Methods for the detection of jc polyoma virus
a technology of jc polyomavirus and detection method, which is applied in the field of detection of human jc polyomavirus, can solve the problems of pml, death, and serious conditions in some subjects, and achieve the effect of increasing the risk profile of pml and achieving the effect of higher risk profil
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Detection of JCV Variants by PCR
[0282]Nucleic acids are isolated from a biological sample using established protocols (e.g., cell lysis). Because the viral DNA may have integrated in the genomic DNA or may still be present as a smaller entity, both genomic DNA and shorter DNA sequences are isolated and subjected to PCR analysis. Upon isolation the nucleic acids are resuspended in a buffer that will facilitate PCR analysis. Buffers that facilitate PCR analysis are known to the skilled artisan (e.g., Maniatis) and are also commercially available from manufacturers of PCR enzymes (e.g., New England Biolabs, Beverly, Mass.). Nucleotide primers are designed to result in the amplification of the JCV-VP1 gene. PCR amplification is an established laboratory technique and comprises the addition of nucleotide primers, a polymerase and single nucleotides, and polymerase buffer and subjection this mixture to cycles of annealing, amplification and dissociation resulting in the amplification of a...
example 2
Detection of JCV Variants Using ELISA
[0283]Proteins and peptides are isolated from a biological sample using standard laboratory techniques (e.g., Maniatis). Both the cellular proteins and proteins of non-cellular components are subjected to the analysis. In one assay the sample is interrogated for the presence of JCV-VP1 polypeptides comprising one or more variants of the invention. The polypeptides are detected using sandwich ELISA comprising antibodies specific for JCV-VP1 polypeptides of the invention. The antibodies are generated by inoculating animals (e.g., rabbits) with the JCV-VP1 polypeptides of the invention resulting in polyclonal antibodies. If so desired, cells can be harvested from the inoculated animal to generate monoclonal antibodies. Methods for the generation of both polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies are routine in the art. The antibodies against JCV-VP1 polypeptide variants are immobilized on a solid surface (e.g., a 96-well plate), with one antibody type per...
example 3
Determining Solvent Accessible Surface Area Composition of VP1 Protein
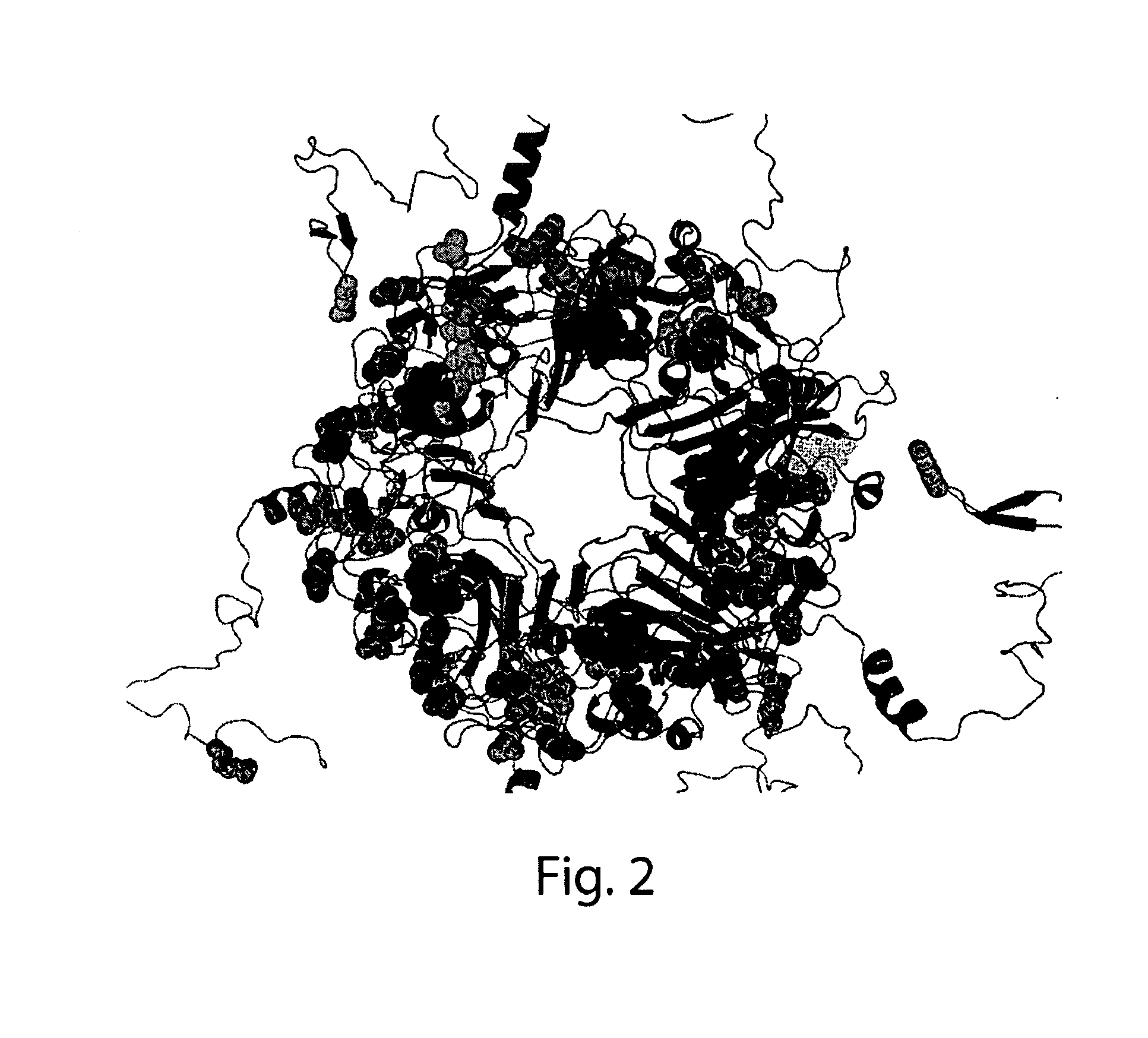
[0285]Accessible surface area calculations require the knowledge of the 3D coordinates of biomolecule. A homology model of JCV VP1 virus-like particle was constructed using structure of CoAl of SV40 virus-like particle as a template (PDB ID: 1SVA). MODELER (A. Sali & T. L. Blundell. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol. Biol. 234, 779-815, 1993) algorithm was used for model building and the SCWRL3 (A. A. Canutescu, A. A. Shelenkov, and R. L. Dunbrack, Jr. A graph theory algorithm for protein side-chain prediction. Protein Science 12, 2001-2014 (2003)) approach was used for side-chain position refinement. The polar and non-polar solvent accessible surface areas of amino acid sidechains were calculated using Lee and Richards's method (B. Lee B & F. M. Richards. The Interpretation of Protein Structures: Estimation of Static Accessibility. J. Mol. Biol 55, 379-400 (1971)). Subsequ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com