Recombinant vwf formulations
a technology of vwf and vwf, which is applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, inorganic non-active ingredients, extracellular fluid disorder, etc., can solve the problem of risk of blood-born pathogens, and achieve the effect of high stability in the pharmaceutical composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Shaking Experiments
[0116]In order to determine the amount of precipitation of rVWF in various formulations, the percent recovery of rVWF following turbulent shaking was tested under a variety of conditions.
[0117]rVWF in Advate buffer (90 mM NaCl, 1.68 mM CaCl2, 10 mM L-histidine, 1 mM tris, 0.26 mM glutathione, 23.4 mM trehalose, 175.7 mM mannitol, and 0.1 g / L TWEEN-80, pH 7.0) or Advate 1:3 buffer (Advate buffer diluted 3-fold in water) was subjected to turbulent shaking on a shaker at room temperature (RT) for 0 min, 1 min, 2.5 hrs, or 4 days, and percent recovery of the rVWF was measured relative to the starting material prior to shaking. As shown in Table 1, losses of about 40-80% were observed in the Advate buffer while losses of about 20-30% were observed in the Advate 1:3 buffer. VWF antigen VWF:Ag corresponds to the amount of VWF which can be detected in an VWF-specific ELISA using polyclonal anti-VWF antibody, while VWF:RCo corresponds to the amount of VWF which causes aggl...
example 2
Stability of Recombinant VWF
[0121]The stability of rVWF was tested by assessing the activity level of rVWF present in a various formulations.
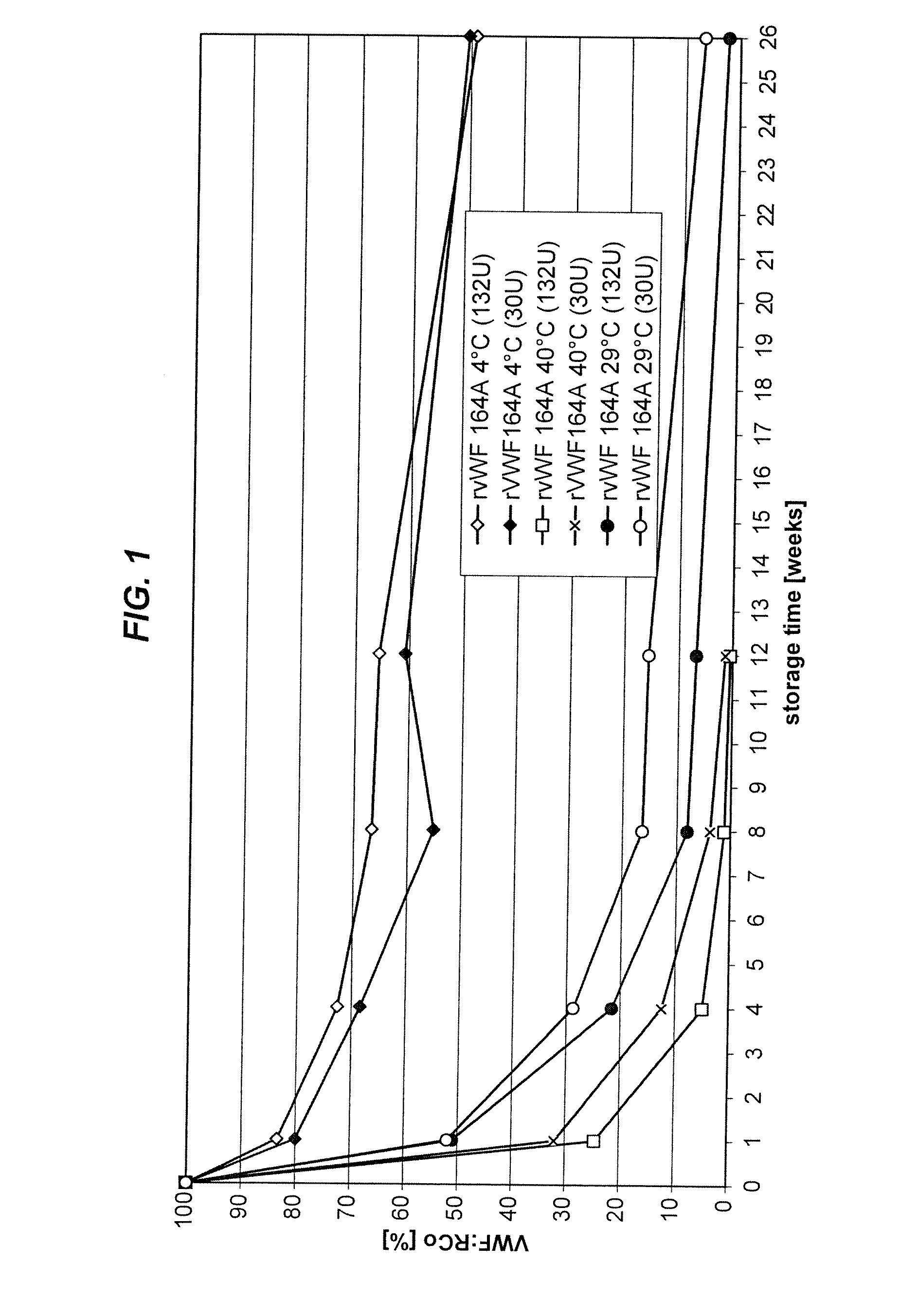
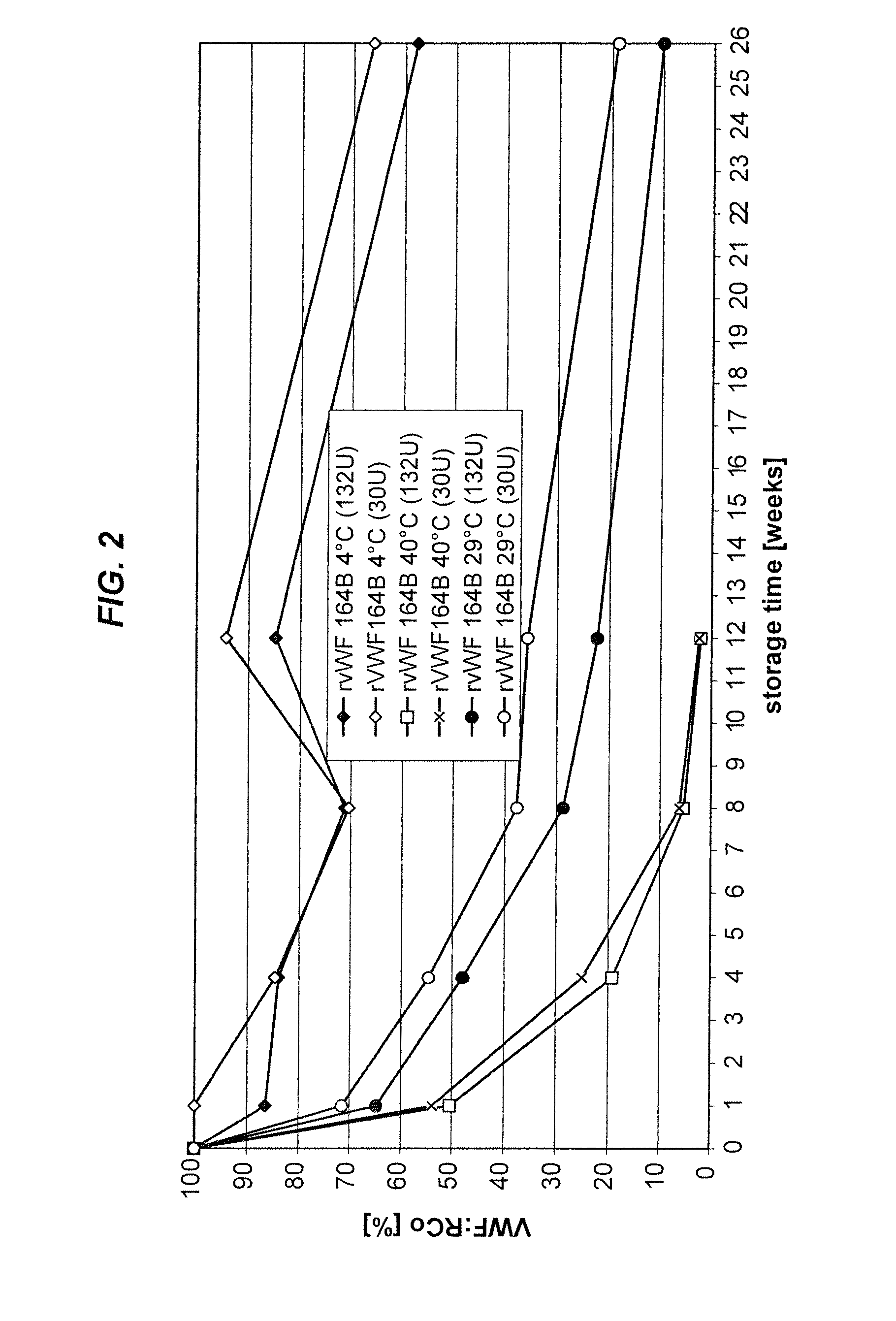
[0122]As shown in FIG. 1, rVWF is not stable in Advate buffer after 26 weeks due to the presence of 0.3 mM glutathione. As shown in FIG. 2, however, rVWF is more stable in Advate 1:3 buffer (e.g., for up 12 weeks at 4° C.)
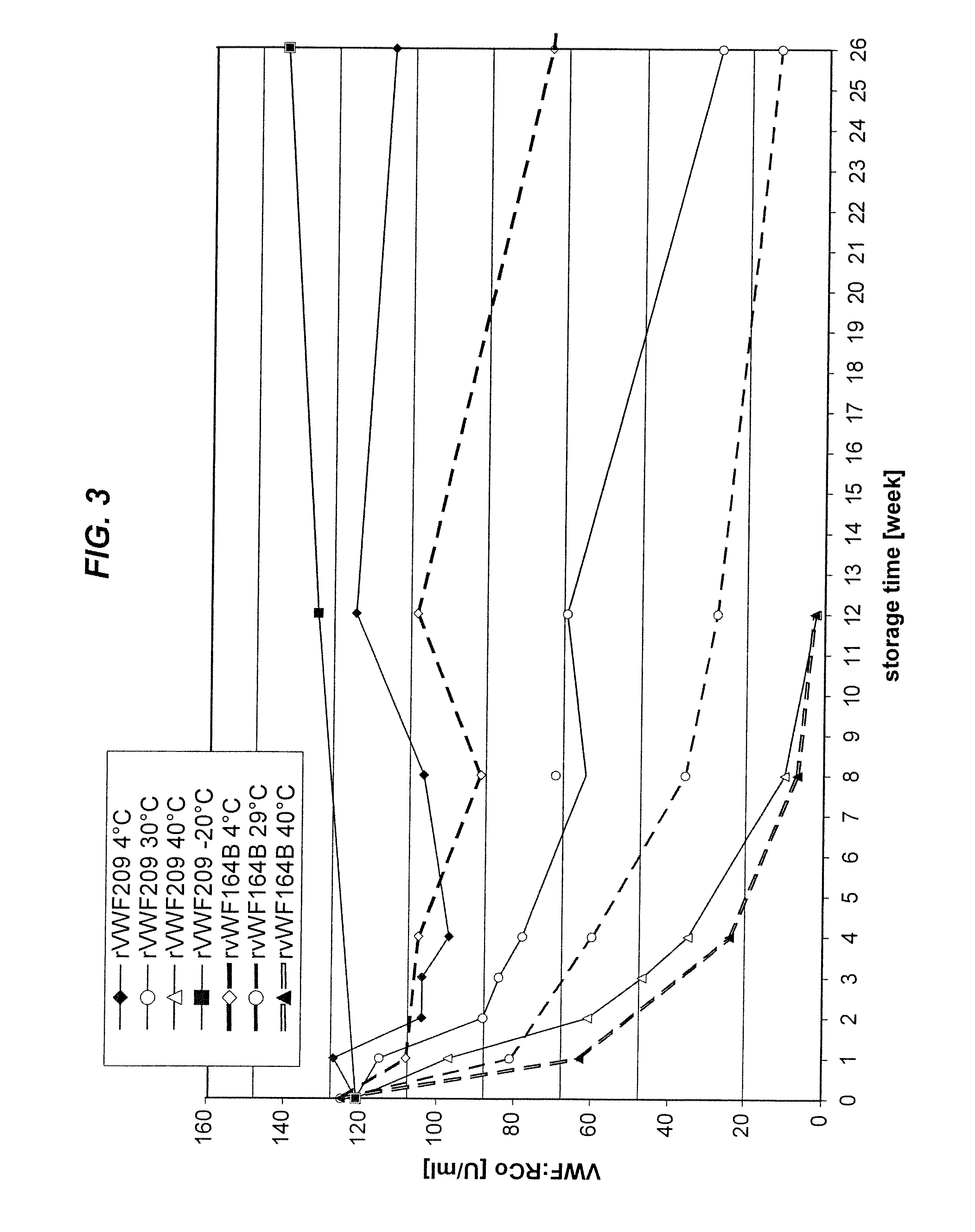
[0123]As shown in FIG. 3, the stability of a citrate-based formulation (15 mM sodium citrate, 10 mM CaCl2, 100 mM NaCl, pH 7.0) is better than Advate 1:3 buffer formulation containing 0.1M glutathione.
[0124]Likewise, the concentration of rVWF was measured over time in various buffers. As shown in FIG. 4, FIG. 5 and FIG. 6, rVWF concentration is stable over time in Advate buffer, Advate 1:3 buffer, and citrate-based buffer, respectively.
example 4
Characterization of the Liquid Formulations
[0125]Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was used to assess the extent of protein (rVWF) unfolding in various buffers. As shown in Table 3, Advate buffer pH 7.0 is the optimum for stabilization.
[0126]DSC is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and references are measured as a function of temperature. The result of a DSC experiment is a curve of heat flux versus temperature or versus time.
[0127]The Differential Scanning Calorimeter can scan through a range of temperatures while heating and cooling and it determines a phase transition, i.e. melting, crystallization, or glass transition, by measuring the amount of heat needed to reach a set temperature. The calorimeter was calibrated with a set of pure metals (zinc, indium, and tin) that have a known heat capacity, Cp and melting point, Tm. The respective reference buffer was placed into the reference c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com