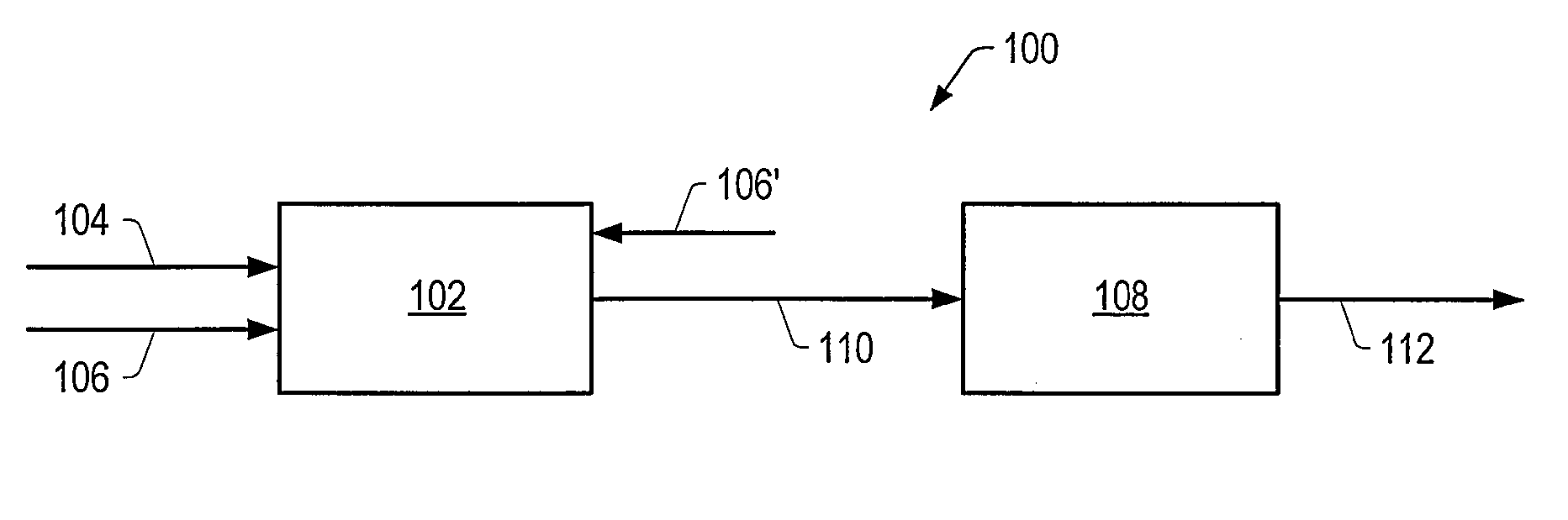
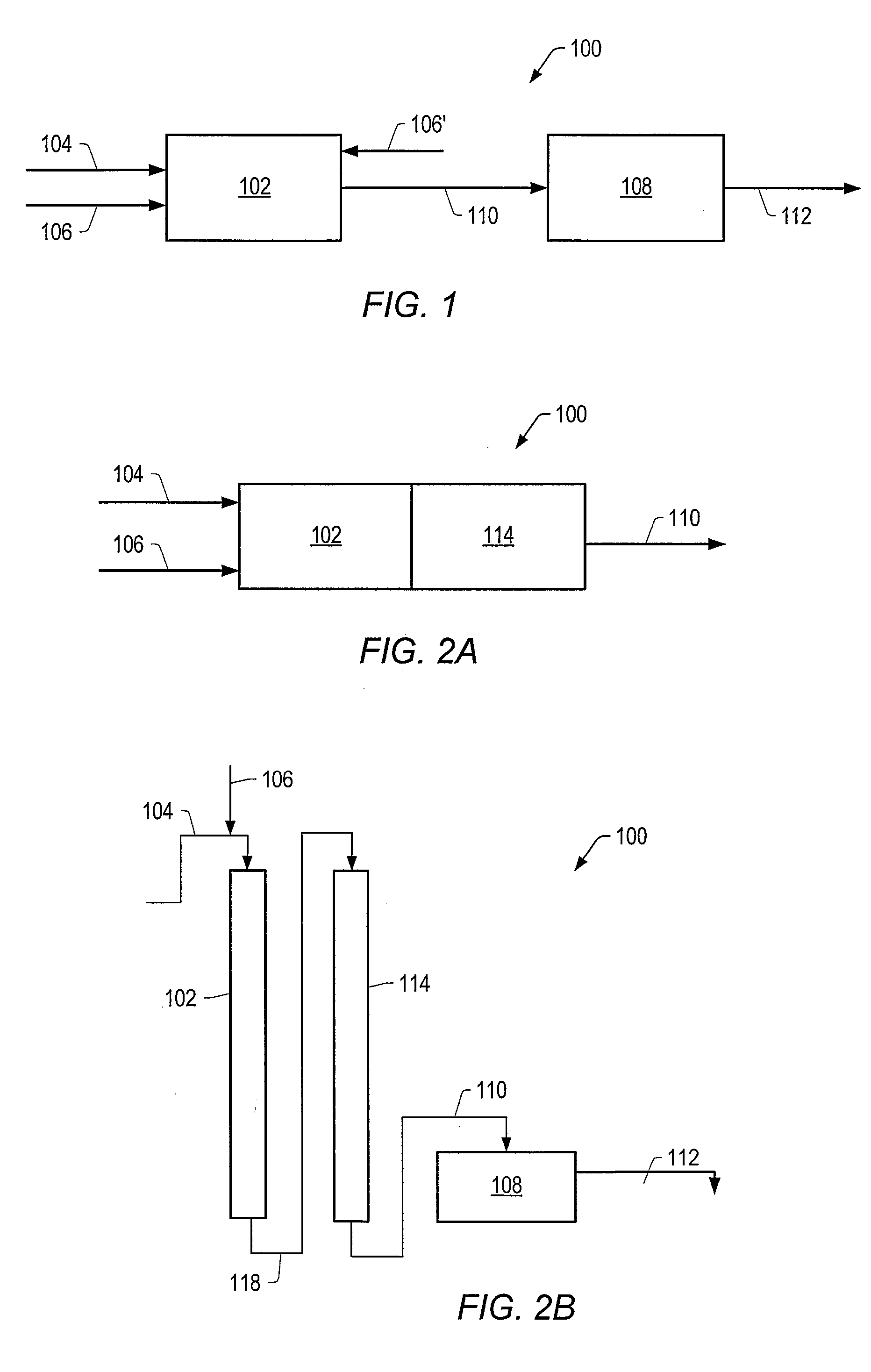
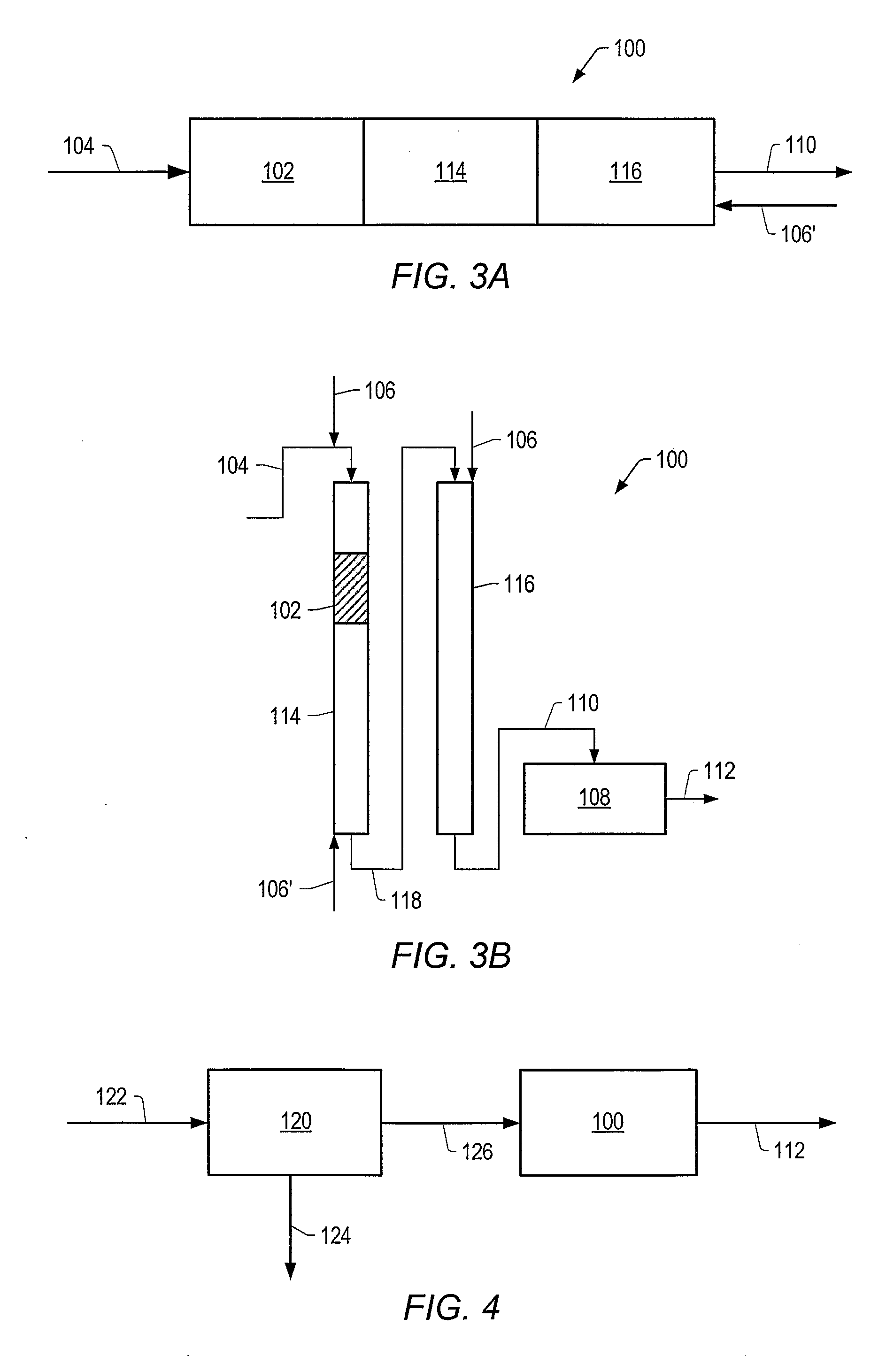
Systems and methods for producing a crude product and compositions thereof
a crude product and crude product technology, applied in the field of systems, methods, catalysts for treating hydrocarbon feeds, can solve the problems of high tan that may contribute to the corrosion of metal components, the use of corrosion-resistant metal in existing equipment may not be desirable, and the high cost of corrosion-resistant metals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of a Catalyst Support
[0268] A support was prepared by mulling 576 grams of alumina (Criterion Catalysts and Technologies LP, Michigan City, Mich., U.S.A.) with 585 grams of water and 8 grams of glacial nitric acid for 35 minutes. The resulting mulled mixture was extruded through a 1.3 Trilobe™ die plate, dried between 90 and 125° C., and then calcined at 918° C., which resulted in 650 grams of a calcined support with a median pore diameter of 182 Å. The calcined support was placed in a Lindberg furnace. The furnace temperature was raised to 1000-1100° C. over 1.5 hours, and then held in this range for 2 hours to produce the support. The support included, per gram of support, 0.0003 grams of gamma alumina, 0.0008 grams of alpha alumina, 0.0208 grams of delta alumina, and 0.9781 grams of theta alumina, as determined by x-ray diffraction. The support had a surface area of 110 m2 / g and a total pore volume of 0.821 cm3 / g. The support had a pore size distribution with a media...
example 2
Preparation of a Vanadium Catalyst Having a Pore Size Distribution with a Median Pore Diameter of at Least 230 Å
[0270] The vanadium catalyst was prepared in the following manner. The alumina support, prepared by the method described in Example 1, was impregnated with a vanadium impregnation solution prepared by combining 7.69 grams of VOSO4 with 82 grams of deionized water. A pH of the solution was 2.27.
[0271] The alumina support (100 g) was impregnated with the vanadium impregnation solution, aged for 2 hours with occasional agitation, dried at 125° C. for several hours, and then calcined at 480° C. for 2 hours. The resulting catalyst contained 0.04 grams of vanadium, per gram of catalyst, with the balance being support. The vanadium catalyst had a pore size distribution with a median pore diameter of 350 Å, a pore volume of 0.69 cm3 / g, and a surface area of 110 m2 / g. Additionally, 66.7% of the total number of pores in the pore size distribution of the vanadium catalyst had a pore...
example 3
Preparation of a Molybdenum Catalyst Having a Pore Size Distribution with a Median Pore Diameter of at Least 230 Å
[0273] The molybdenum catalyst was prepared in the following manner. The alumina support prepared by the method described in Example 1 was impregnated with a molybdenum impregnation solution. The molybdenum impregnation solution was prepared by combining 4.26 grams of (NH4)2Mo2O7, 6.38 grams of MoO3, 1.12 grams of 30% H2O2, 0.27 grams of monoethanolamine (MEA), and 6.51 grams of deionized water to form a slurry. The slurry was heated to 65° C. until dissolution of the solids. The heated solution was cooled to room temperature. The pH of the solution was 5.36. The solution volume was adjusted to 82 mL with deionized water.
[0274] The alumina support (100 grams) was impregnated with the molybdenum impregnation solution, aged for 2 hours with occasional agitation, dried at 125° C. for several hours, and then calcined at 480° C. for 2 hours. The resulting catalyst contained ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| partial pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com