Use of activity dependent neurotrophic factor for enhancing learning and memory: pre-and post-natal administration
a neurotrophic factor and activity-dependent technology, applied in the field of pre- and post-natal administration, can solve the problems of uncertain efficacy of these compounds in normal people, and achieve the effect of improving short term memory and reference memory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Enhanced Learning and / or Memory after Postnatal Administration of an ADNF Polypeptide
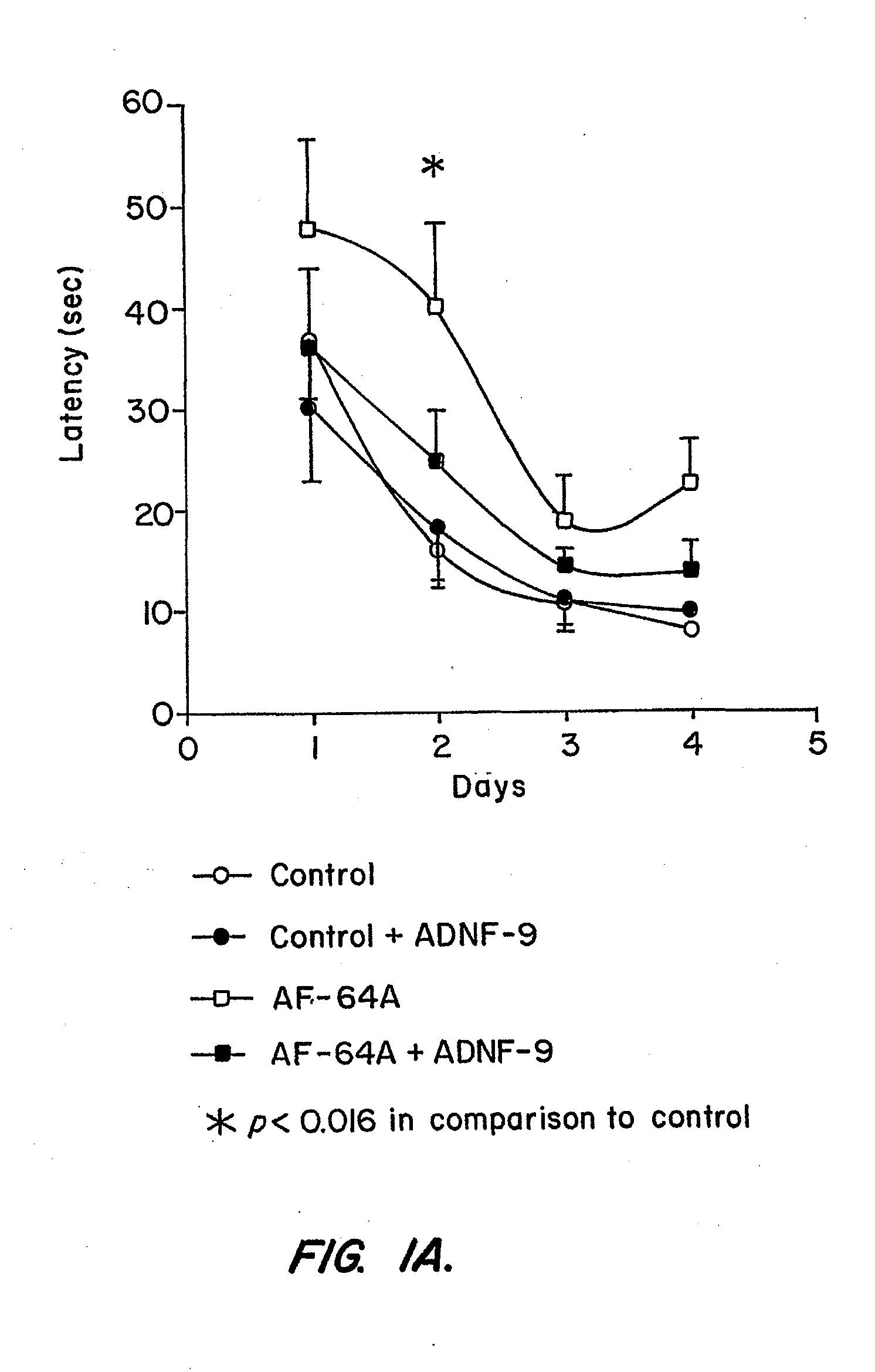
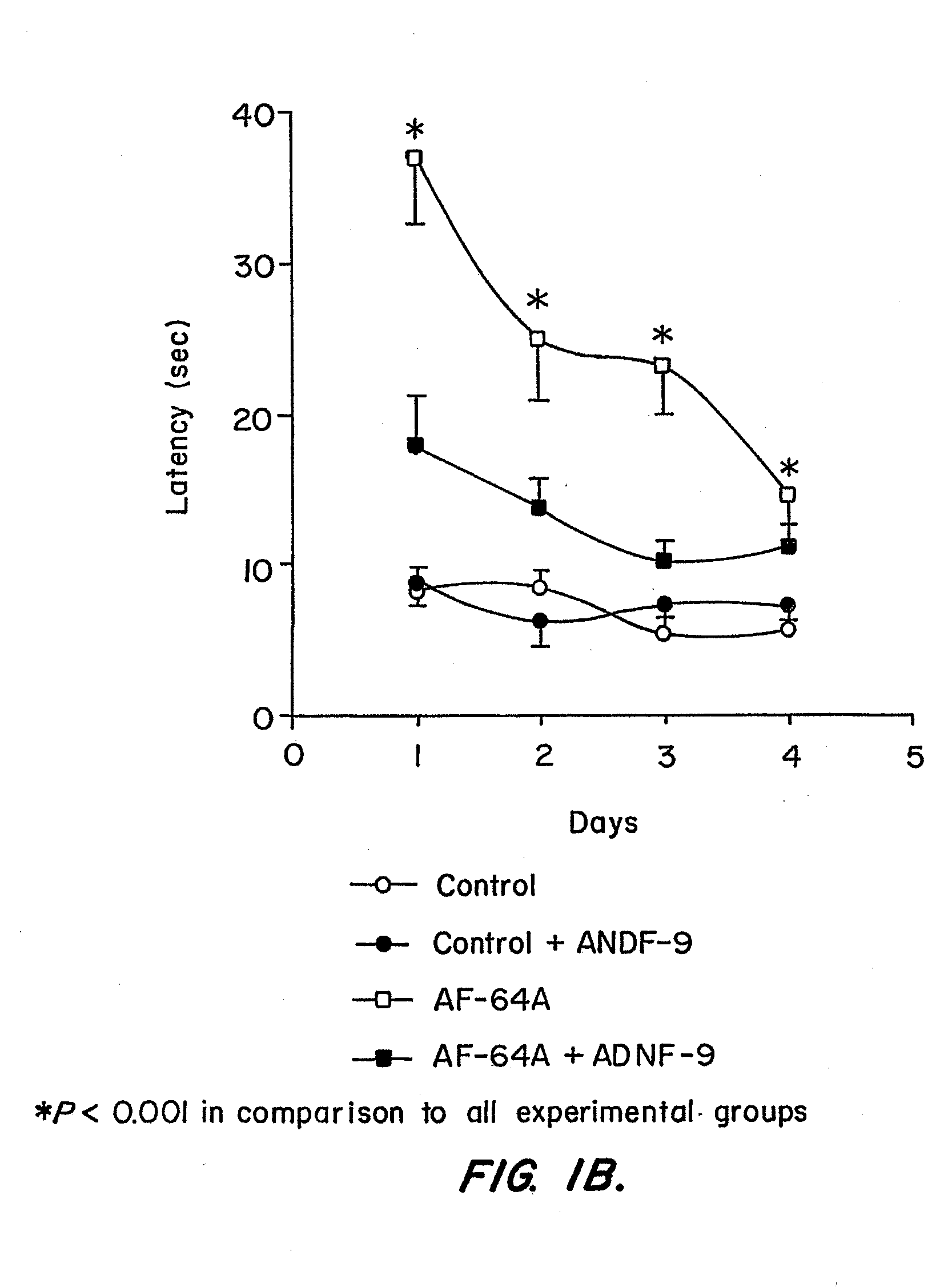
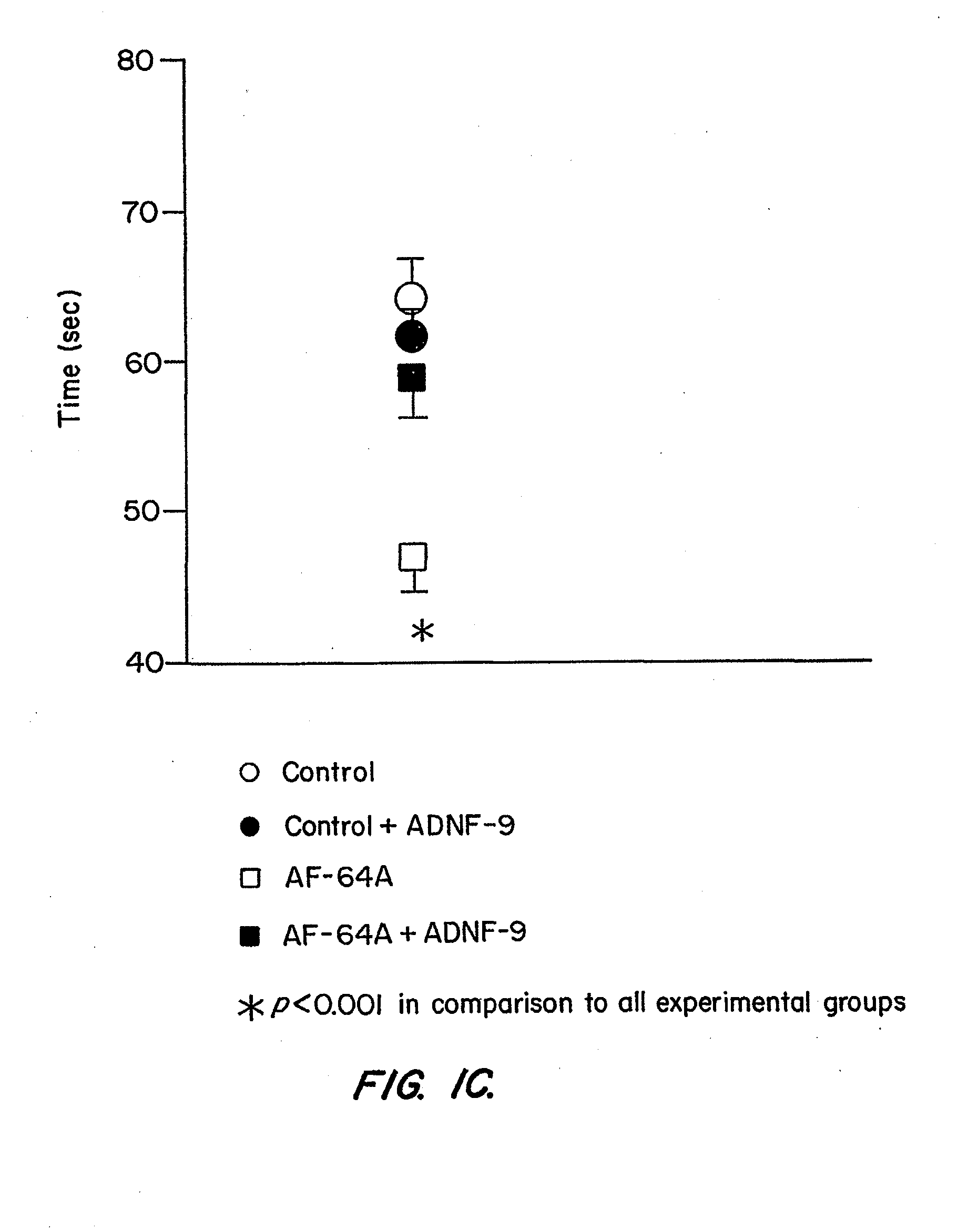
[0144]Example I describes properties of the ADNF polypeptides, such as SALLRSIPA (“ADNF-9”; SEQ ID NO:1), derived from ADNF I, and NAPVSIPQ (“NAP”; SEQ ID NO:2), derived from ADNF-III or ADNP, in control animals or animals exposed to the cholinotoxin, ethylcholine aziridium (AF64A), a blocker of choline uptake (Fisher et al., Neurosci. Lett. 102:325-331 (1989)). An intact cholinergic system is required for normal brain function, whereas Alzheimer's disease is associated with the death of cholinergic cells (Brumback and Leech, 1994). Thus, rats treated with AF64A provide an accepted model for testing in vivo efficacy of drugs that protect against cognitive impairments, that may result from cholinotoxicity (Fisher et al., Neurosci. Lett. 102:325-331 (1989); Gozes et al., Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. U.S.A. 93:427-432 (1996); Gozes et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96:4143-4148 (1999)). The experiments de...
example ii
Prenatal Administration of ADNF Polypeptides Provides Postnatal Enhanced Learning and / or Memory
[0184]Materials and Methods
[0185]Animals and Treatment
[0186]C57-B16J female mice (Jackson Labs) were kept under a 12 h light, 12 h dark regimen with food and water available at all times. The mice received humane animal care in compliance with the “Guideline for Care and Use of Experimental Animals.” Six week old females (21-24 grams) were mated with C57-B16J males for 4 h. The presence of a vaginal plug was considered day 0 pregnancy.
[0187]Animals were injected intraperitoneally on pregnancy day 8, or treated on pregnancy day 8 after 1 hour fast with gavage dose of ADNF polypeptides. NAP was diluted in 50 μl DMSO and diluted in filtered Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline (DPBS). SAL was dissolved and diluted in filtered DPBS. Control animals were treated with a vehicle (i.e., DPBS). All treatments were coded.
[0188]Delivery occurred on day 20, weaning on day 20 of life. Male offspring we...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com