Low-voltage IC test for defect screening
a low-voltage ic and defect screening technology, applied in the direction of electrochemical generators, instruments, batteries, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the level of electromigration and other reliability problems, damage to shorted circuits as well as microelectronic circuits in its vicinity, and reducing the defect signal. , the effect of strong maverick signal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
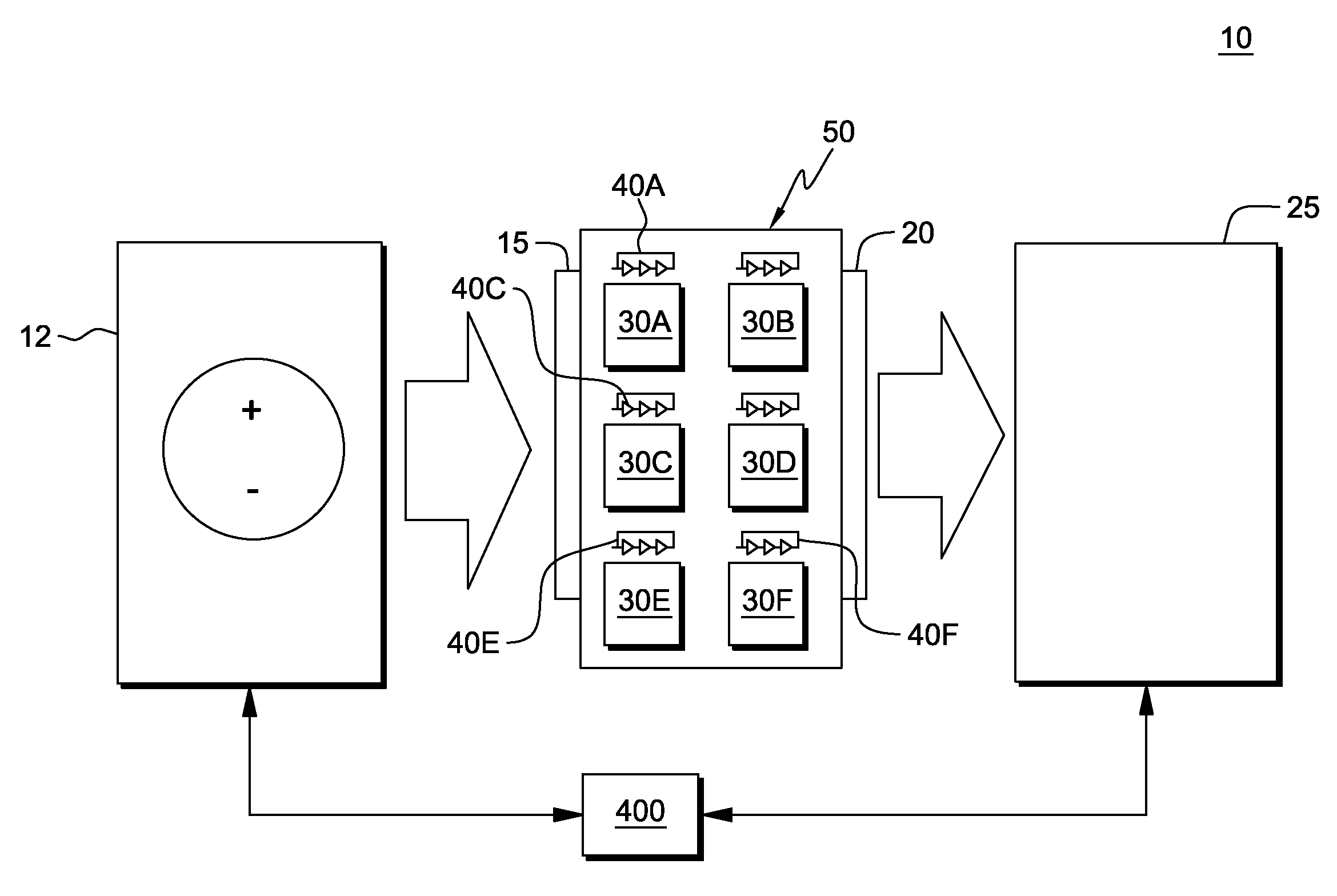
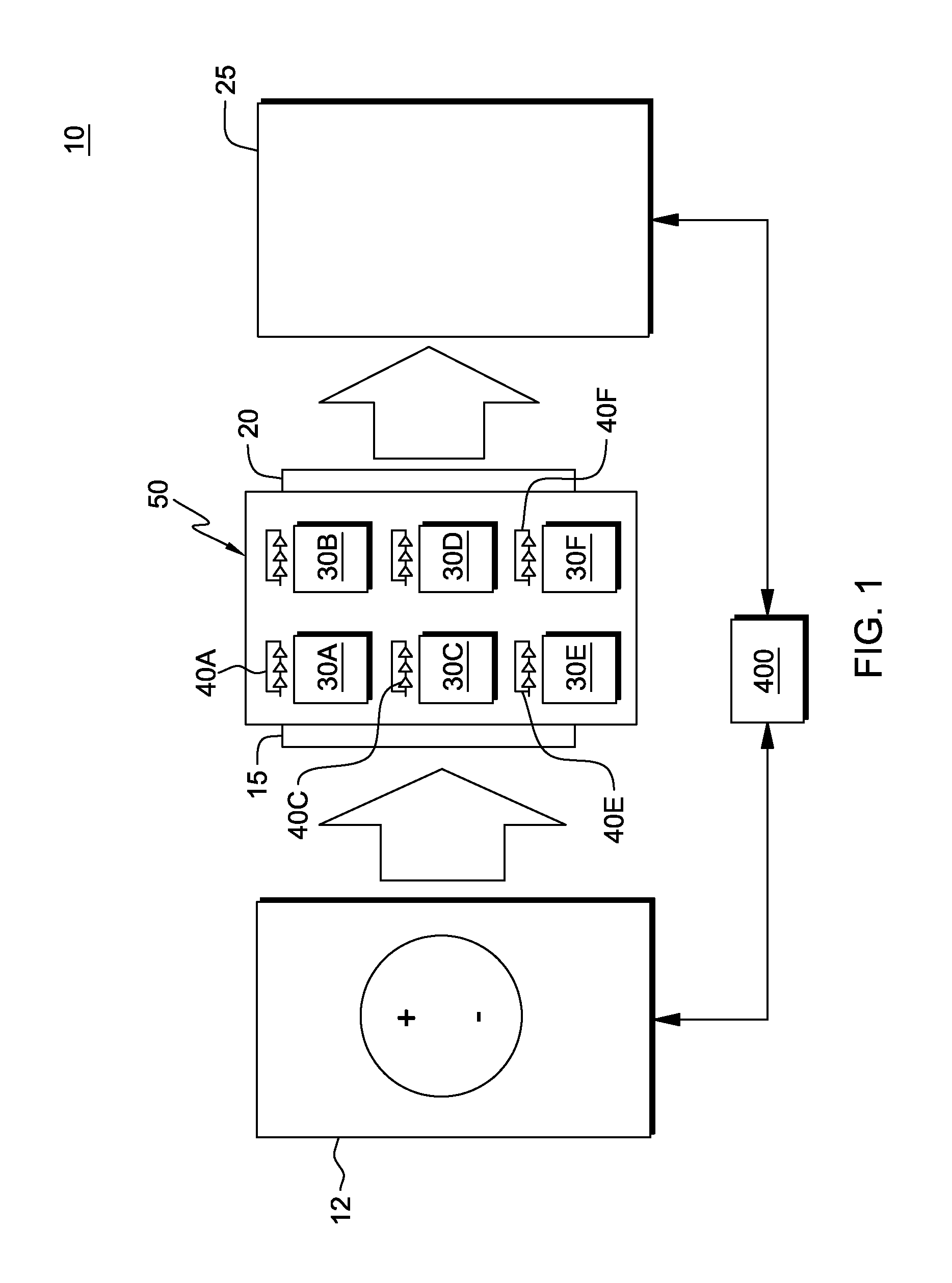
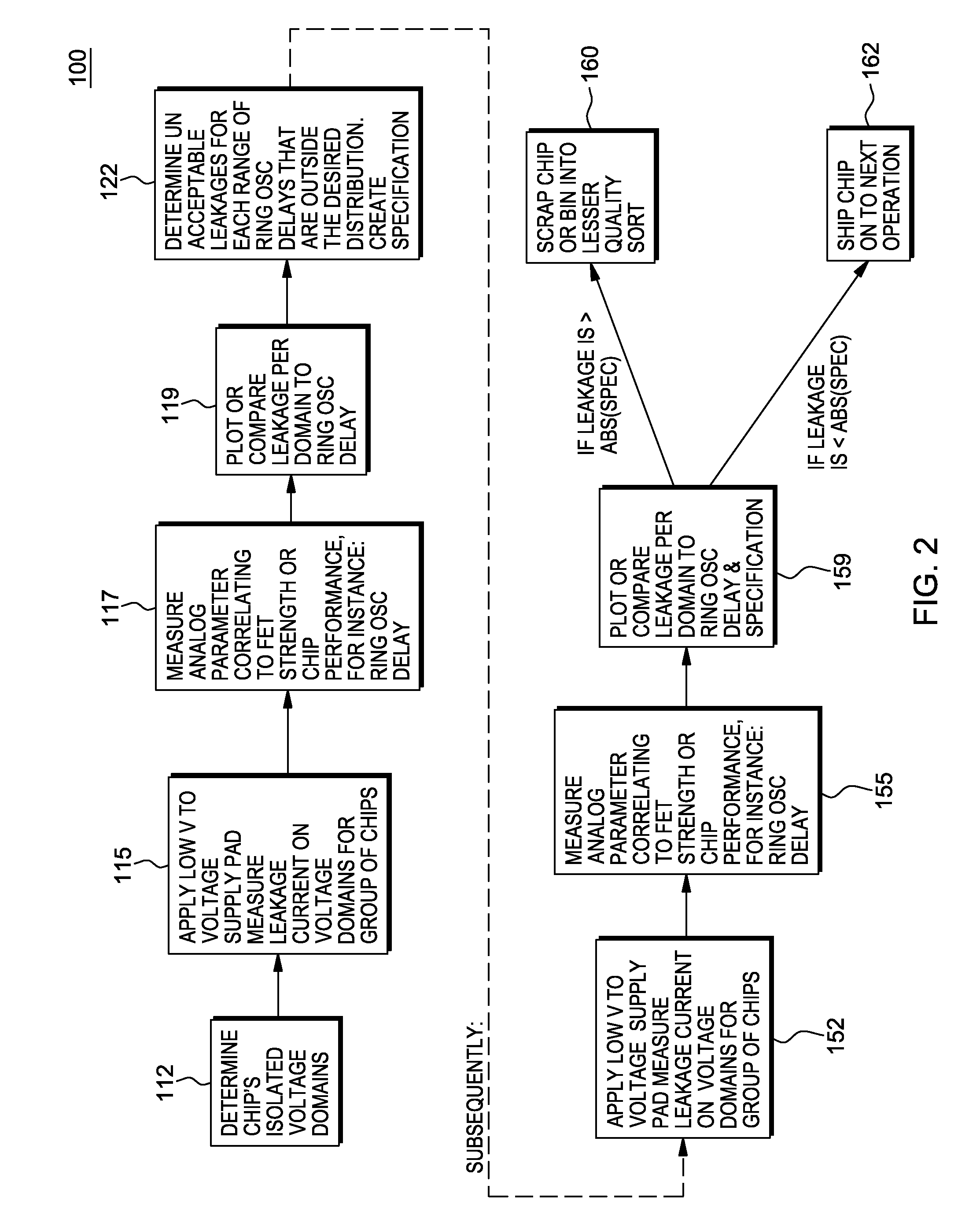
[0035]In one embodiment, the system and method for low voltage defect screening includes utilizing a low voltage current measurement at the beginning of a testing sequence. In one aspect, this is done to protect tester-to-product probing hardware from harmfully high currents. In one embodiment, this applied low voltage is below the threshold voltage of the FETs in the circuits. Resolution is also helped by testing at a lower temperature where less leakage currents are drawn. The low voltage does not therefore turn on FET gated leakage paths thus making shorts defects between power and ground more detectable from the background leakage. The low voltage also decreases the current densities through the power and ground wiring to the shorts defects often preventing these wires from ablation.
[0036]In a further aspect, a current screen may then be subsequently used to sort as failures chips that have greater than a defined current limit. Current limits are normalized by a parameter that c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com