Pressure sensing
a technology of pressure sensing and biological fluids, applied in the field of fluid management, can solve the problems of cross contamination, cross contamination, and backpressure on the blood column in the connector line, and achieve the effects of avoiding cross contamination between patients and/or operators, minimizing the air-blood interface, and convenient setting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
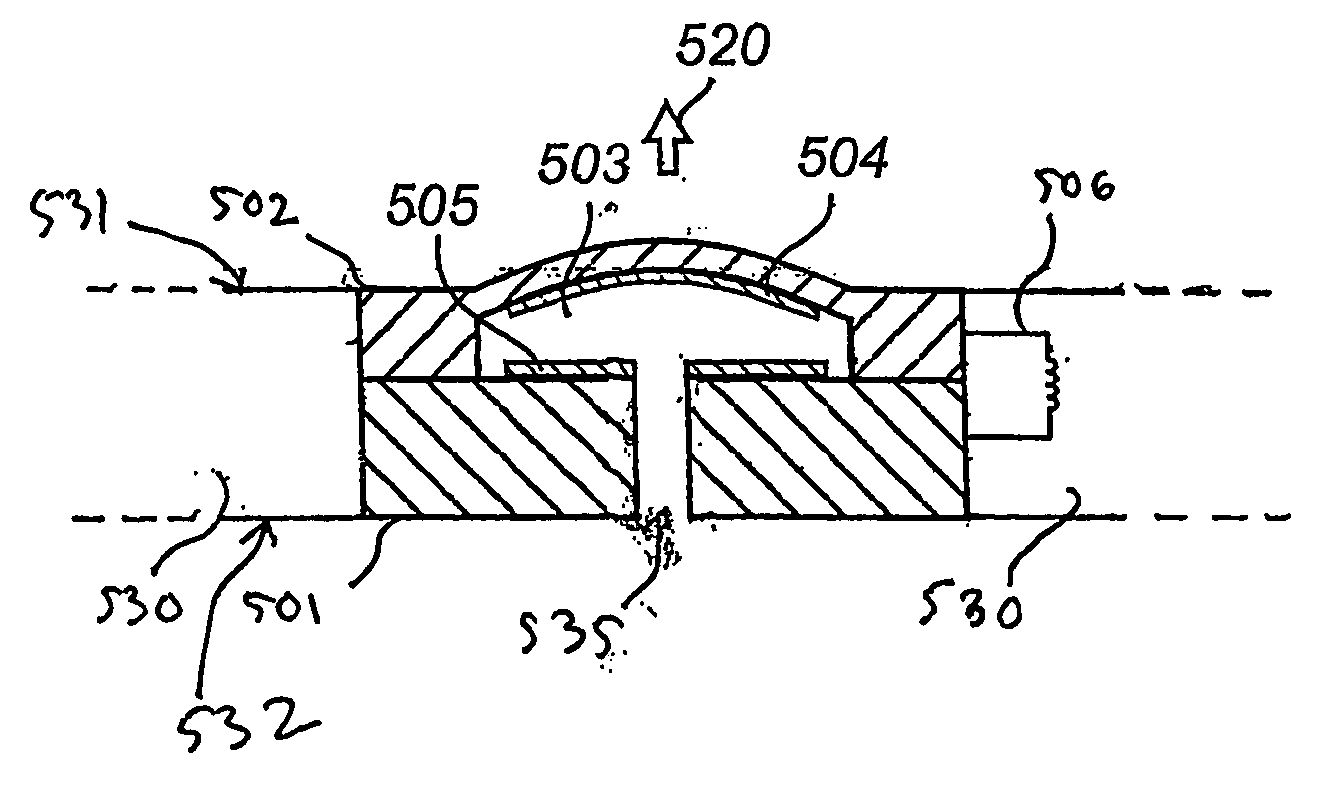
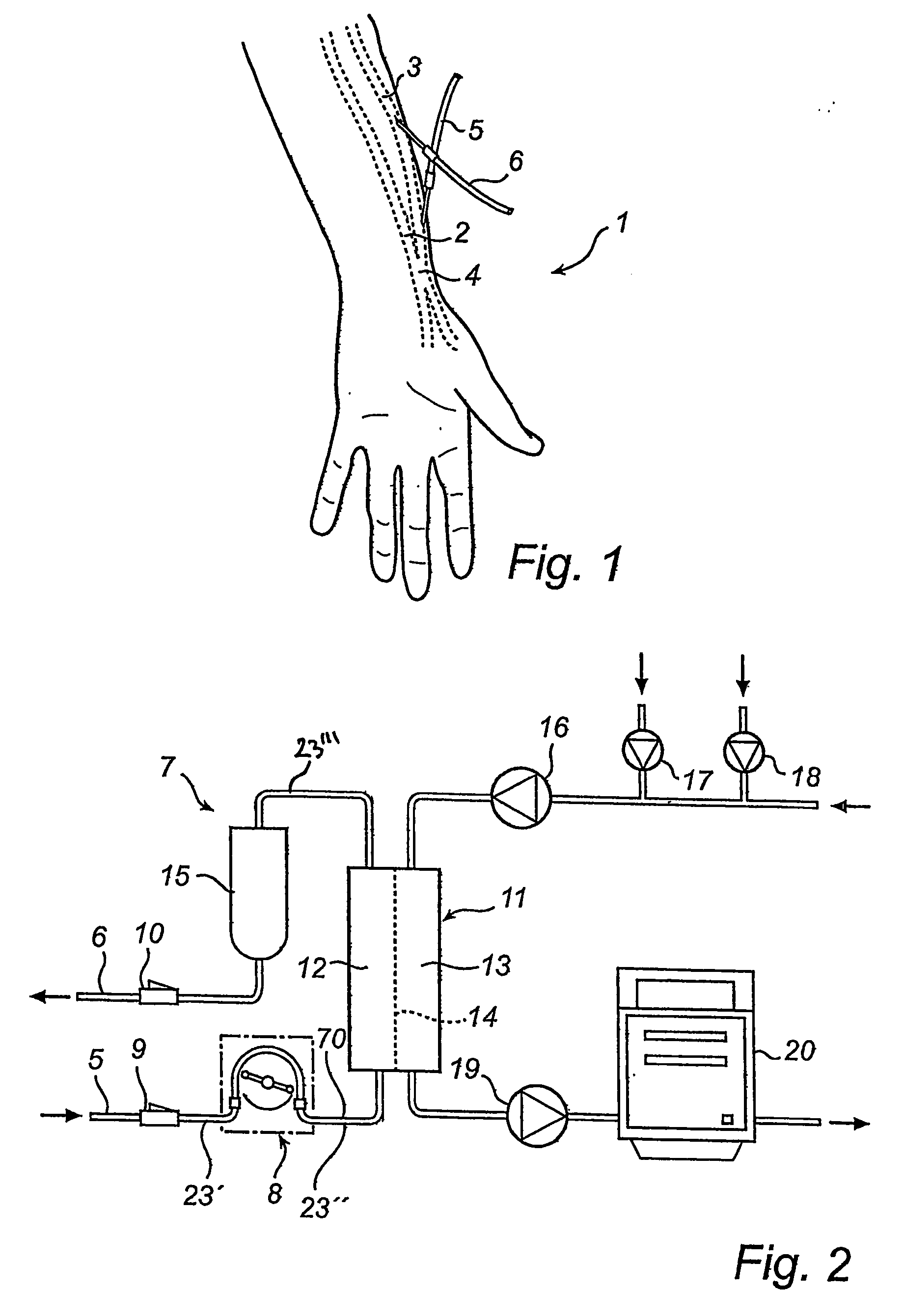
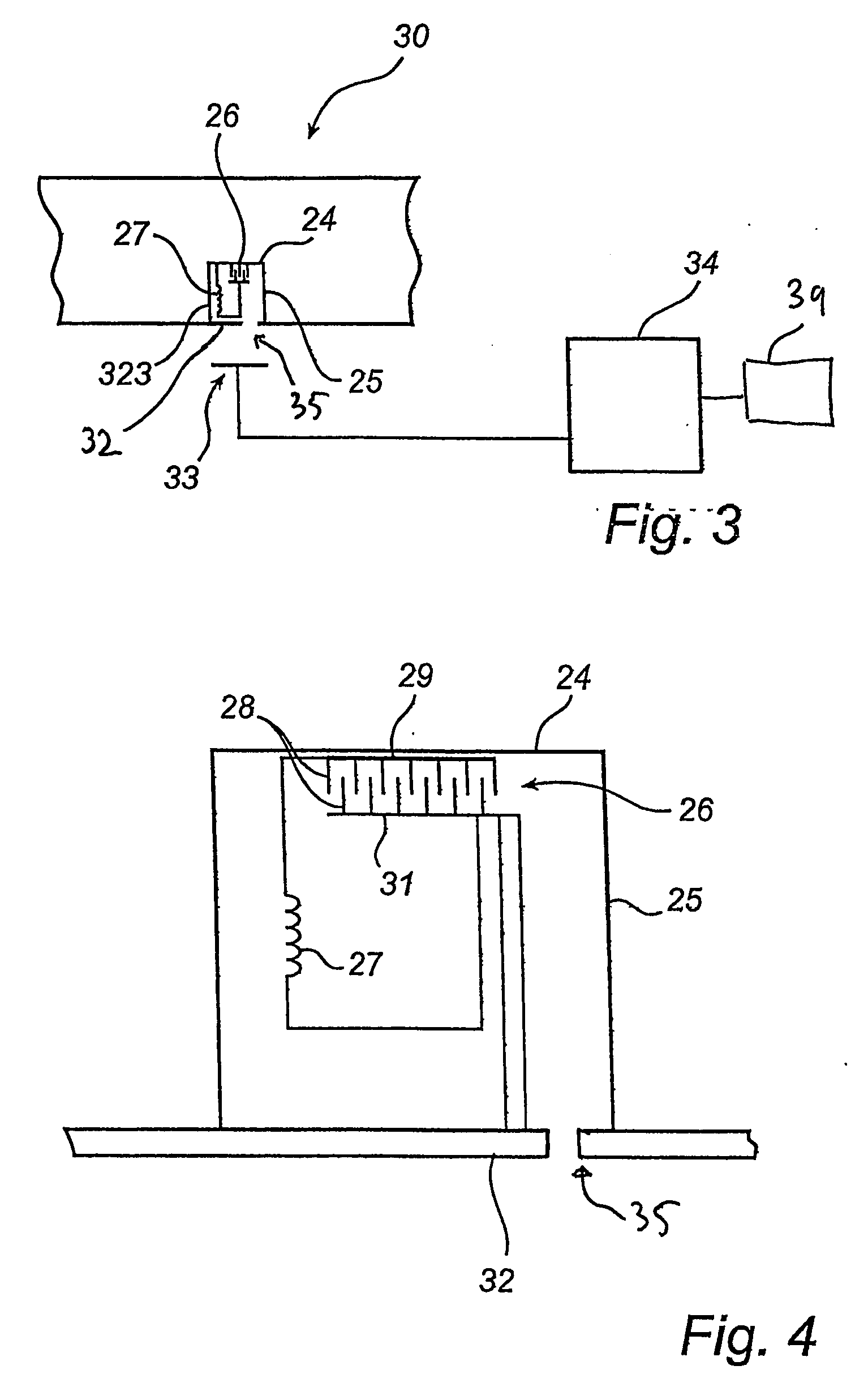
[0034] The invention will be described initially by way of illustration of an extracorporeal blood circuit during the process of dialysis followed by a description of pressure sensors and concluding with a description of a system comprising a blood circuit, pressure sensors, a transmitter and a receiver.
[0035]FIG. 1 discloses a forearm 1 of a human patient. The forearm comprises an artery 2, in this case the radial artery, and a vein 3, in this case the cephalic vein. Openings are surgically created in the artery 2 and the vein 3 and the openings are connected to form a fistula 4, in which the arterial blood flow is cross-circuited to the vein. Due to the fistula, the blood flow through the artery and vein is increased and the vein forms a thickened area downstream of the connecting openings. When the fistula has matured after a few months the vein is thicker and may be punctured repeatedly. Normally, the thickened vein area is called a fistula. As the skilled person will realize, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| inductance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| capacitance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| resonant frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com