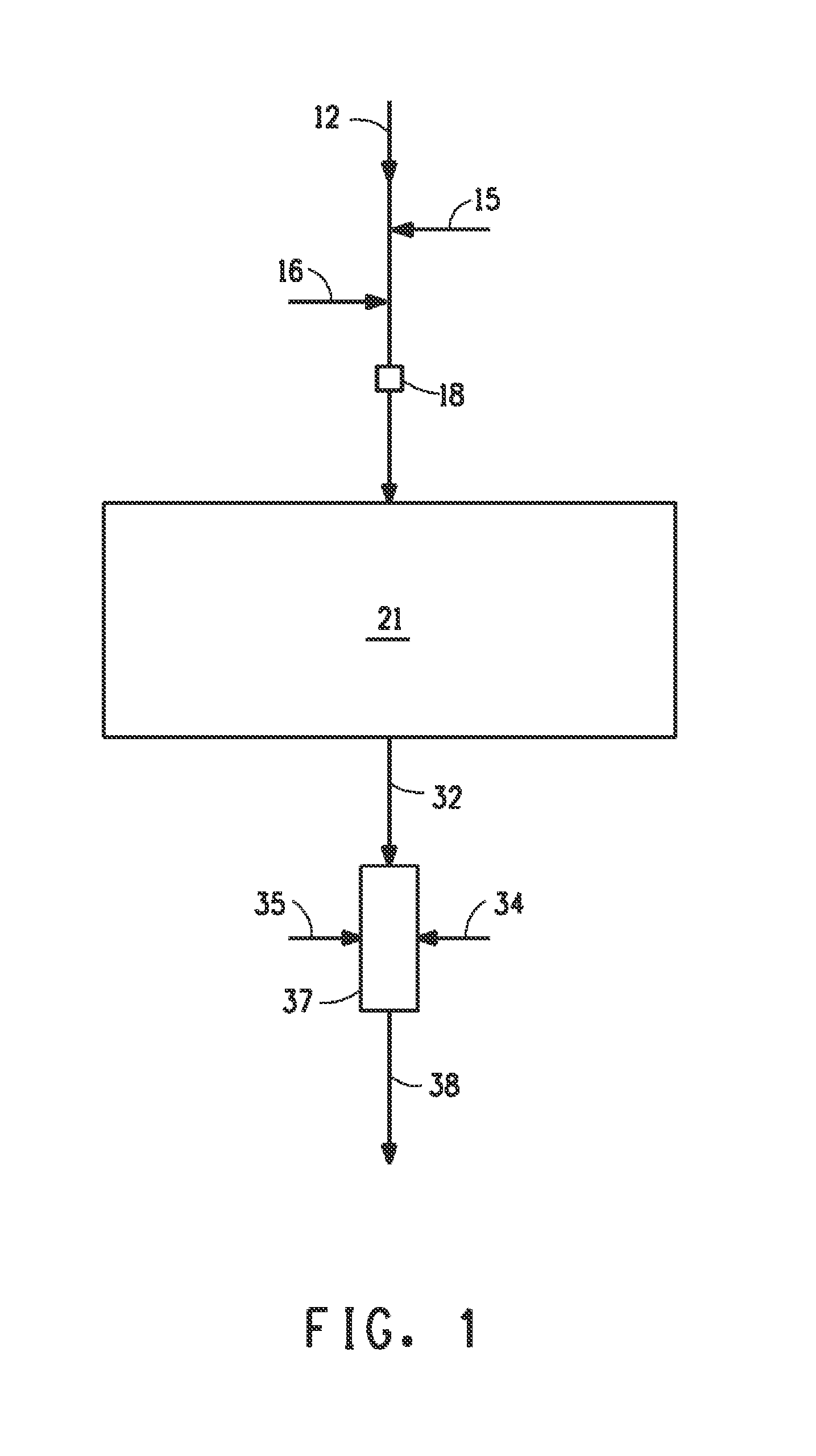
PROCESS FOR HYDRAULIC FRACTURING WITH pH CONTROL
a hydraulic fracturing and control technology, applied in the direction of fluid removal, survey, borehole/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the pumping pressure during the fracturing, and affecting the performance of organic polymer friction reducers such as anioni
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0039]This example provides the results of friction loop tests which demonstrate the effect of pH on friction reduction of various friction reducing polymers.
[0040]Friction loop tests were carried out at Stim-Lab, Inc. located in Duncan, Okla., using a standard apparatus known to those skilled in the art. For each test, approximately 9 gallons of test fluid was circulated at 10 gallons / minute (approx. Reynolds number of 75,000). The friction reduction was calculated from the pressure drop across a precise length of the test loop.
[0041]The water used to prepare the test fluids was a blend of 40% produced water from the Marcellus shale formation and 60% surface water collected from a location in Pennsylvania. The unadjusted pH of the water was 5.8. For tests run at lower pH, the water was acidified with sulfuric acid. In some cases the acidified water was also treated to contain about 10 mg / L residual ClO2. The test temperature was about 24° C. (75° F.).
[0042]For each test, a baseline...
example 2
[0044]This example demonstrates the pH lowering effect of oxidizing biocide in combination with divalent iron.
[0045]Unbuffered deionized water was adjusted to a pH of 6.0-6.2 with 1N NaOH or HCl as needed. Samples 2B and 2C were prepared from this water and 99.5% iron(II) heptahydrate so that the added Fe2+ content was 25 and 50 mg / L, respectively. Sample 2A was a control sample and contained no added iron. To each of samples 2A-2C, 30 mg / L ClO2 was applied, after which the pH and residual ClO2 was measured about 30 minutes later. Results, which were gathered at ambient laboratory temperatures of about 20-22 C, are summarized in the following table.
Fe2+pHpHClO2 mg / LClO2 mg / LSamplemg / Linitialfinalappliedresidual2A06.186.243028.52B256.103.613018.12C506.103.33014.5
[0046]Control sample 2A, without Fe2+, shows no substantial change in pH with addition of ClO2 and substantially no consumption of ClO2 (the applied and residual amount is substantially the same). In contrast, ClO2 addition t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com