Polyamide/polyphenylene ether fibers and fiber-forming method
a polyphenylene ether and polyamide technology, applied in the field of polyamide/polyphenylene ether fibers and fiber-forming methods, to achieve the effect of improving strength and smoothness, and simplifying the number of polymers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-4
, Comparative Examples 1-16
[0109]Components used to form fiber-spinning compositions are summarized in Table 1.
TABLE 1ComponentDescriptionPPE, 0.46Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether), CAS Reg. No.25134-01-4, having an intrinsic viscosity of about 0.46 deciliterper gram measured in chloroform at 25° C., and a weight averagemolecular weight of about 65,000 atomic mass units; obtained asPPO 646 from SABIC Innovative Plastics.PPE, 0.40Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether), CAS Reg. No.25134-01-4, having an intrinsic viscosity of about 0.40 deciliterper gram measured in chloroform at 25° C., and a weight averagemolecular weight of about 55,000 atomic mass units; obtained asPPO 640 from SABIC Innovative Plastics.PPE, 0.30Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether), CAS Reg. No.25134-01-4, having an intrinsic viscosity of about 0.30 deciliterper gram measured in chloroform at 25° C., and a weight averagemolecular weight of about 45,000 atomic mass units; obtained asPPO 630 from SABIC Innova...
examples 3 and 4
, Comparative Examples 20-22
[0116]These examples illustrate fiber production. Five compositions were prepared by blending the components and amounts summarized in Table 5. The composition of Example 4 was prepared by blending a composition prepared according to Example 3 with an equal quantity of the polyamide in a second run through the extruder.
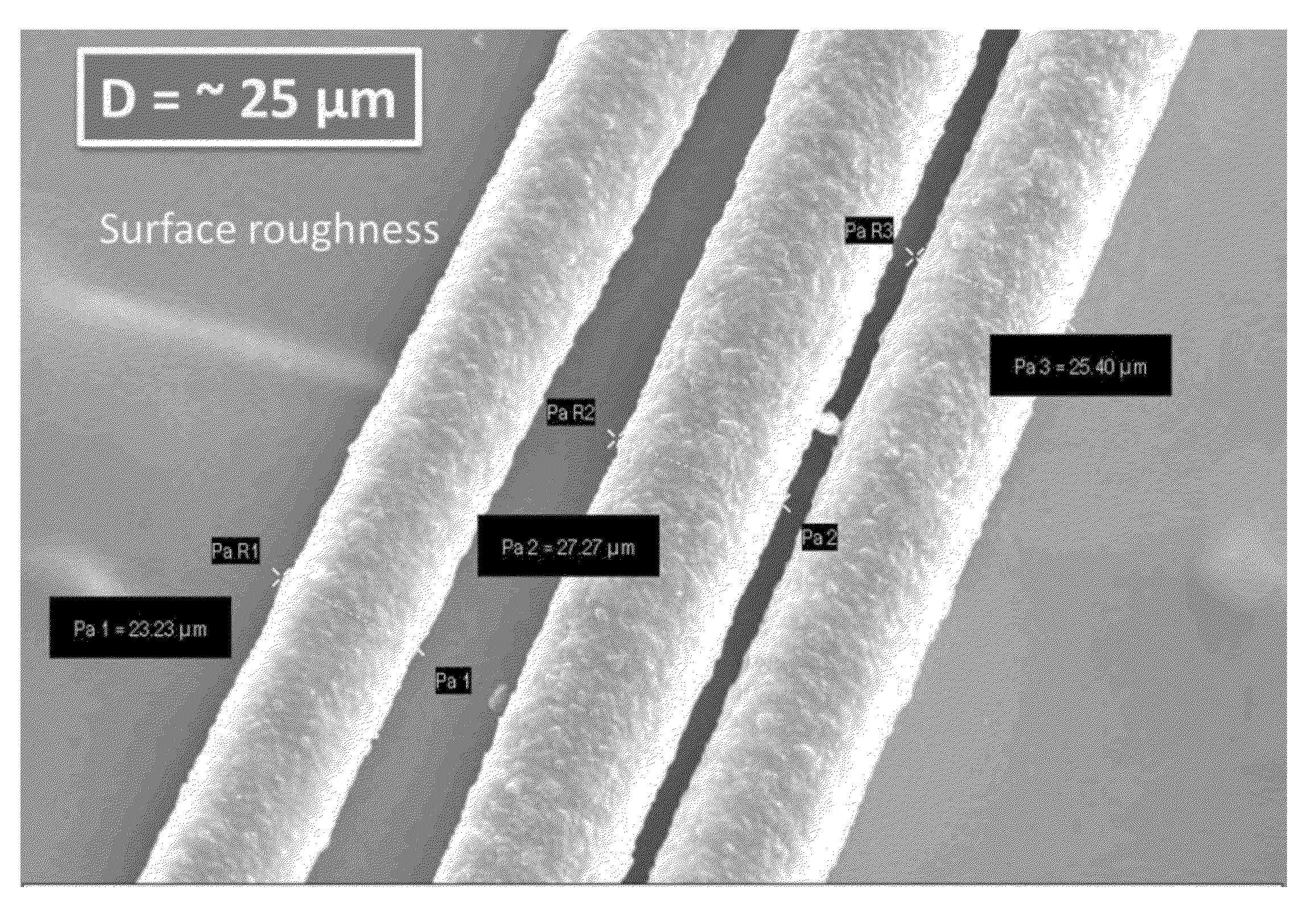
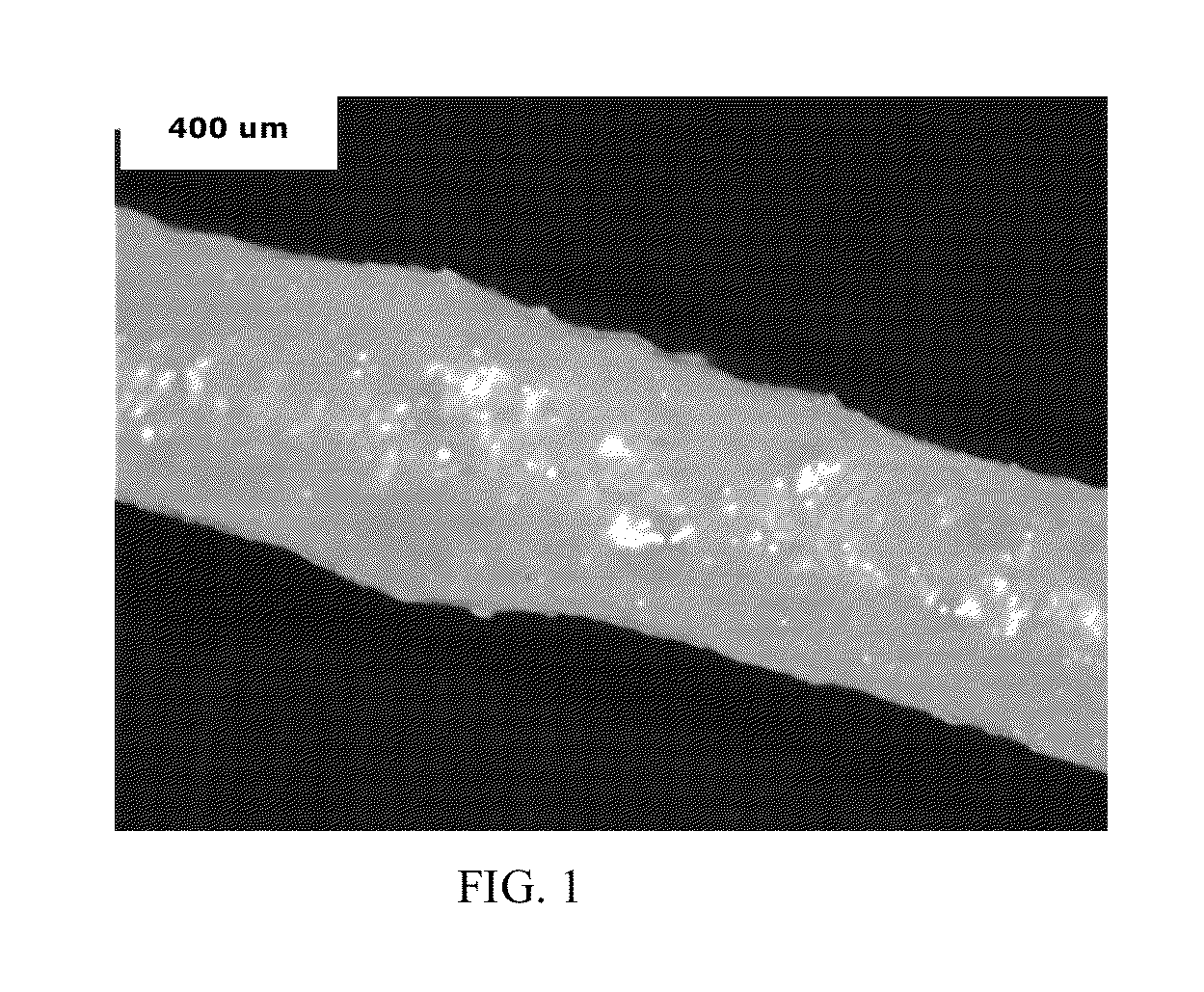
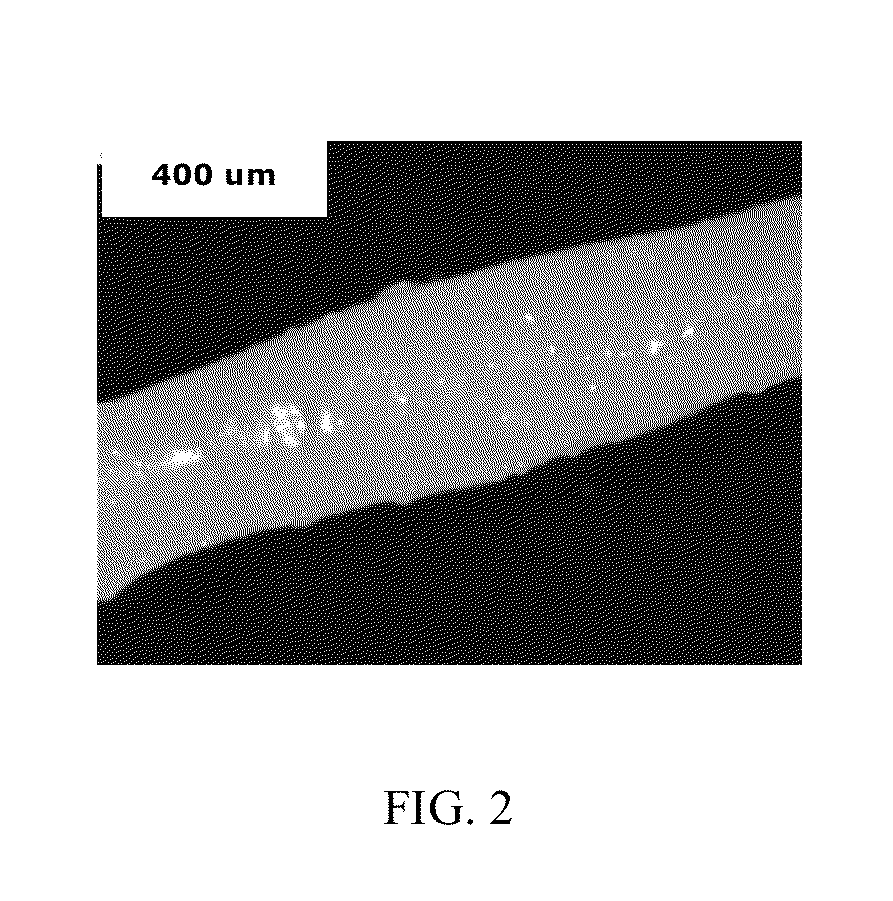
[0117]Micrographs corresponding to Examples 3 and 4, and Comparative Examples 20 and 21 are presented in FIGS. 14-17, respectively. Image analysis was done using commercially available software Clemex Vision PE and Vision Lite 6.0 and FIGS. 14-17 were colored for illustration, with red signifying the polyamide-containing continuous phase, and blue signifying the polyphenylene ether-containing disperse phase. Polyphenylene ether particle size was plotted using Minitab software, version 15, from Minitab, Inc. The compositions of Examples 3 and 4 had finely divided polyphenylene ether disperse phases, while the compositions of Comparative Exam...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com