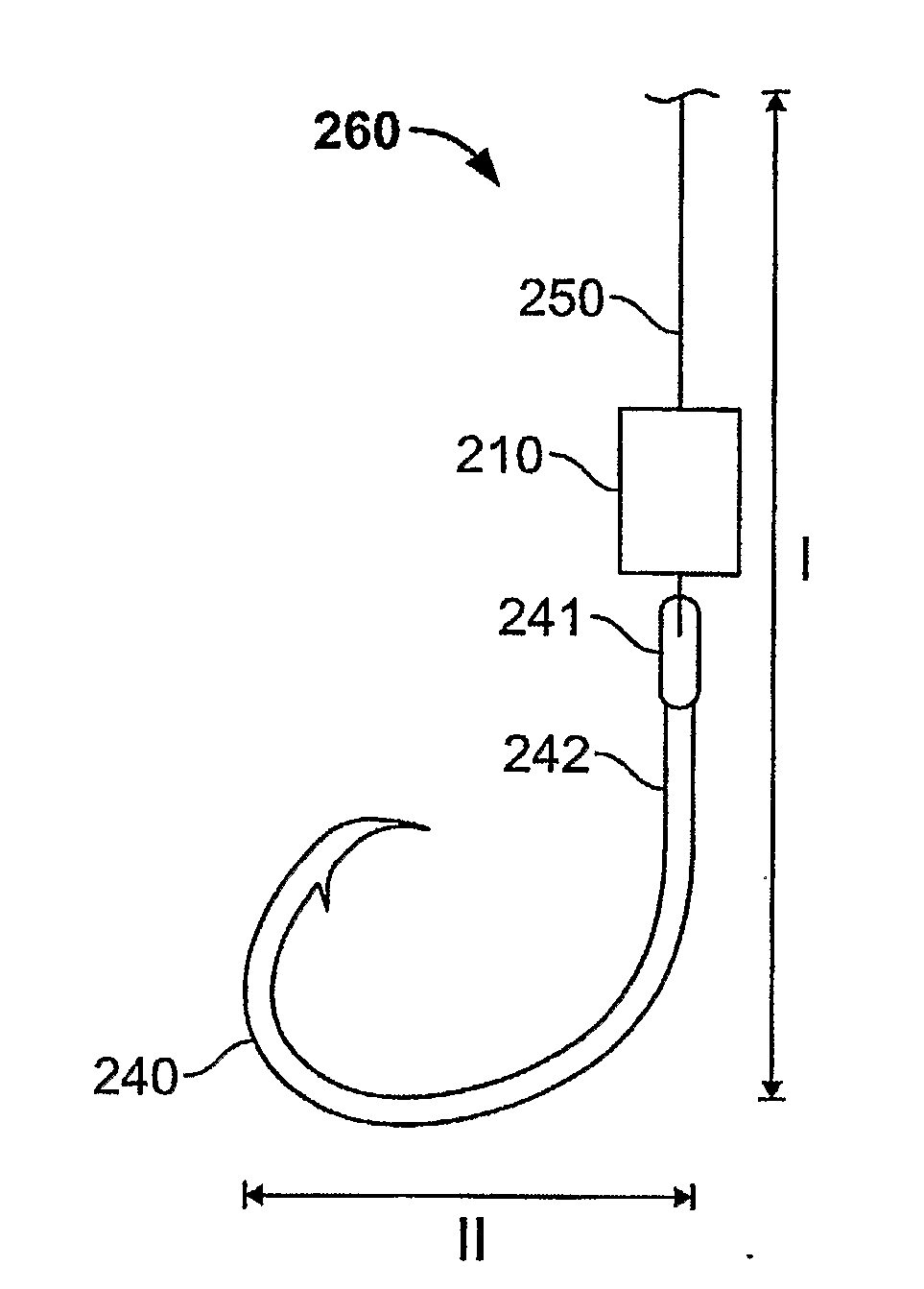
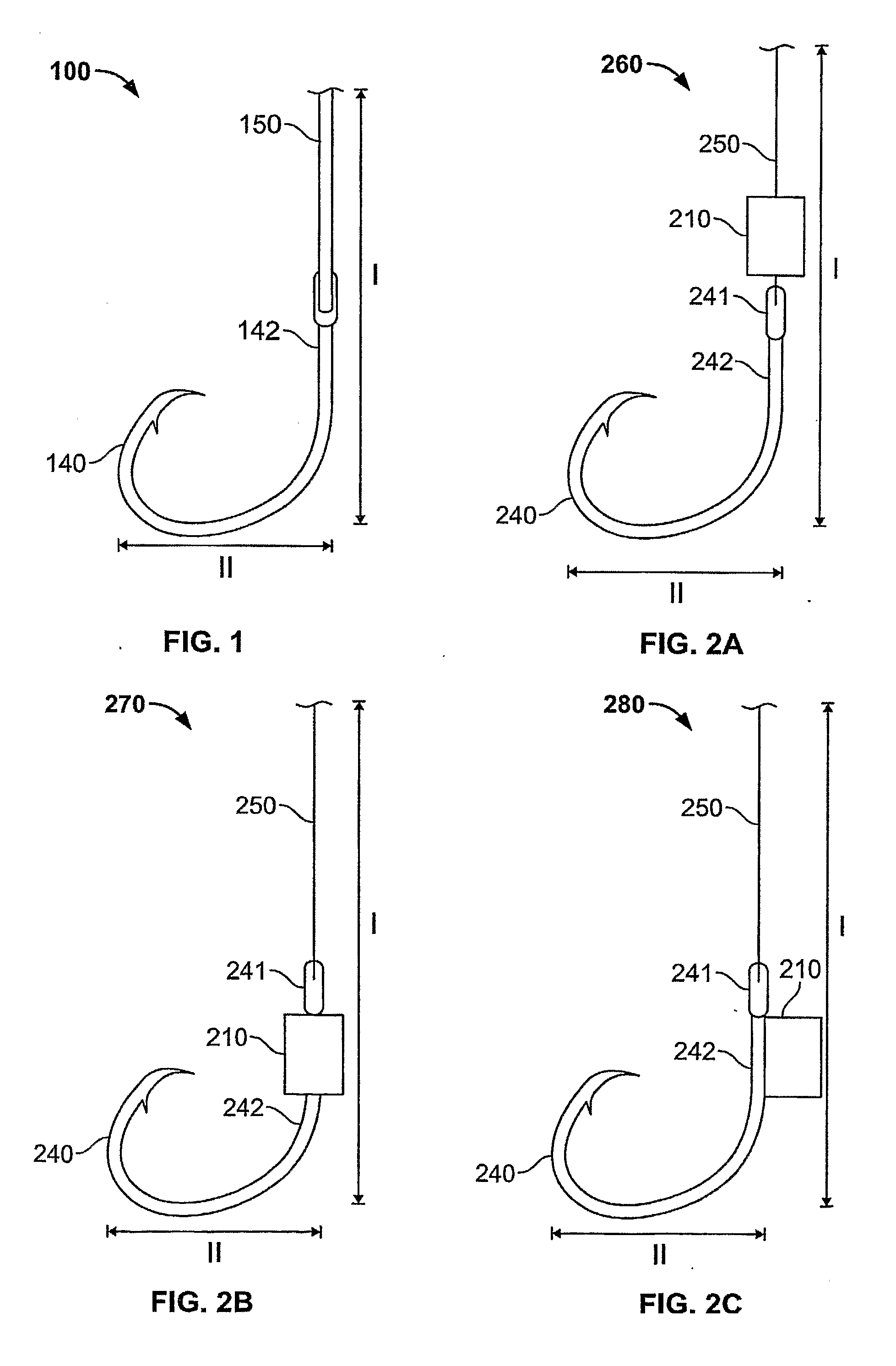
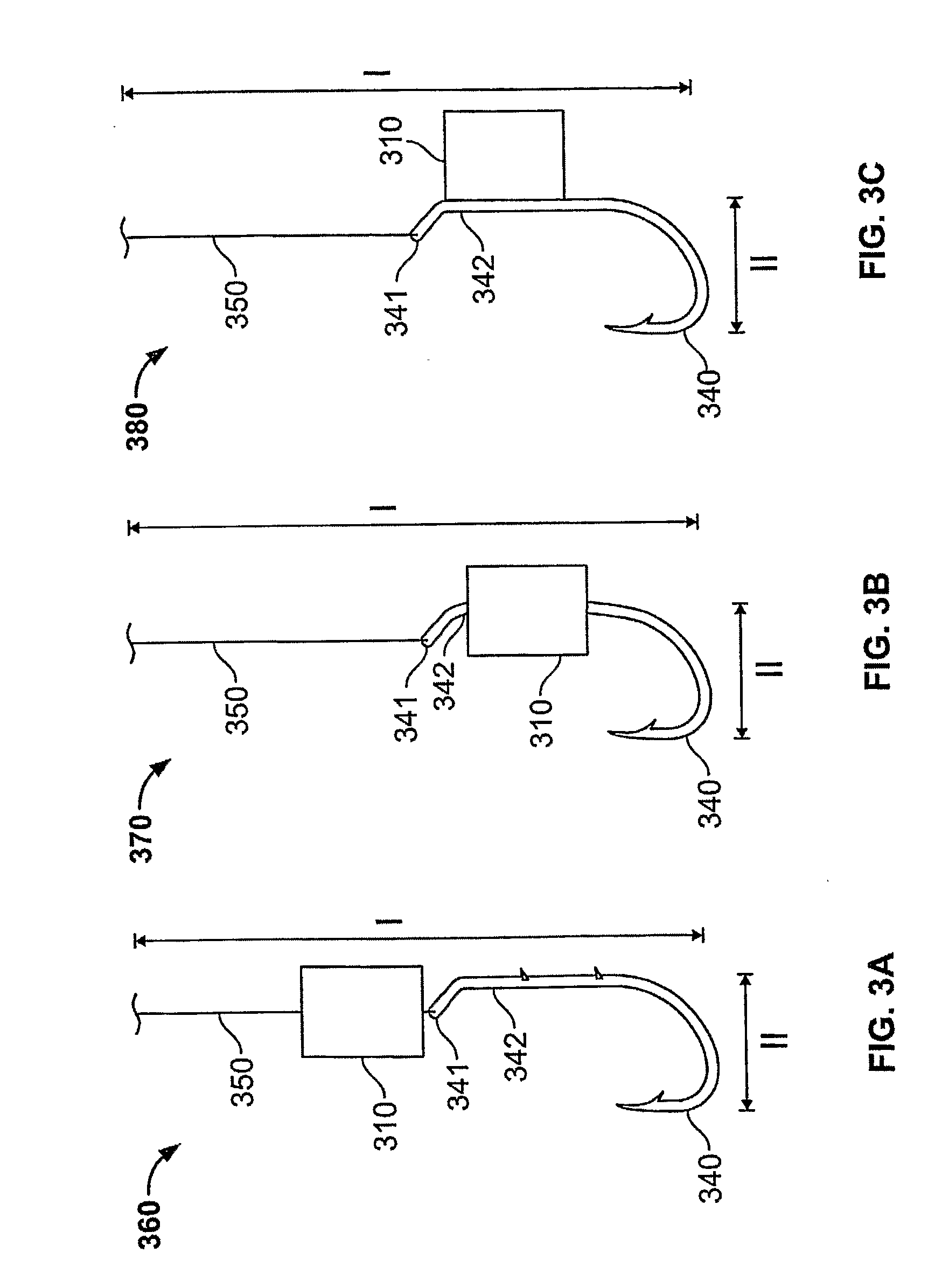
Elasmobranch-Repelling Magnets and Methods of Use
a technology of magnets and branch, applied in the field of elasmobranchrepelling magnets and methods of use, can solve the problems of affecting fishing operations, real threat to several shark species, and no return on investment for fishing operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Pull Force of High-Pull-Force Magnets
[0098]Some of the high-pull-force magnets that have been used in examples in this application are listed below in Table 1 with calculation of the pull force of the respective high-pull-force magnets based on the geometry, size, grade and nominal strength (conservative BR) of the high-pull-force magnet.
TABLE 1ConservativePull ForceGeometrySizeGradeBr (Gauss)(pounds)Puck4″× 1.5″N3813000521magnetBar6″× 2″× 0.5″N4813800191.31Hollow1″× 1″ with 3 / 16″N421320072.75cylinderhollow center2 stacked0.472″× 1.97″×N501410046.7hollow0.24″ hollowcylinderscenterCube1″× 1″× 1″N4813800110.5longlines
[0099]Pull force is descriptive of the attractiveness of a magnet to a steel flat surface. A shark is not a magnetic steel surface, but it does have a surface (likely the ampullae of Lorenzini) that interacts with the magnetic field of the magnet. As such, pull force is an appropriate method for measuring interaction of an elasmobranch with a magnetic field.
example 2
High-Pull-Force Magnets as Repellents on Longlines
[0100]The following example demonstrates the elasmobranch repellent activity of high-pull-force magnets of greater than about 150 pounds of pull force on long lines. High-pull-force magnet treatments were evaluated on one demersal longline located in the middle of a large lagoon. Adjacent longlines in the same lagoon produced large shark catch (generally greater than two sharks over the 15 hooks on a line).
[0101]Seven hooks on a demersal longline of about 1000 feet were treated with 2″×0.25″×2″ NdFeB N48 magnets (nominal force 14,000 gauss; pull force about 161 pounds). The high-pull-force magnets were secured at even-numbered hooks on the longline, directly above the eye of the hook and strapped to the gangion leader with black vinyl electrical tape. All hooks received bait. If the bait was lost during the experiment, the hook was re-baited while the high-pull-force magnets were not removed or replaced; only the bait was exchanged.
[...
example 3
High-Pull-Force Magnets as Repellents on Longlines
[0103]The following example demonstrates the elasmobranch repellent activity of high-pull-force magnets of greater than 50 pounds of pull force on long lines. A first demersal longline with eight hook sets was baited with barracuda flesh and placed in open water. No high-pull-force magnets were placed on the hooks. Five sharks were captured on the longline over 24 hours representing 5 separate shark species ranging in size from 97 cm to 240 cm. See Table 3.
TABLE 3HookSpecies11. Tiger (F), 235 cm2. Nurse (F) 231 cm3. Sharpnose (F), 97 cm234Nurse 240 cm567891011121314Blacknose 115 cm15
[0104]A second demersal longline with fifteen hook sets was baited with squid and placed in the same position in open water as the first demersal longline discussed above for 67 hours. The trial with the second demersal longline was run three months after the trial with the first demersal longline. Seven of the fifteen hooks were treated with 1″×1″×1″ neo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com