Method and system for producing energy from waste
a technology of waste energy and waste, applied in the field of thermal reactors, can solve the problems of waste, environmental protection, landfills, etc., and achieve the effect of destroying waste in a safe and controlled environmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0065]It should be noted that the following detailed description is directed to a method and system for producing heat energy by destroying waste and is not limited to any particular size or configuration but in fact a multitude of sizes and configurations within the general scope of the following description.
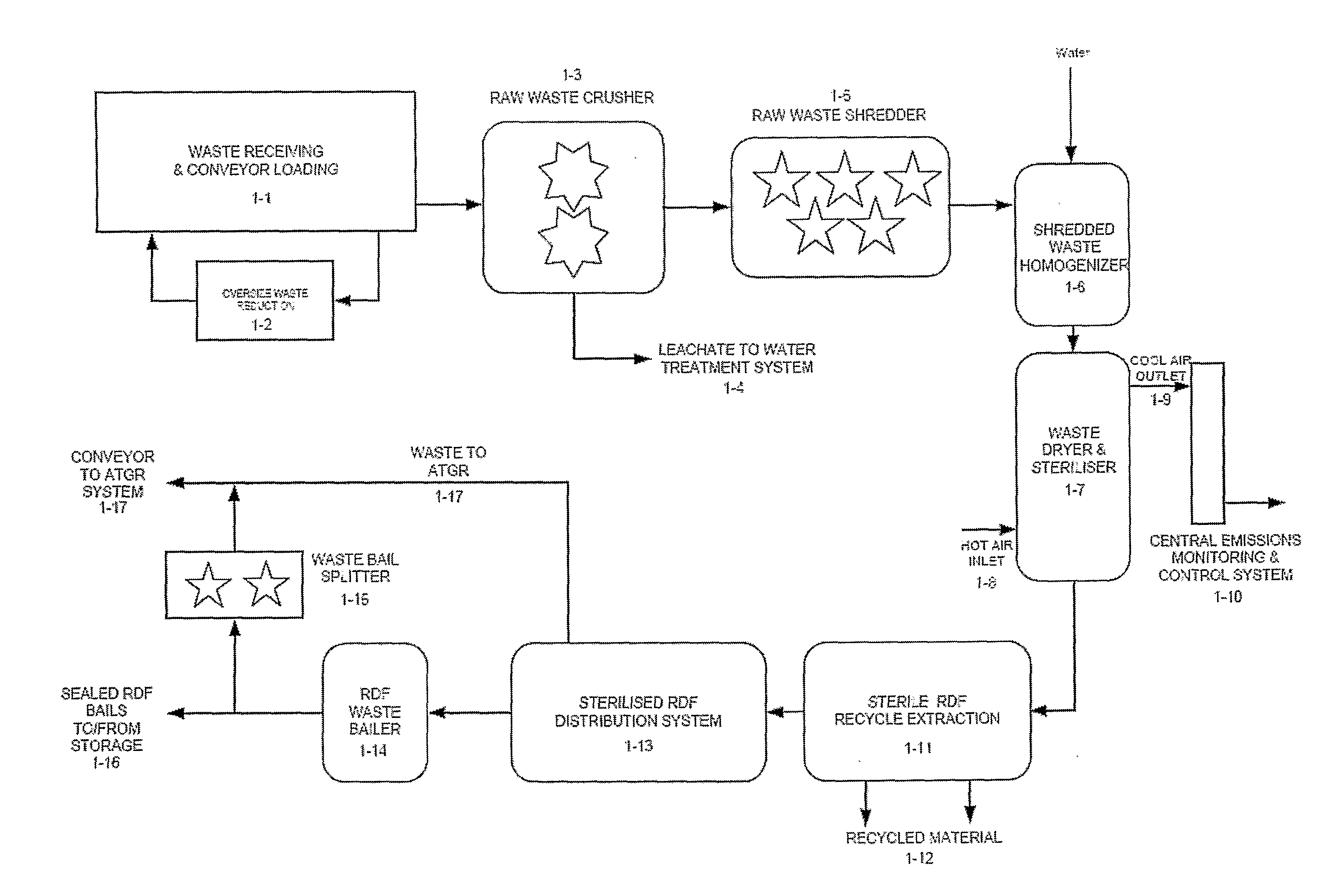
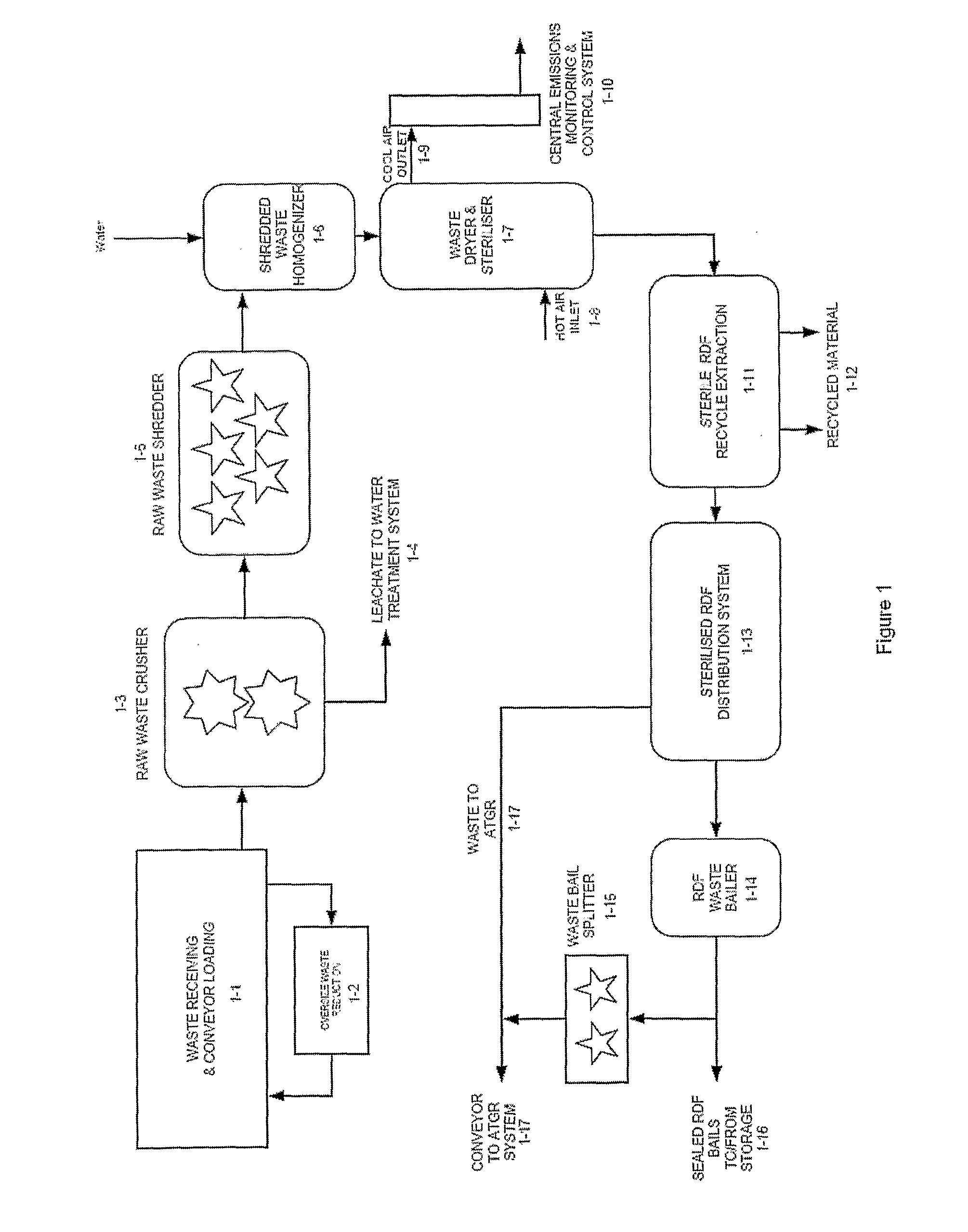
[0066]Stage 1—Waste Receiving, Sorting and RDF Production
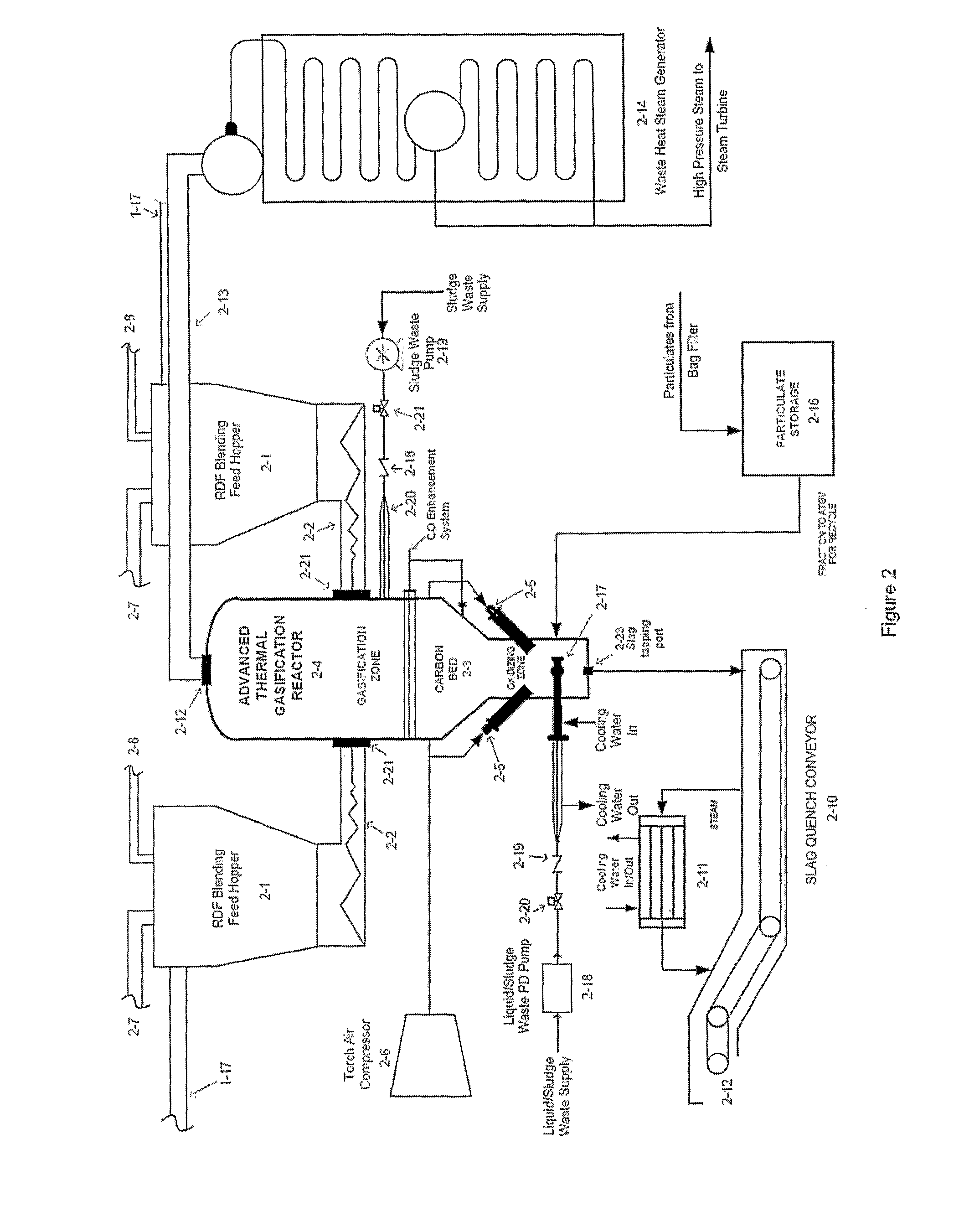
[0067]This stage will be-described in reference to FIG. 1 and FIG. 2. Waste delivered to the plant is initially checked for oversized components [1-1]. Oversized items are extracted from the main stream and size reduced [1-2] before being returned to the main waste input stream [1-1]. The raw waste is then crushed [1-3] and moisture is extracted from the waste and after being treated is used as process and cooling water within the plant [1-4]. Sludge produced in the treatment of the moisture extracted from the waste is returned to the waste stream for destruction in a reactor (2-4). After crushing, the waste is shredded t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com