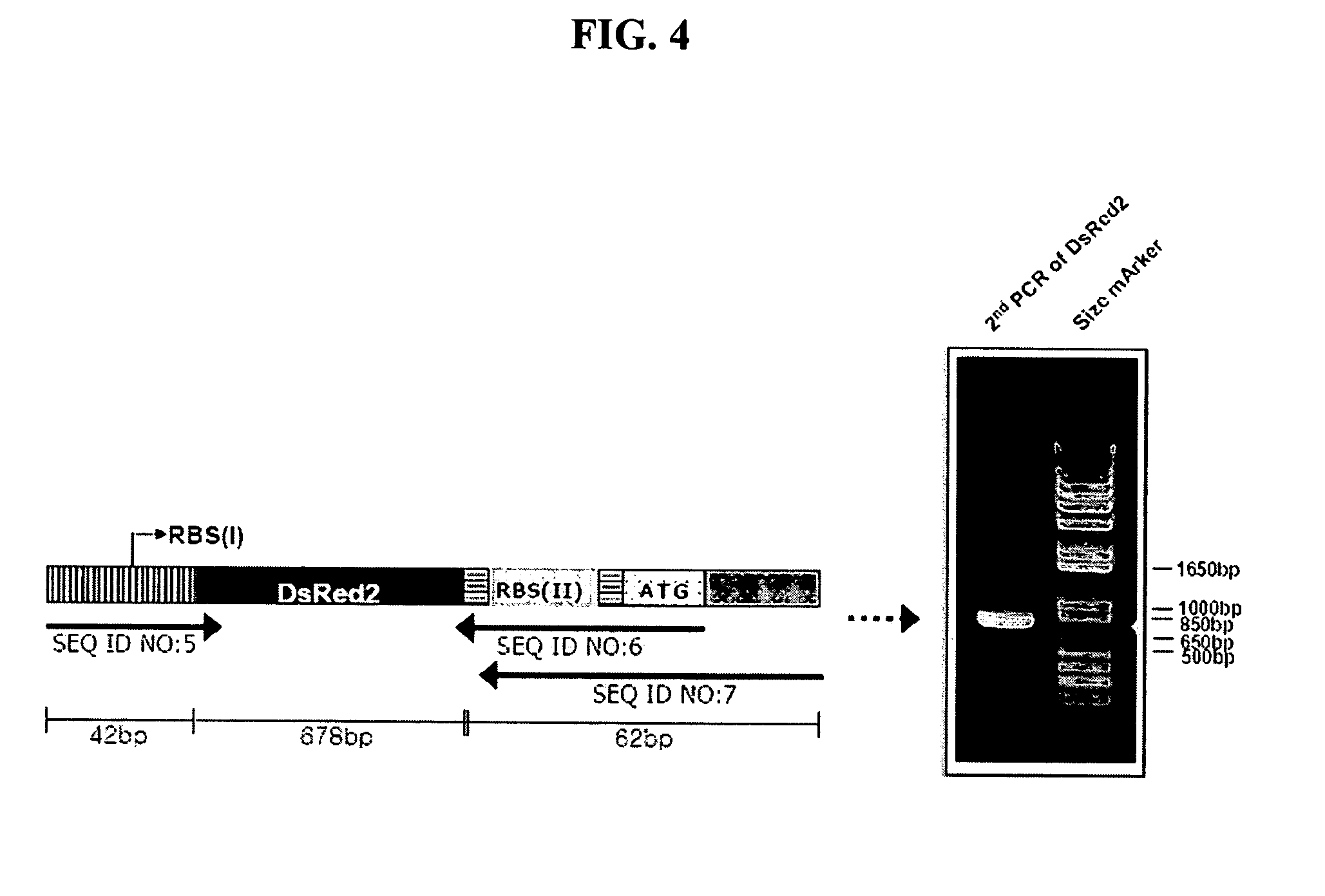
[0100] The red fluorescent protein gene (DsRed2) was amplified by PCR in the following manner. The red fluorescent protein gene (DsRed2) was amplified using a pDsRed2 (Clontech, USA) vector as a template with the following primers of SEQ ID NOS: 5 and 6.
SEQ ID NO: 5:5′-TCTAGAAATAATTTTGTTTAACTTTAAGAAGGAGATATACATATGGCCTCCTCCGAGAACG-3′SEQ ID NO: 6:5′-CTCATGTATATCTTATCTACAGGAACAGGTGGTGGCG-3′
[0101] Wherein, underlined regon represents forward homologous region and italic characters represent antisense sequence of start codon and forward ribosome binding site, respectively.
[0102] The primer of SEQ ID NO: 5 contains a base sequence homologous to a given length of the region downstream of the T7 promoter of pRMT, and the primer o...
example 3
Transformation Using Electroporation
[0107] The electro-competent cells containing pRMT & pKD46, prepared in Example 1, were transformed with 100 ng iTGR (a linear DNA fragment containing a DsRed2 gene) prepared in Example 2 by electroporation and then left to stand overnight at room temperature to induce homologous recombination. Because a chloramphenicol-resistant gene as the first selection marker gene is expressed in transformed cells where pRMT and iTGR were successfully homologously recombined with each other, the cells were spread on LB agar medium containing chloramphenicol so as to select colonies (FIG. 5).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| OD | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| antibiotic resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com