Dye sensitized solar cell and dye-sensitized solar cell module
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
production example 1
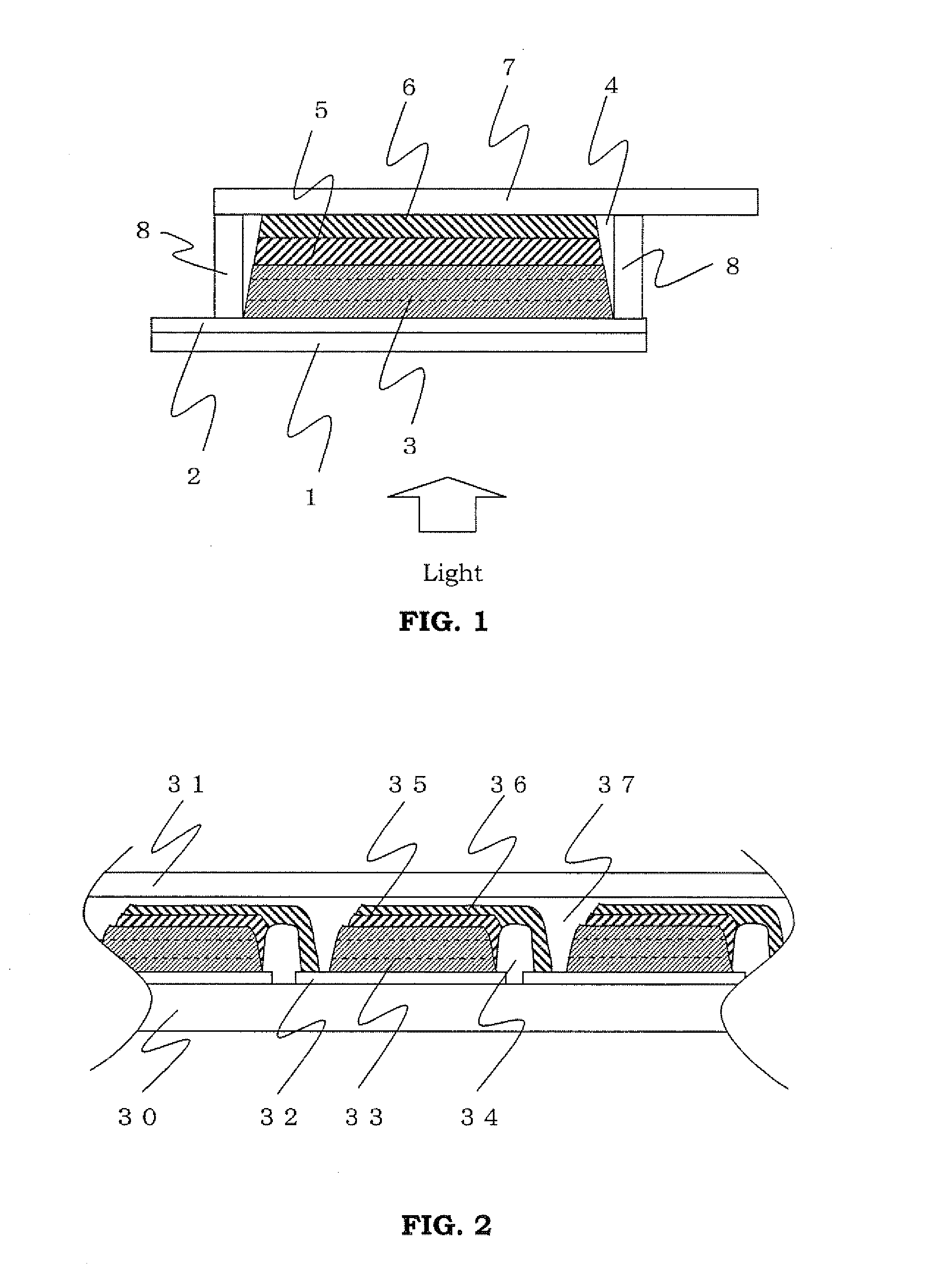
[0170]A solar cell (unit cell) shown in FIG. 1 was produced.
[0171]FIG. 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a main part showing the layer structure of a solar cell of the present invention.
[0172]In FIG. 1, a reference numeral 1 denotes a support: a reference numeral 2 denotes a conductive layer: a reference numeral 3 denotes a photoelectric conversion layer filled with a carrier transporting material: a reference numeral 4 denotes a carrier transporting material: a reference numeral 5 denotes a catalyst layer: a reference numeral 6 denotes a counter electrode conductive layer: a reference numeral 7 denotes an output electrode: and a reference numeral 8 denotes a sealing material.
[0173]A glass substrate (trade name: SnO2 film-bearing glass, manufactured by Nippon Sheet Glass Co., Ltd.) obtained by forming a conductive layer 2 of a SnO2 film on a glass support 1 was used. A commercialized titanium oxide paste (trade name: Ti-Nanoxide T / SP, average primary particle diameter of tita...
production example 2
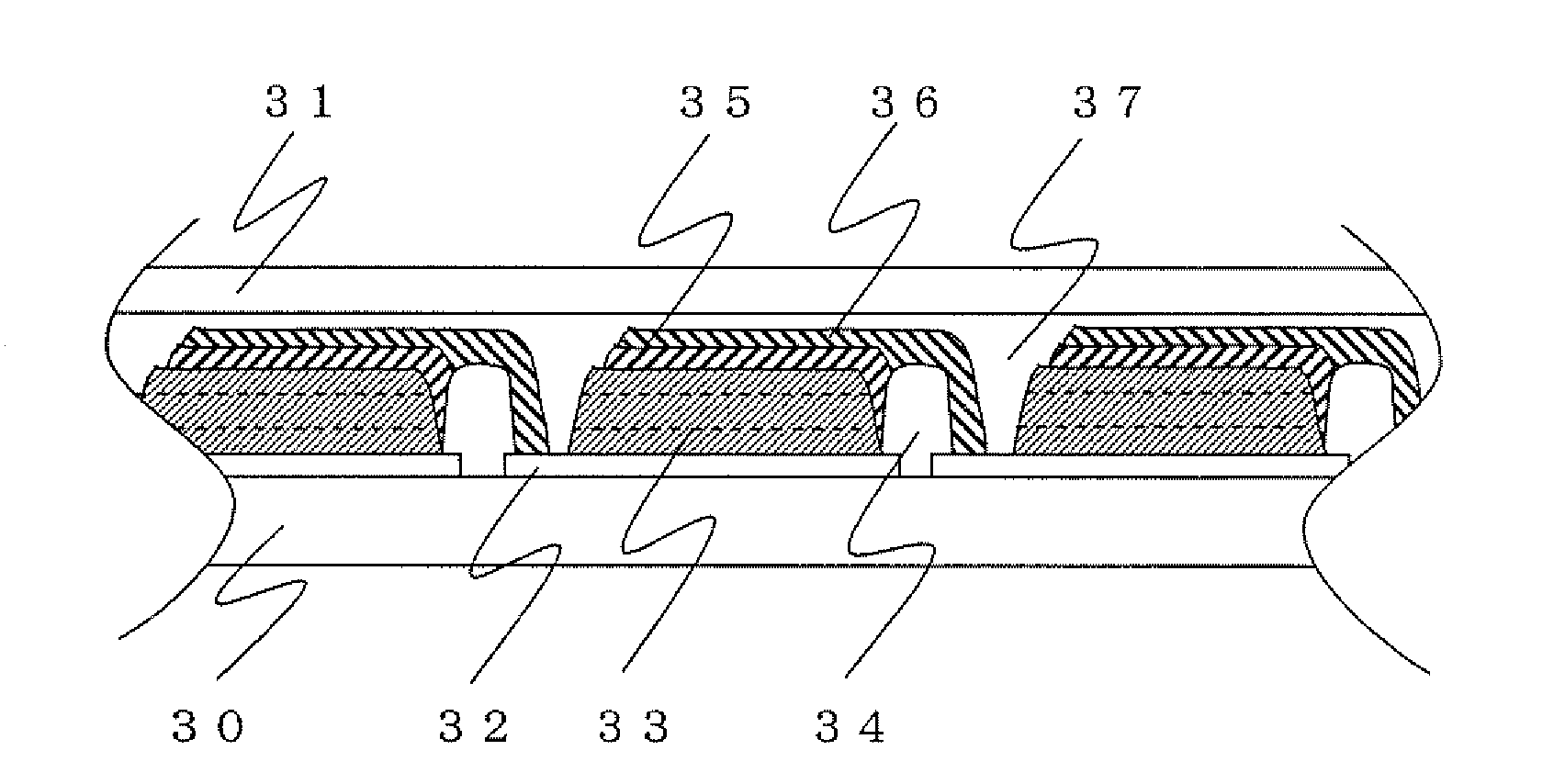
[0185]A solar cell module shown in FIG. 2 was produced.
[0186]FIG. 2 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a main part showing a layer structure of a solar cell module of the present invention. In the drawing, a reference numeral 30 denotes a support: a reference numeral 31 denotes a cover: a reference numeral 32 denotes a conductive layer: a reference numeral 33 denotes a photoelectric conversion layer filled with a carrier transporting material: a reference numeral 34 denotes an inter-cell insulating layer: a reference numeral 35 denotes a catalyst layer: a reference numeral 36 denotes a counter electrode conductive layer: and a reference numeral 37 denotes an insulating layer.
[0187]A glass substrate (trade name: SnO2 film-bearing glass, manufactured by Nippon Sheet Glass Co., Ltd.) obtained by forming a conductive layer 32 of a SnO2 film on a glass support 1 was used. A scribe line was formed in a prescribed site of the conductive layer 32 of the glass substrate by radiating lase...
production example 3
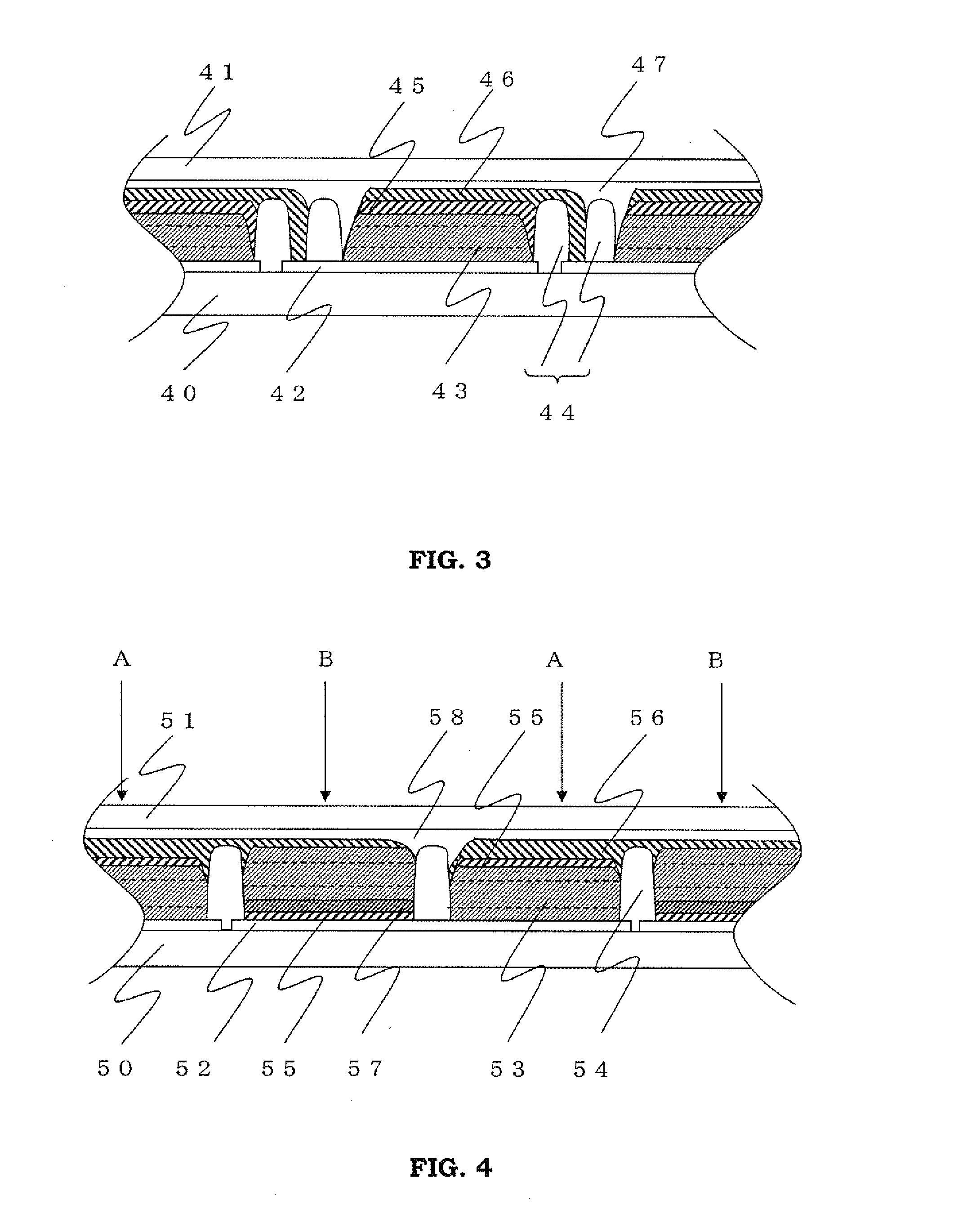
[0191]A solar cell module shown in FIG. 3 was produced.
[0192]FIG. 3 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a main part showing a layer structure of a solar cell module of the present invention. In the drawing, a reference numeral 40 denotes a support: a reference numeral 41 denotes a cover: a reference numeral 42 denotes a conductive layer: a reference numeral 43 denotes a photoelectric conversion layer filled with a carrier transporting material: a reference numeral 44 denotes an inter-cell insulating layer: a reference numeral 45 denotes a catalyst layer: a reference numeral 46 denotes a counter electrode conductive layer: and a reference numeral 47 denotes an insulating layer.
[0193]A solar cell module was completed in the same manner as in Production Example 2, except that after the porous semiconductor layers were formed, two rows of the inter-cell insulating layers 44 were formed an thereafter, the counter electrode conductive layer 46 was formed between the inter-cell insulati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com