Electronic component and method of manufacturing the same
a technology of electronic components and manufacturing methods, applied in the field of electronic components, can solve the problems of inability to secure the insulation between bumps, i.e. between terminals, and achieve the effect of reducing resistance values and shortening feed lines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0095]This embodiment relates to a surface acoustic wave device having feed lines which branch and one end of which reach the edge of the substrate, and a method of manufacture of such a component.
[0096]FIG. 4 is a plane view, seen through a resin layer covering the main surface of the piezoelectric substrate 24, of a surface acoustic wave device 22 of this embodiment. As shown in FIG. 4, in the surface acoustic wave device 22 of this embodiment, filters, reflectors, and other surface acoustic wave elements 26 are integrated. Also, the surface acoustic wave device 22 of this embodiment is packaged using WLCSP.
[0097]Below, the configuration of the surface acoustic wave device 22 of this embodiment is explained, with a description of the manufacturing procedure.
[0098](1) Manufacturing Procedure
[0099]FIG. 5 is a flow diagram showing the manufacturing procedure for the surface acoustic wave device 22 of this embodiment. FIG. 6 to FIG. 10 are process cross-sectional diagrams which explai...
second embodiment
[0176]This embodiment relates to a method of manufacture of an electronic component in which protrusions are provided on the side faces of dicing lines.
[0177]The method of manufacture of electronic components according to this embodiment is substantially the same as the method of manufacture of the first embodiment, except for the formation of a plurality of protrusions 82 on the side faces of dicing lines.
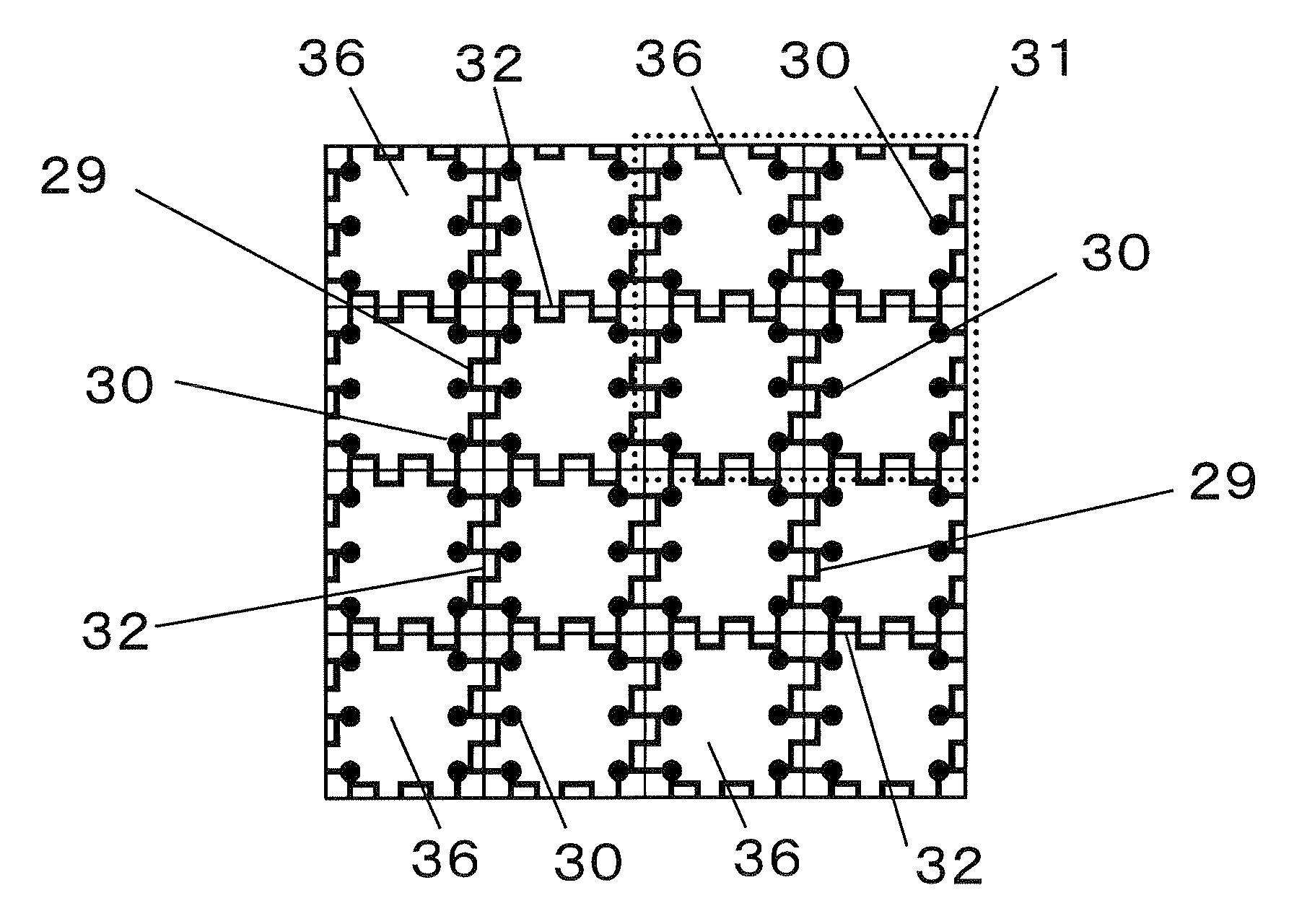
[0178]FIG. 17 is a plane view explaining dicing lines 32 formed on the outer periphery of the region 36 which is to become the electronic component. FIG. 18 is an enlarged view of the region A surrounded by the broken line in FIG. 17.
[0179]In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 18, dicing lines having protrusions on side faces are formed. Hence when cutting the substrate to cut away electronic components, dicing lines can easily be distinguished from feed lines 29, and so productivity is improved.
[0180]The dicing lines 32 of this embodiment differ from the dicing lines of the first ...
modified example
[0191]FIG. 21 and FIG. 22 show a modified example of the first embodiment.
[0192]In the electronic component manufacturing method of the first embodiment, as shown in FIG. 14, feed lines 29 are formed having first portions 42 which connect in a straight line pairs of first terminal electrodes 40 arranged in direct opposition on either side of a first intended cutting region 34, and crank-shape second portions46 which branch from first portions 42.
[0193]However, the shape of feed lines formed in this invention is not limited to such shapes, and the second portions 46′ may be straight lines traversing the cutting region 14 diagonally, as in FIG. 22.
[0194]Further, in FIG. 14 the second portions 46 branch midway from the first portions 42, but may branch directly from the first terminal electrodes 30, as in FIG. 22.
[0195]Further, in the first and second embodiment, the substrate is a piezoelectric substrate, and surface acoustic wave elements are formed as functional elements. However, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com