Process and device for converting biomass to gaseous products
a technology of biomass and gaseous products, which is applied in the direction of molten salt/metal gasification, supercritical condition processes, sludge treatment by oxidation, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable ratio between suspended biomass and supercritical heating water, slow process, and clogging up the reactor, so as to achieve efficient sorption and increase the reactivity of biomass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
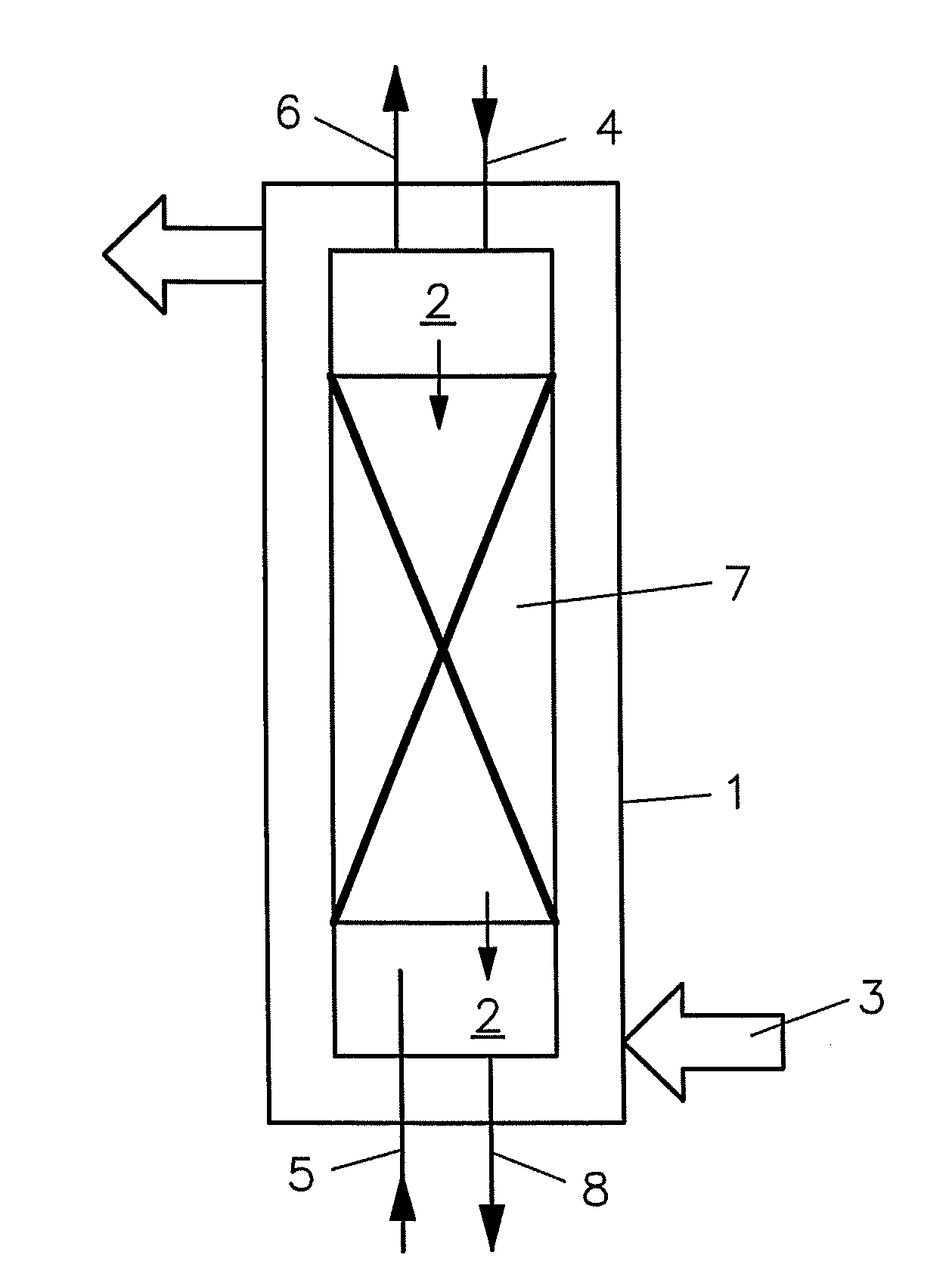
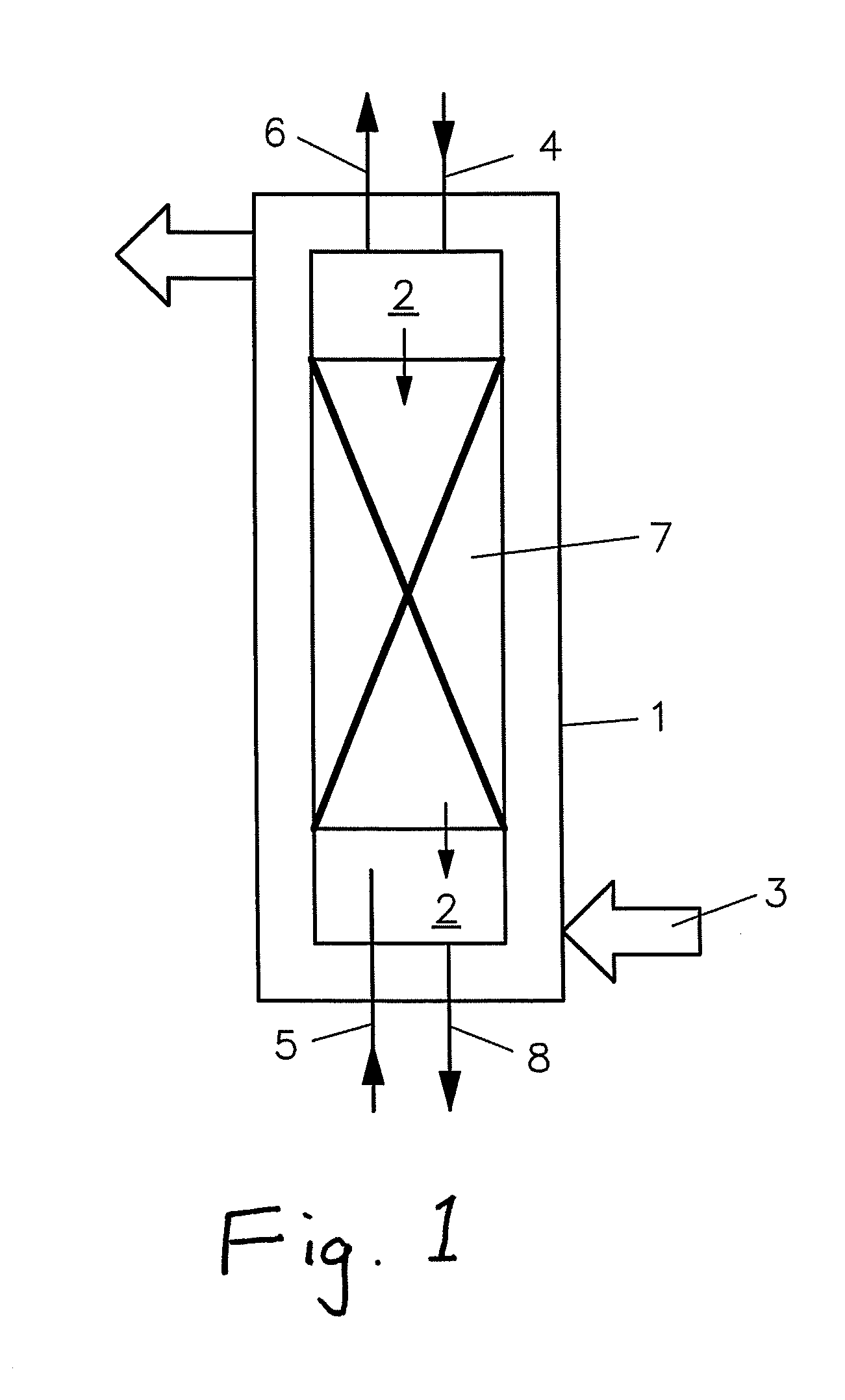
[0057]According to the illustrated embodiment, there is shown a high-pressure reactor (autoclave) 1 that is filled from above via a first feeding pipe 4 with a molten salt 2, intended for producing a hydrothermal molten salt bath that is heated with the aid of a heating 3. The reactor 1 for this example is filled for the most part with a packing 7, consisting of the filler bodies Raschig® rings or Braunschweiger Wendeln (packed columns). A hydrothermal molten salt bath forms as a result of the increased temperature, which has a clearly higher density than water under reaction conditions and therefore spreads out over the packing 7 and flows downward.
[0058]A mixture of biomass and water is fed from the bottom into the reactor 1 via a second feeding pipe 5, wherein this mixture is still at the pre-heated temperature that prevents the destruction of the organic compounds in the biomass.
[0059]An intensive contact occurs on the filler bodies of the packing 7 between the hydrothermal molt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com