Solvent/polymer solutions as suspension vehicles
a technology of solvents and polymers, applied in the field of suspension vehicles, can solve the problems of affecting the stability of the biomolecular substance delivered by the implantable drug delivery device, the biomolecular substance is problematic, and the biomolecular substance is marginally stable in the aqueous environment, and the effect of degrading
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Stability and In Vitro Release of Omega-INF in a Benzyl Benzoate and a Benzyl Benzoate / Benzyl Alcohol Suspension Vehicle
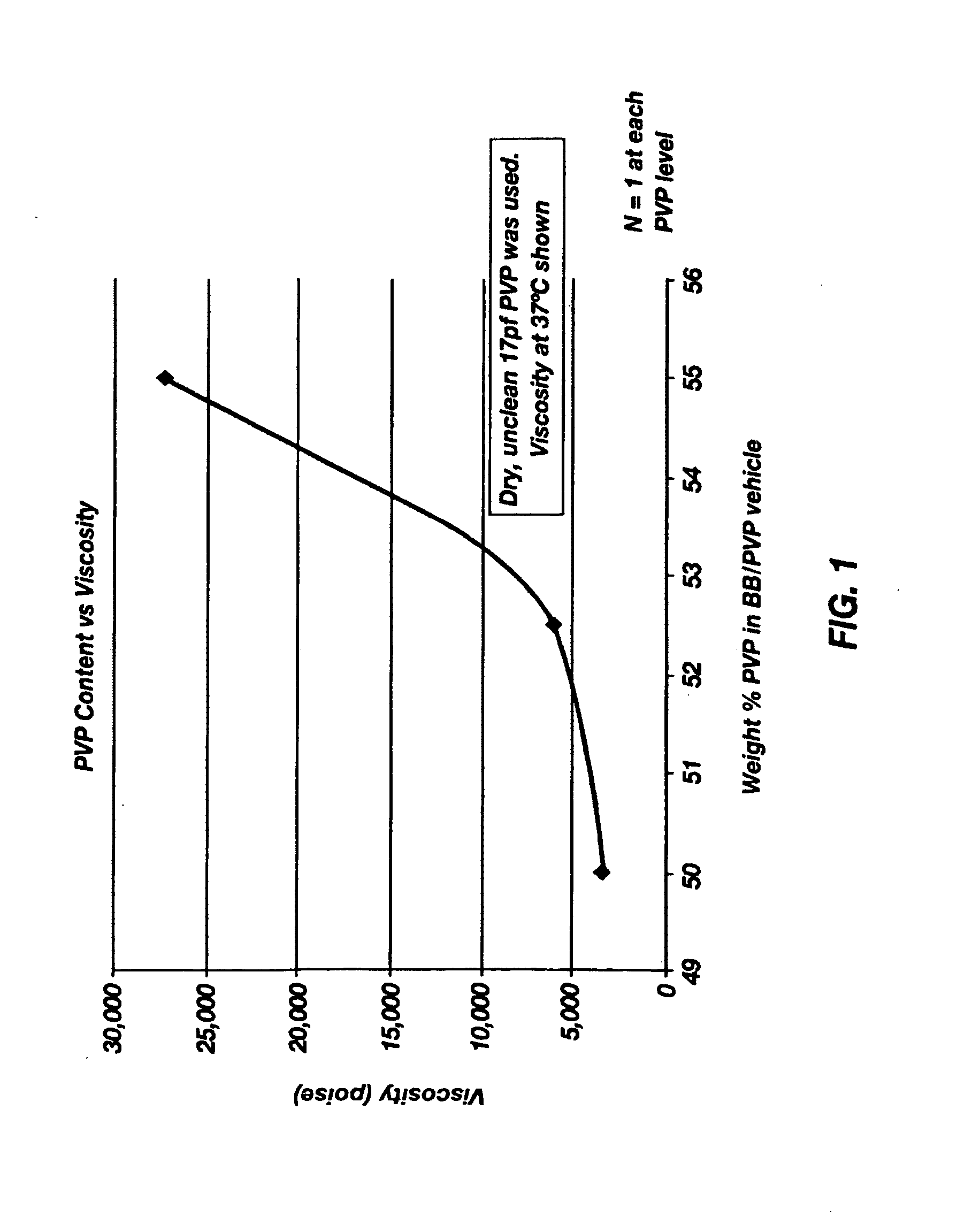
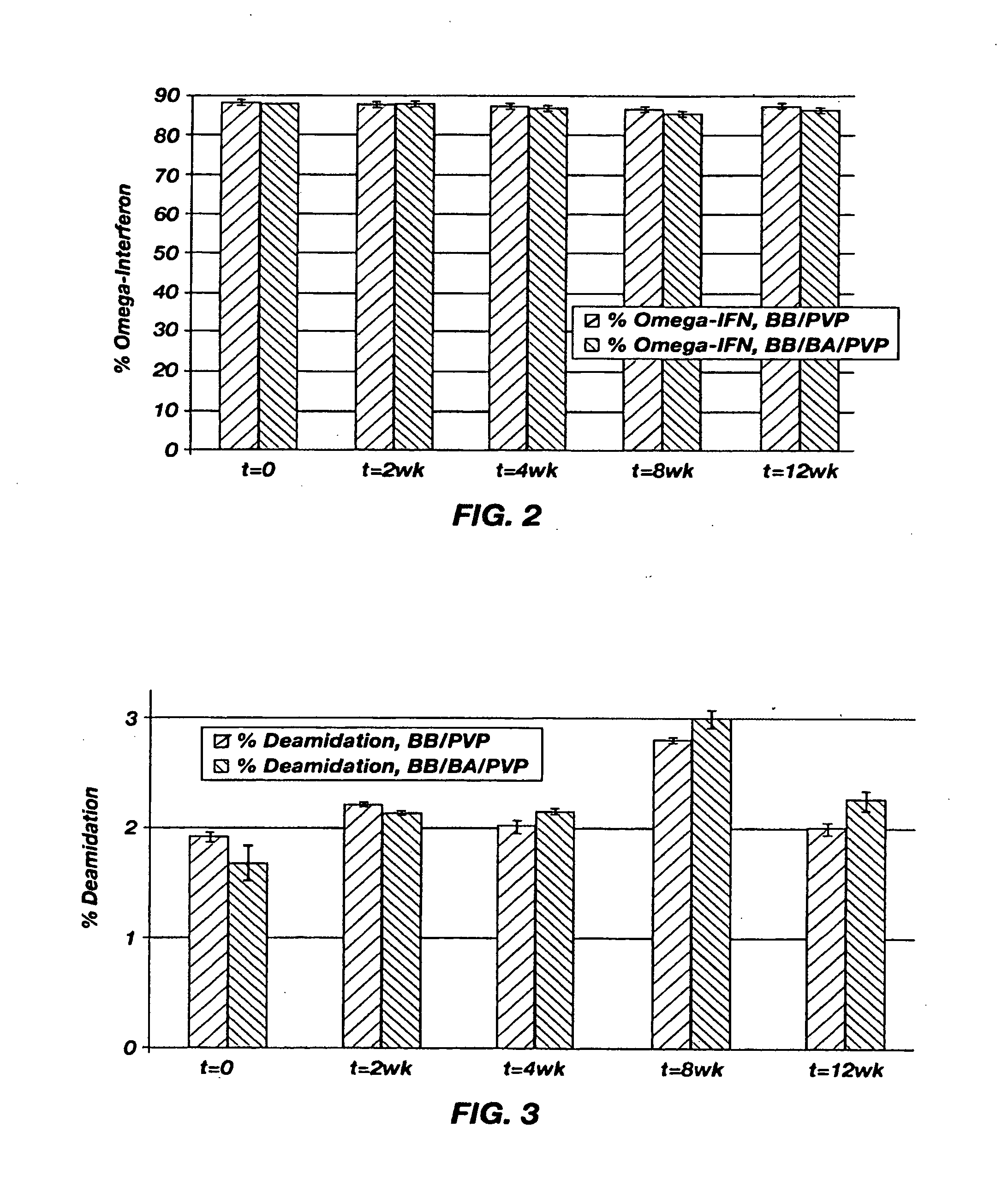
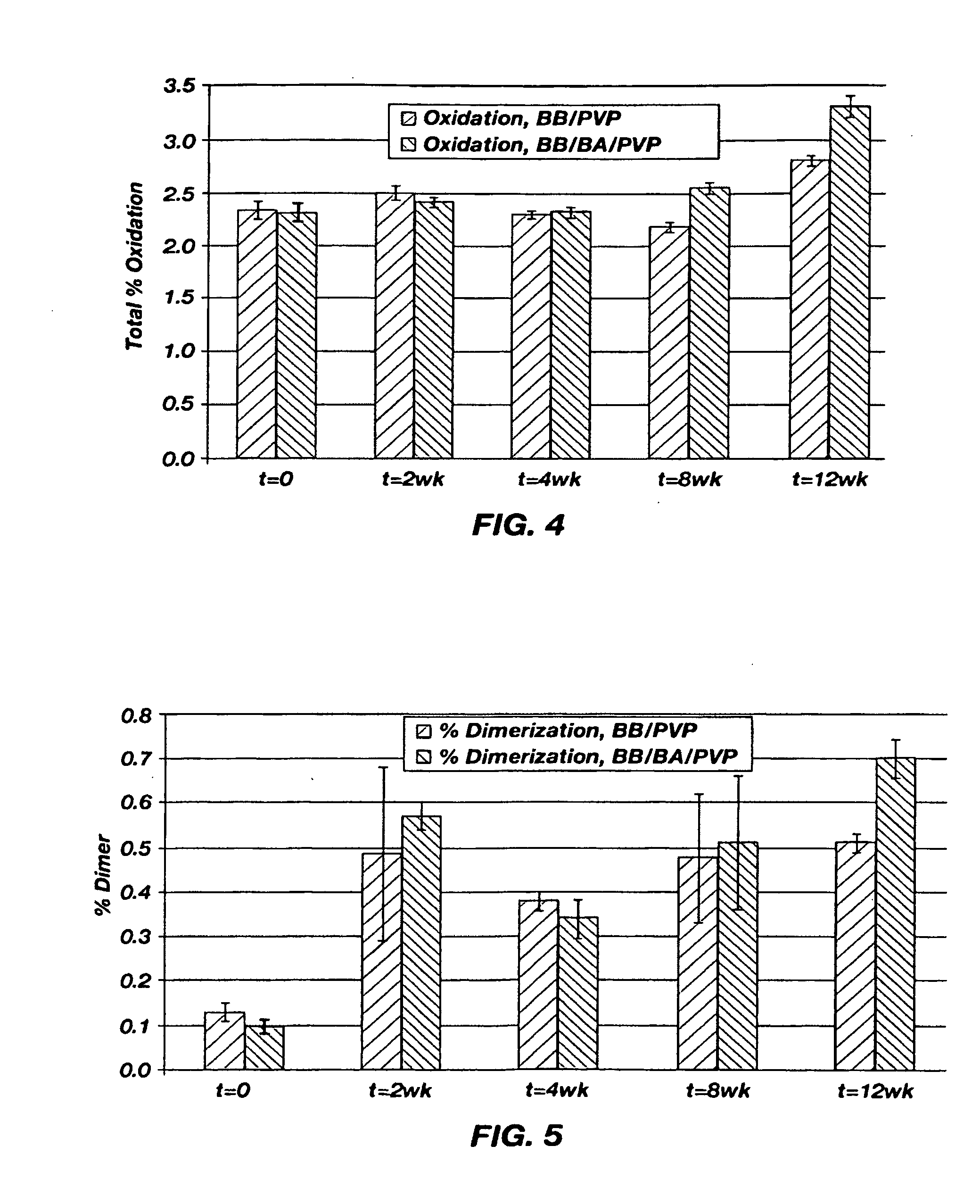
[0040]The stability of omega-INF for three months at 40° C. in two suspension vehicles was determined. One of the suspension vehicles included PVP dissolved in benzyl benzoate. The second suspension vehicle included PVP dissolved in a 90 / 10 benzyl benzoate / benzyl alcohol mixture. A release rate study at 37° C. was also performed. The materials used in the stability and release rate studies are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1Materials to be used in the Stability and Release Rate Studies.Spray-dried omega-IFN:sucrose:methionine:citrate(1:2:1) in 25 mM citrate bufferBenzyl benzoate (BB)Benzyl alcohol (BA)Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)Citrate BufferPhosphate Buffered Saline (PBS)Piston, fluoroelastomerDUROS ® Osmotic TabletTecophilic HP-60D-33 Membrane (g2) Blue NB7443: 155Titanium Reservoir (g2)Polyethylene Glycol 400Silicone Fluid, MDM 350Spiral Diffusion Moderator (DM), high d...
example 2
In Vivo and In Vitro Testing of Suspension Formulations
Using a Straight Diffusion Moderator
[0052]Four suspension formulations were tested under in vivo conditions over 90 days in rats to determine stability and in vivo release of the omega-INF. The suspension formulations included omega-INF as the active agent, PVP or dioleoyl-phosphocholine (DOPC) as the thickening agent, and lauryl alcohol (LA), benzyl benzoate, benzyl alcohol, or Vitamin E as the solvent. This experiment was designed to concentrate on the suspension formulations and used a straight polyetheretherketone (PEEK) diffusion moderator having a 0.25 mm diameter and a 15 mm length to minimize water ingress. During the experiment, efforts were made to minimize the moisture levels to which the suspension formulation was exposed. The suspension formulations were tested to determine omega-INF release in vivo from the DUROS® systems at t=5, 9, and 13 days; failure rates (system integrity) of in vivo systems at 45 days (n=3) a...
example 3
In Vivo and In Vitro Testing of Suspension Formulations Using a Spiral Diffusion Moderator
[0059]The suspension formulations described in Example 2 were investigated for system integrity and in vivo release of omega-INF. This experiment differed from that described in Example 2 in that this experiment was focused on the ability of the suspension formulations to both release measurable omega-INF in vivo as well as maintain system integrity using a two-piece, spiral PEEK-on-PEEK diffusion moderator with a 0.25 mm diameter and a 15 mm length. The suspension formulations were tested to determine: omega-INF release in vivo from DUROS® systems after 2, 6, 9, and 13 days of in vivo operation (n=25); failure rates (system integrity) of in vivo systems at 29 days (n=3), 61 days (n=3), and 90 days (n=19) after implantation; the stability of omega-IFN in the suspension formulations over several months at 5° C. and 40° C.; and in vitro release rate pumping into air and aqueous media. The materia...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wt % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com