Biomass pellet fuel heating device, system and method
a technology of biomass pellets and heating devices, applied in the direction of household stoves or ranges, solid heating fuels, lighting and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of significant burnback risk, ineffective heating, and inefficiency of current pellet delivery methods, so as to achieve dramatic increases in thermal efficiency and reduce the effect of particulate emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
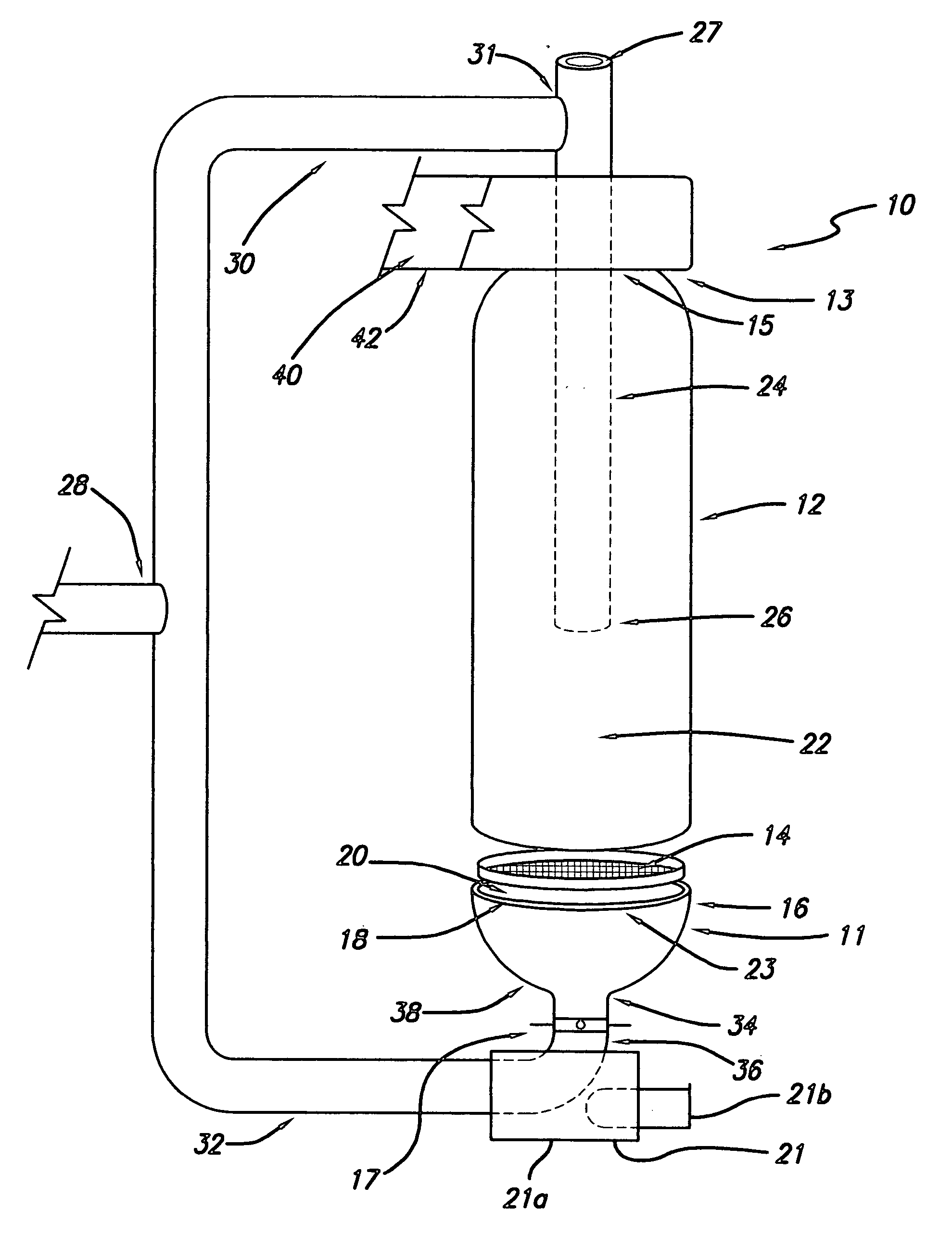
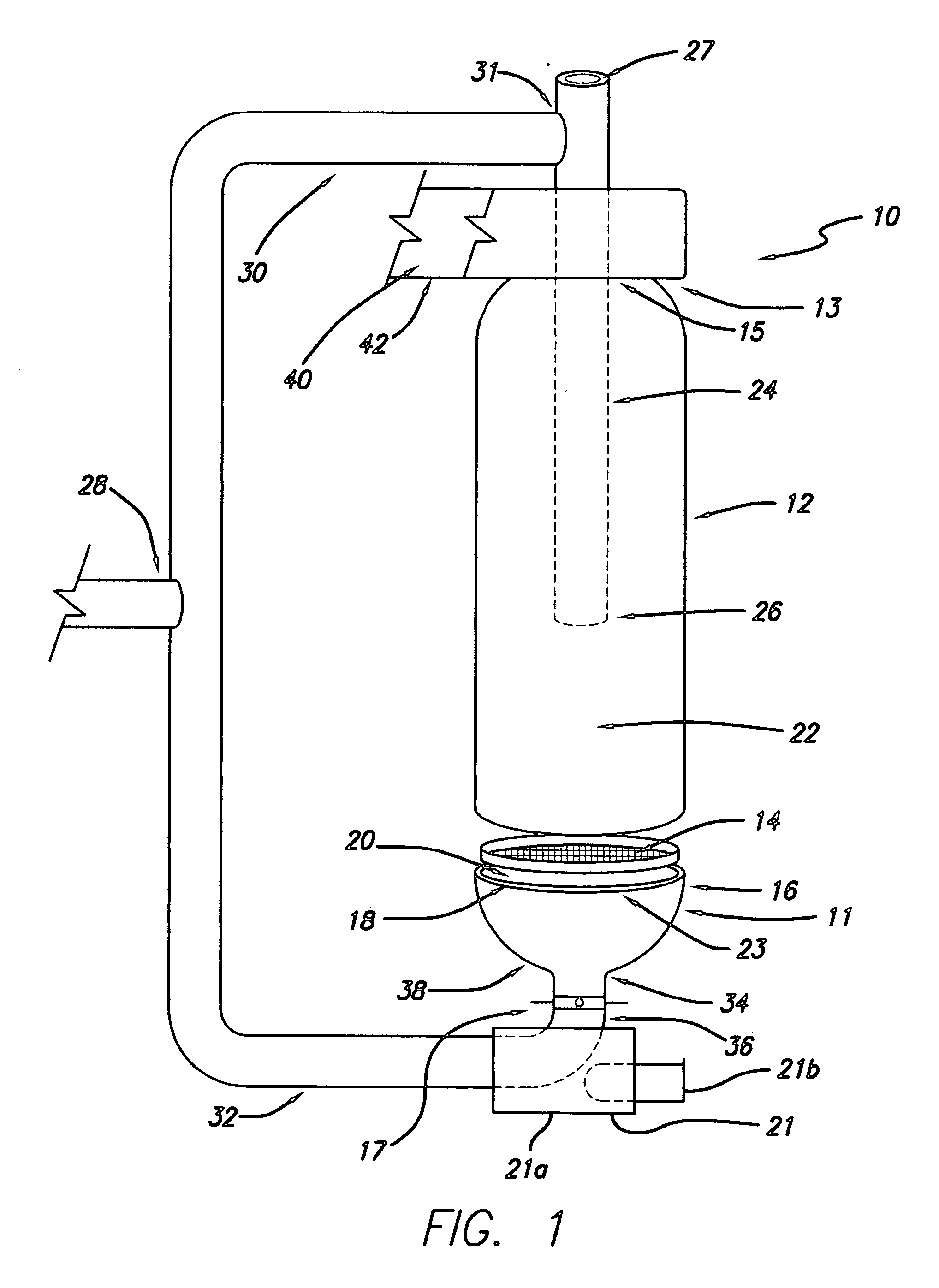
[0020]Referring to FIG. 1 there is shown a pellet fuel heating device, which for simplicity is generally referred to herein as a pellet stove, designated generally by the reference numeral 10. The pellet stove 10 as shown includes a burn pot 11 and a tubular chamber housing 12. The burn pot 11 includes a flat grate 14 and a pot member 16. As shown, and in preferred embodiment, the pot member 16 is an open-topped cylindrical receptacle with a surround or rim 18 encircling an open, upwardly facing, mouth 20.
[0021]The grate 14 is shown in FIG. 1 elevated above the pot member 16 for illustration purposes. In use the grate 14 is seated in the pot member 16 as described in more detail below. The chamber housing 12 is shown in FIG. 1 spaced apart from the pot member 16 for illustration purposes only. In use the chamber housing 12 is mated with the pot member 16. The chamber housing 12 and pot member 16, in combination, form, determine and / or enclose a burn or combustion chamber 22.
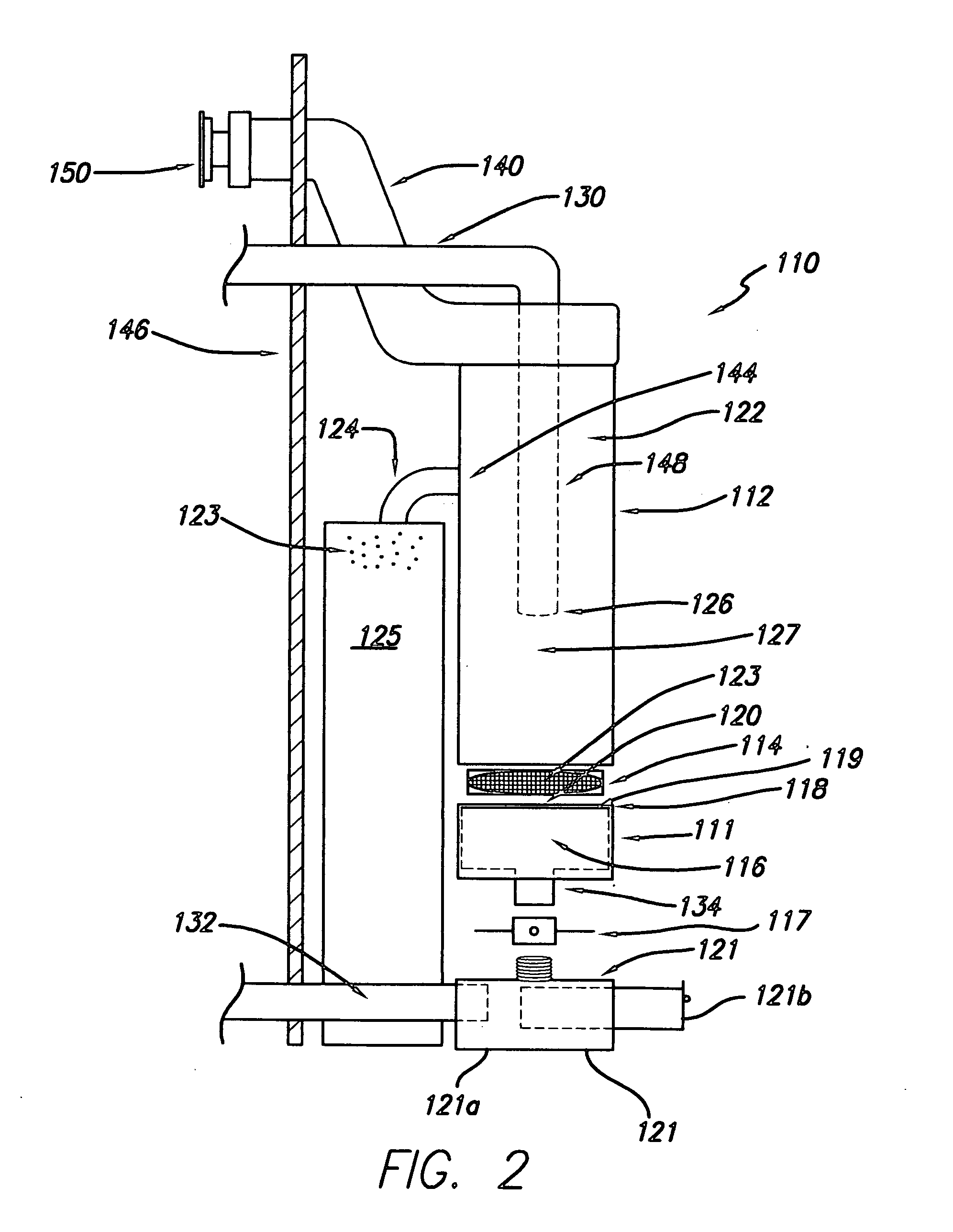
[0022]As...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com