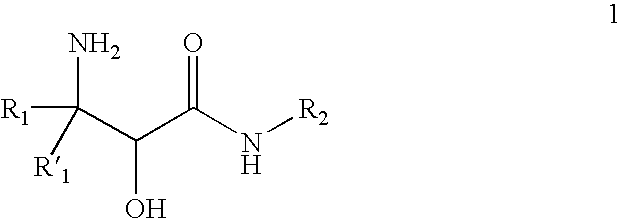
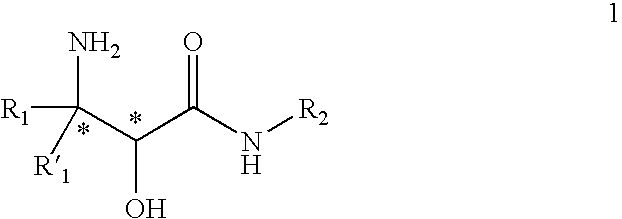
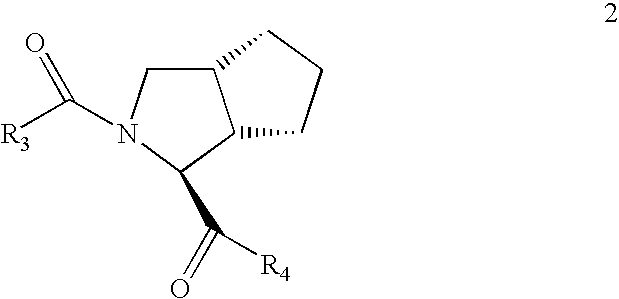
Processes and intermediates for preparing steric compounds
a technology of steric compounds and intermediates, which is applied in the preparation of carboxylic compounds, peptides, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of progressively worsening liver inflammation and no broadly effective treatment for the debilitating progression of chronic hcv
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
3-Propyloxirane-2-carboxylic acid
[0115]
[0116] A flask equipped with an overhead stirrer, thermometer and addition funnel was placed under a nitrogen atmosphere then charged with trans-2-hexenoic acid (69.8 g, 611 mmol), water (420 mL) and acetone (420 mL). Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3, 224 g, 2.66 mol) was then added portion-wise keeping the reaction temperature at 25±5° C. Once all of the sodium bicarbonate had been added, a solution of OXONE® (454 g, 738 mmol) in 4×10−4 M ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt dehydrate (Na2EDTA; 1.32 L) was charged to the addition funnel and added over 90 minutes keeping the reaction temperature at 25±5° C. and the pH between 9.5 and 7.5. The reaction mixture was then allowed to stir for 16 h, after which time no (E)-hex-2-enoic acid was observed by HPLC analysis. The mixture was cooled to 0±5° C., acidified to pH 2 with 6 N HCl (515 mL, 2.8 mol) and extracted with ethyl acetate (EtOAc; 3×250 mL). The combined organic phases were dried over...
example 2
N-cyclopropyl-3-propyloxirane-2-carboxamide
[0118]
[0119] A flask equipped with an overhead stirrer, thermometer and addition funnel was placed under a nitrogen atmosphere then charged with the acid of Example 1 (20.0 g, 154 mmol), and isopropyl acetate (IPAc; 200 mL) then cooled to 0±5° C. 4-Methylmorpholine (NMM, 154 mL, 17 mL) was charged to the addition funnel then added maintaining the temperature at 0±5° C. Once addition was complete the addition funnel washed with IPAc (10 mL) and then charged with isobutyl chloroformate (IBCF, 137 mmol, 19.5 mL) which was added keeping the temperature at 0±5° C. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0±5° C. for 90 min after which time a solution of cyclopropylamine (154 mmol, 10.7) in IPAc (80 mL) was added keeping the temperature at 0±5° C. Upon completion of addition the reaction was warmed to 25±5° C. and allowed to stir for 18 h. Sodium hydroxide (231 mL, 1.0 N) was added and the biphasic mixture stirred vigorously for 30 min, then the laye...
example 3
Alternate preparation of N-cyclopropyl-3-propyloxirane-2-carboxamide
[0121]
[0122] A flask equipped with a stir bar, thermometer and addition funnel was placed under a nitrogen atmosphere then charged with the acid of Example 1 (5.0 g, 38 mmol), N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI; 8.1 g, 42 mmol), 1-hydroxybenzotriazole hydrate (HOBt; 5.7 g, 42 mmol) and N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF; 50 mL) then cooled to 0±5° C. The addition funnel was charged with NMM (5.9 mL, 54 mmol) which was then added to the reaction mixture maintaining the temperature at 0±5° C. The mixture was stirred for 30 minutes then cyclopropylamine (2.9 mL, 42 mmol) was added and the reaction allowed to warm to 25±5° C. over 16 hours. Hydrochloric acid (50 mL, 1.0 N) and IPAc (50 mL) were added and then the mixture stirred for an additional 30 minutes. The contents were transferred to separatory funnel, the layers separated then the organic layer washed sequentially with HCl (50 mL, 1.0 N)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com