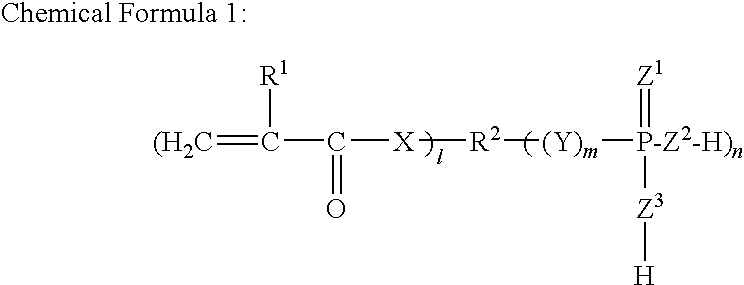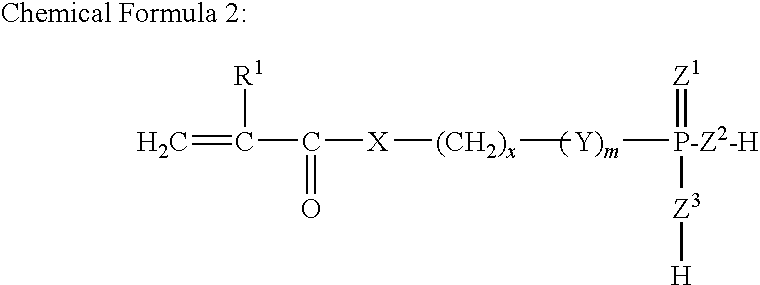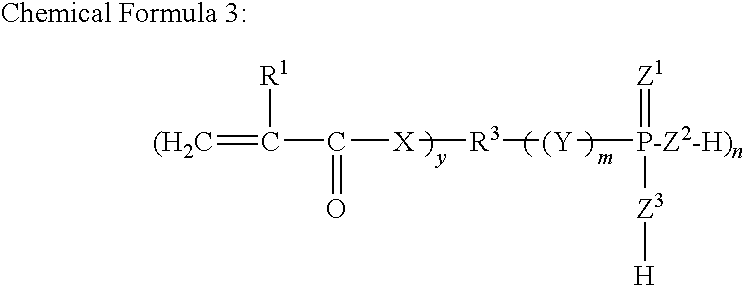Redox-curing type nonaqueous curable composition
a non-aqueous curable, redox-curing technology, applied in dental prosthetics, impression caps, surgery, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient adhesive strength, achieve the effect of high adhesive strength, improve the curing property of polymeric materials, and secure the time necessary
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0068]Agents A1-1 and A1-2 having compositions described below were prepared and combined, so as to produce a divided type nonaqueous curable composition (present composition) including these agents in a weight ratio of 1:1. In the composition obtained by mixing the agents A1-1 and A1-2, sodium sulfite was in a dispersed state. The divided type nonaqueous curable composition was subjected to a curing time test (P1) and a tensile bond strength test (Q1) described below, so as to obtain a curing time and tensile bond strength. The results are listed in Table 1 below. It is noted that the average particle diameter of a powdered water-soluble reducing compound (that is, a sodium sulfite powder in Embodiment 1) was measured by using ethanol as a dispersing medium with a laser diffraction particle size analyzer SALD-2100 (manufactured by Shimadzu Corporation) (which measurement method was similarly employed in other embodiments below).
Agent A1-1:Bis-GMA40 parts by weightHEMA20 parts by we...
embodiment 2
[0071]An agent A2-2 having a composition described below was prepared by replacing 3 parts by weight of a sodium sulfite powder of the agent A1-2 of Embodiment 1 with 2 parts by weight of a potassium sulfite powder, and the agent A2-2 was combined with the agent A1-1 of Embodiment 1, so as to produce a divided type nonaqueous curable composition (present composition) including these agents in a weight ratio of 1:1. In the composition obtained by mixing the agents A2-2 and A1-1, potassium sulfite was in a dispersed state. This divided type nonaqueous curable composition was subjected to the aforementioned curing time test (P1) and tensile bond strength test (Q1) so as to obtain a curing time and tensile bond strength. The results are listed in Table 1 below.
Agent A2-2:Bis-GMA40 parts by weightHEMA40 parts by weightTEGDMA20 parts by weightPotassium sulfite powder (with an average 2 parts by weightparticle diameter of 9.9 μm)
embodiment 3
[0075]Agents B1-1 and B1-2 having compositions described below were prepared and combined, so as to produce a divided type nonaqueous curable composition (present composition) including these agents in a weight ratio of 1:1. In the composition obtained by mixing the agents B1-1 and B1-2, sodium sulfite was in a dispersed state. This divided type nonaqueous curable composition was subjected to the aforementioned curing time test (P1) for obtaining a curing time and was also subjected to a tensile bond strength test (Q2) described below for obtaining tensile bond strength. The results are listed in Table 2 below.
Agent B1-1:Bis-GMA40 parts by weightHEMA30 parts by weightNPG30 parts by weightBPO 1 part by weight
Agent B1-2:Bis-GMA40 parts by weightHEMA30 parts by weightNPG30 parts by weightSodium sulfite powder (with an average particle 1 part by weightdiameter of 6.1 μm)
[Tensile Bond Strength Test (Q2)]
[0076]The labial surface of a lower anterior tooth of a bovine was polished with #80 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| solubility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com