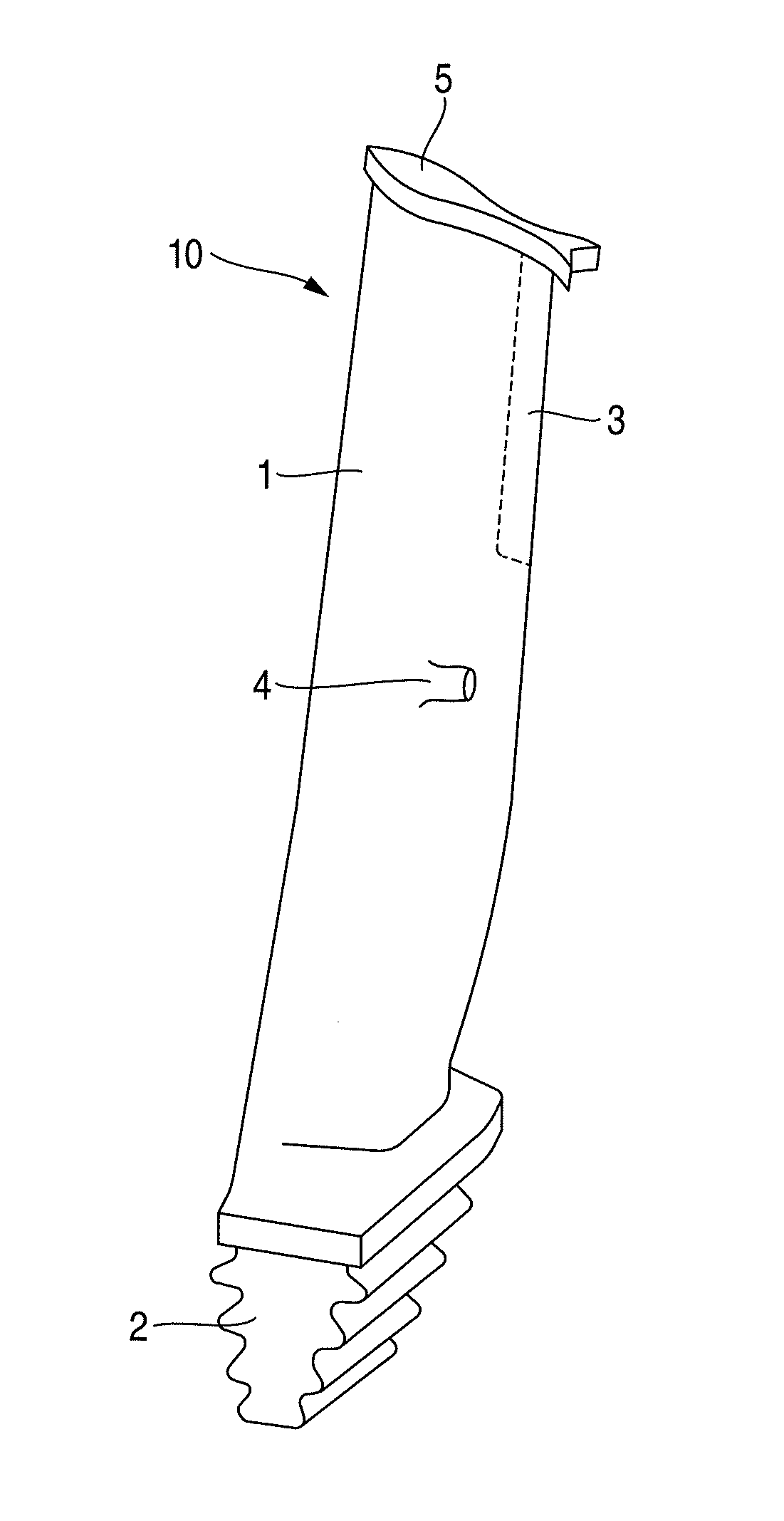
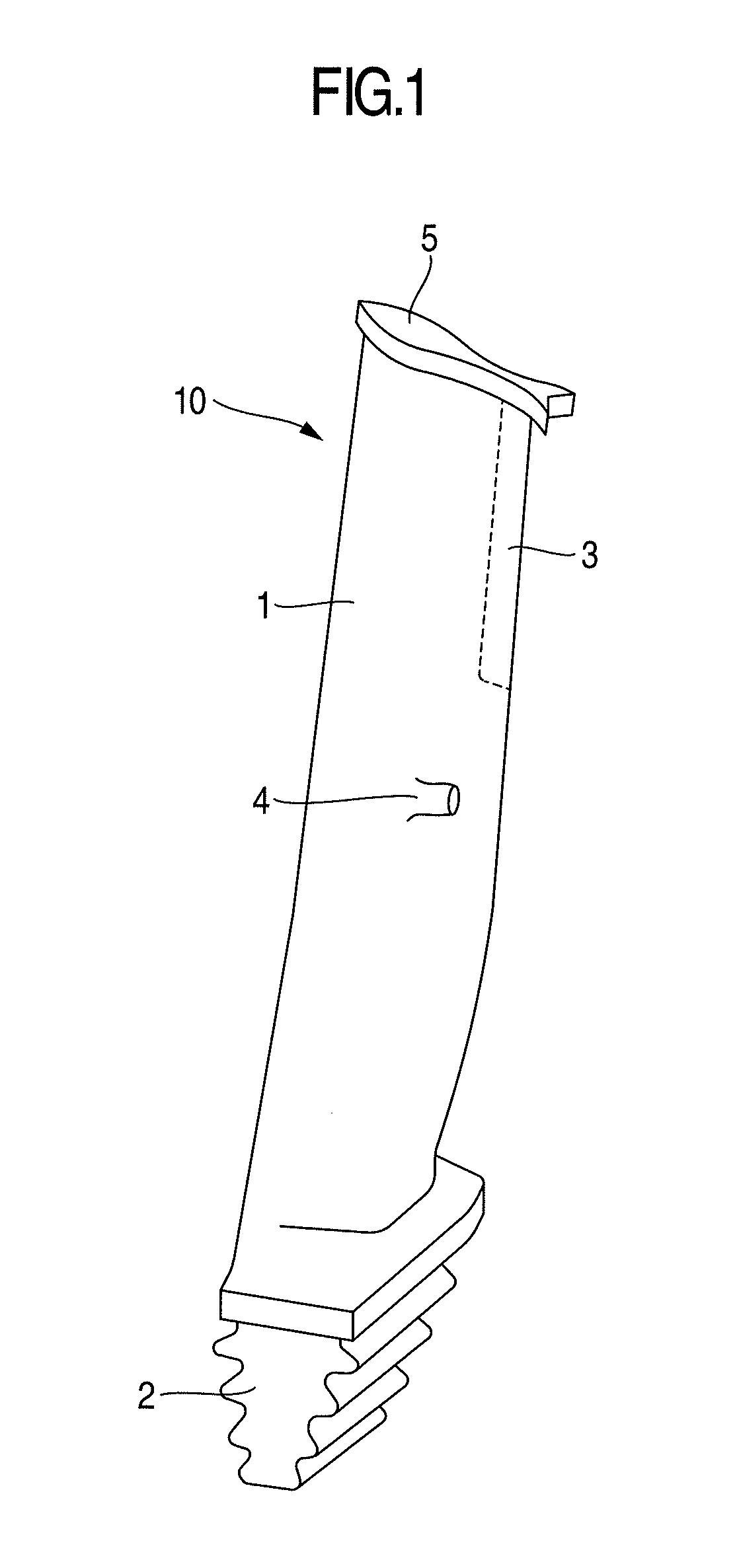
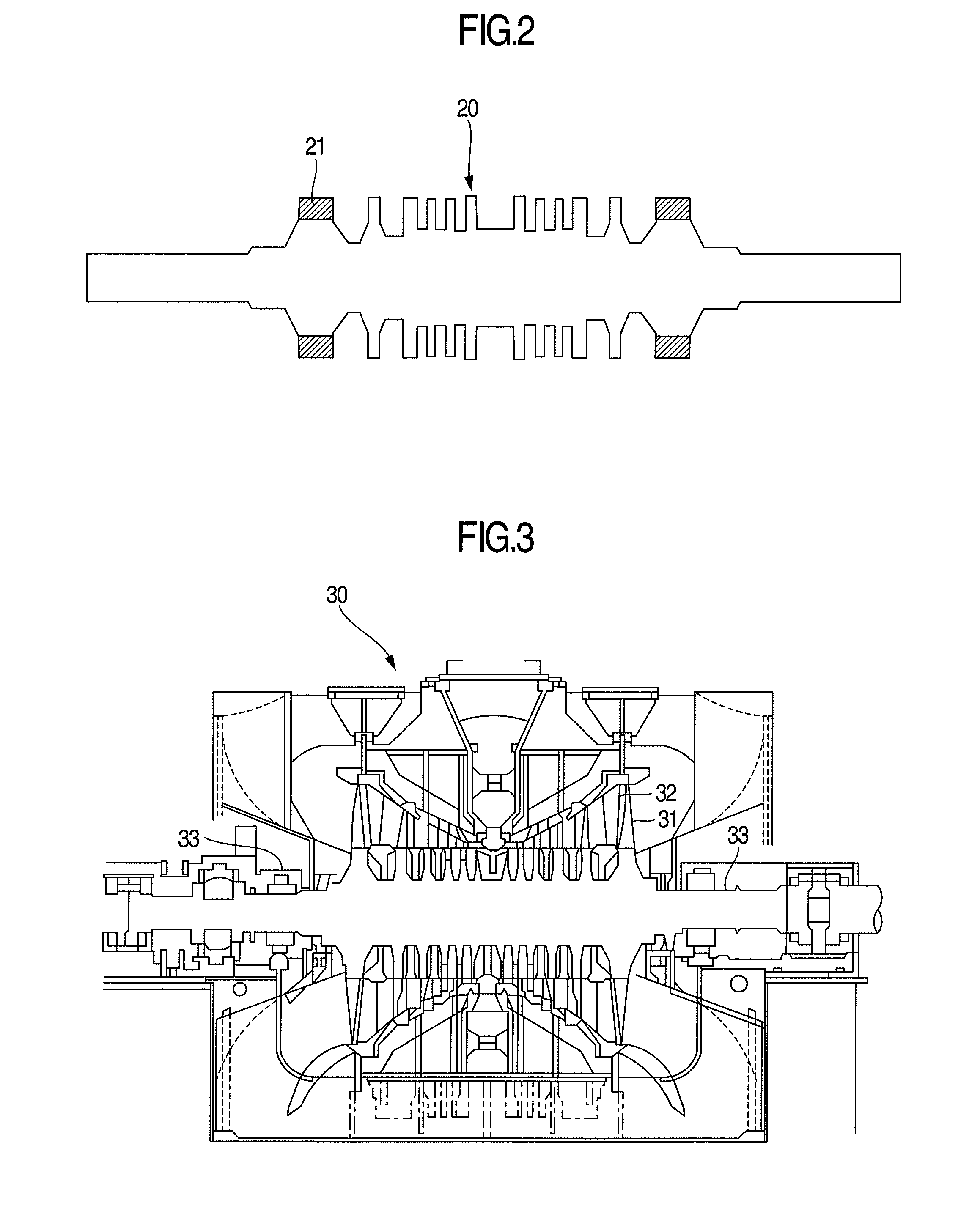
Precipitation Hardening Martensitic Stainless Steel and Long Blade for Steam Turbine Using the Same
a technology of martensitic stainless steel and precipitation hardening martensitic stainless steel, which is applied in the direction of blade accessories, machines/engines, waterborne vessels, etc., can solve the problems of poor balance between strength and toughness, and achieve excellent texture stability, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Sample
[0036]Test samples were prepared to evaluate a relationship between the chemical composition of the precipitation hardening martensitic stainless steel of the present invention, tensile strength thereof, 0.02% yield strength, Charpy impact absorption energy, pitting potential, and micro-texture. Table 1 illustrates a chemical composition of each test sample.
[0037]First, raw materials were melted by using a high-frequency vacuum melting furnace (5.0×10−3 Pa or less, 1600° C. or higher) to obtain compositions listed in Table 1. The obtained ingot was hot-forged by using a press forging machine and a hammer forging machine, and formed into a square bar having a width×thickness×length of 100 mm×30 mm×1000 mm. Next, the square bar was cut and processed to a width×thickness×length of 50 mm×30 mm×120 mm, thereby giving stainless steel starting materials.
[0038]Next, the stainless steel starting materials were subjected to various heat treatments by using a box electric ...
example 2
[0046]The following describes the steam turbine long blade to which the alloy of the present invention is applied. In this embodiment, by using Alloy 1 illustrated in Table 1 of materials of the present invention, an axial-entry-type steam turbine long blade having a blade length of 48 inch was produced. As a method for producing the long blade, vacuum carbon deoxidation was first performed in a high vacuum state of 5.0×10−3 Pa or less to deoxidize molten steel by a chemical reaction of C+O→CO. Subsequently, the steel was formed into an electrode bar by extend forging. Electro-slag remelting was thus performed to give a high-grade steel ingot by self-dissolving the electrode bar by Joule heat generated upon the application of current at the time when this electrode bar was immersed in molten slag, and then coagulating it in a water-cooled die. Next, the steel ingot was hot-forged, and then press-forged by using a 48-inch blade die. After that, as a solution treatment, the resulting ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com