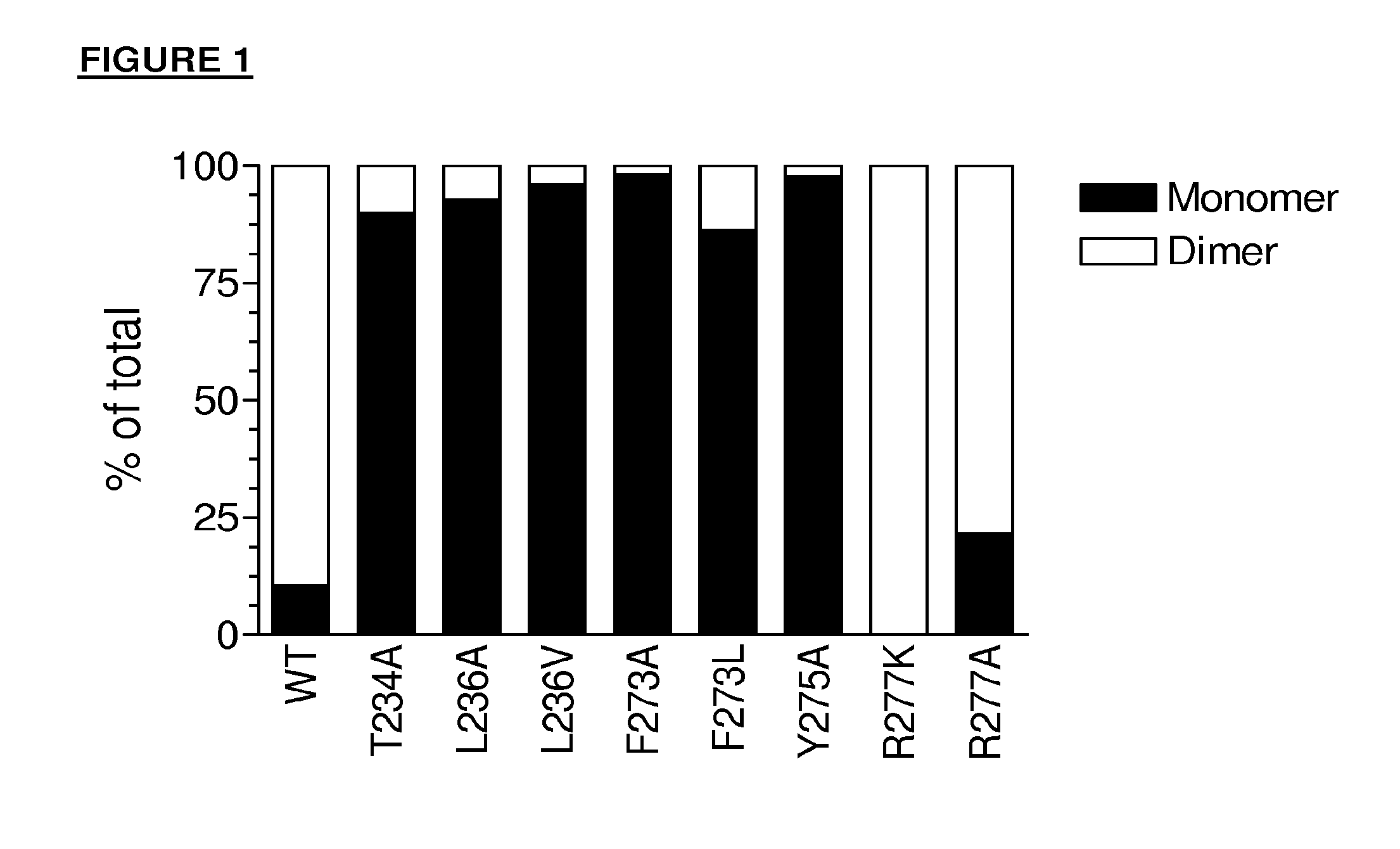
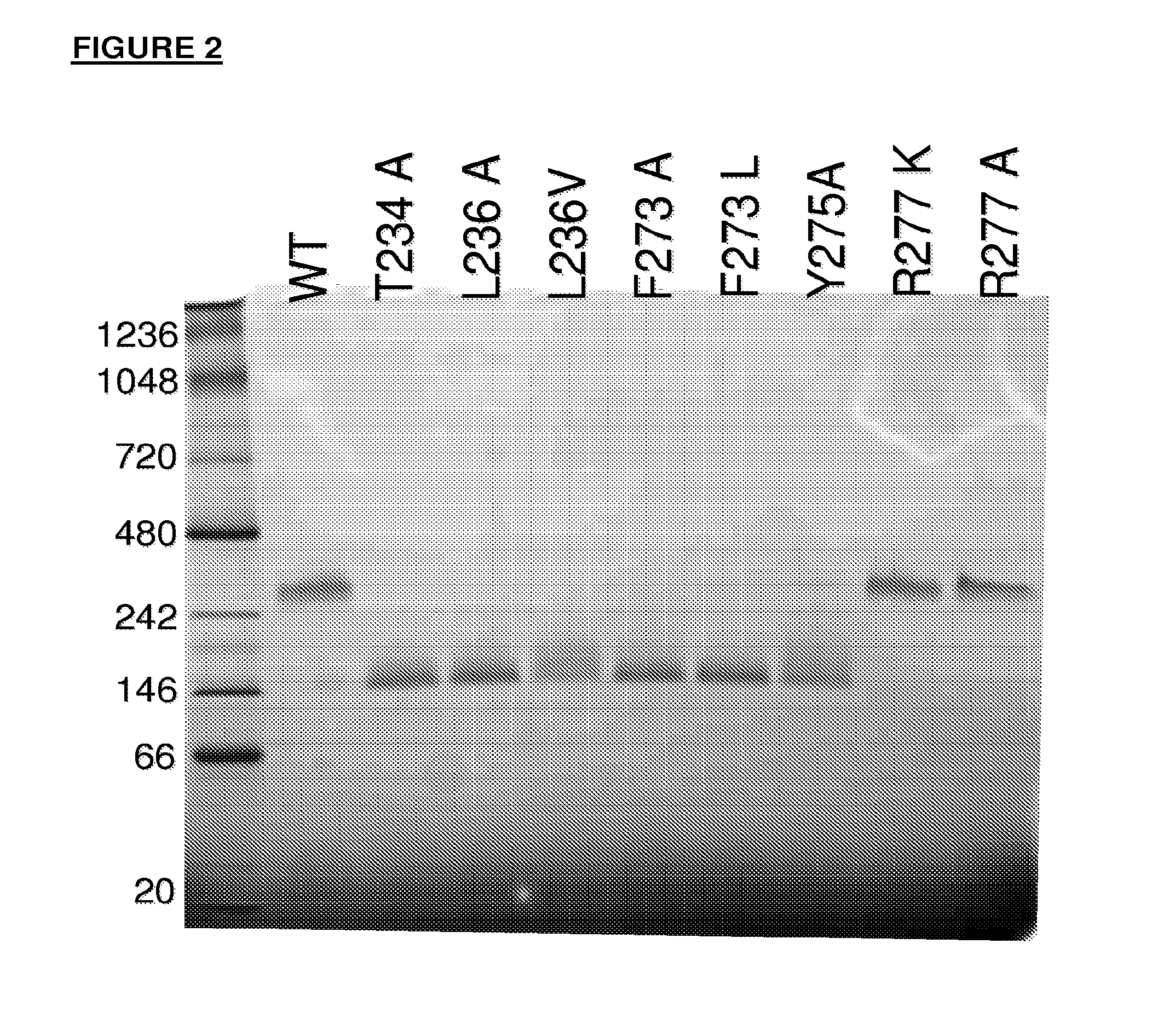
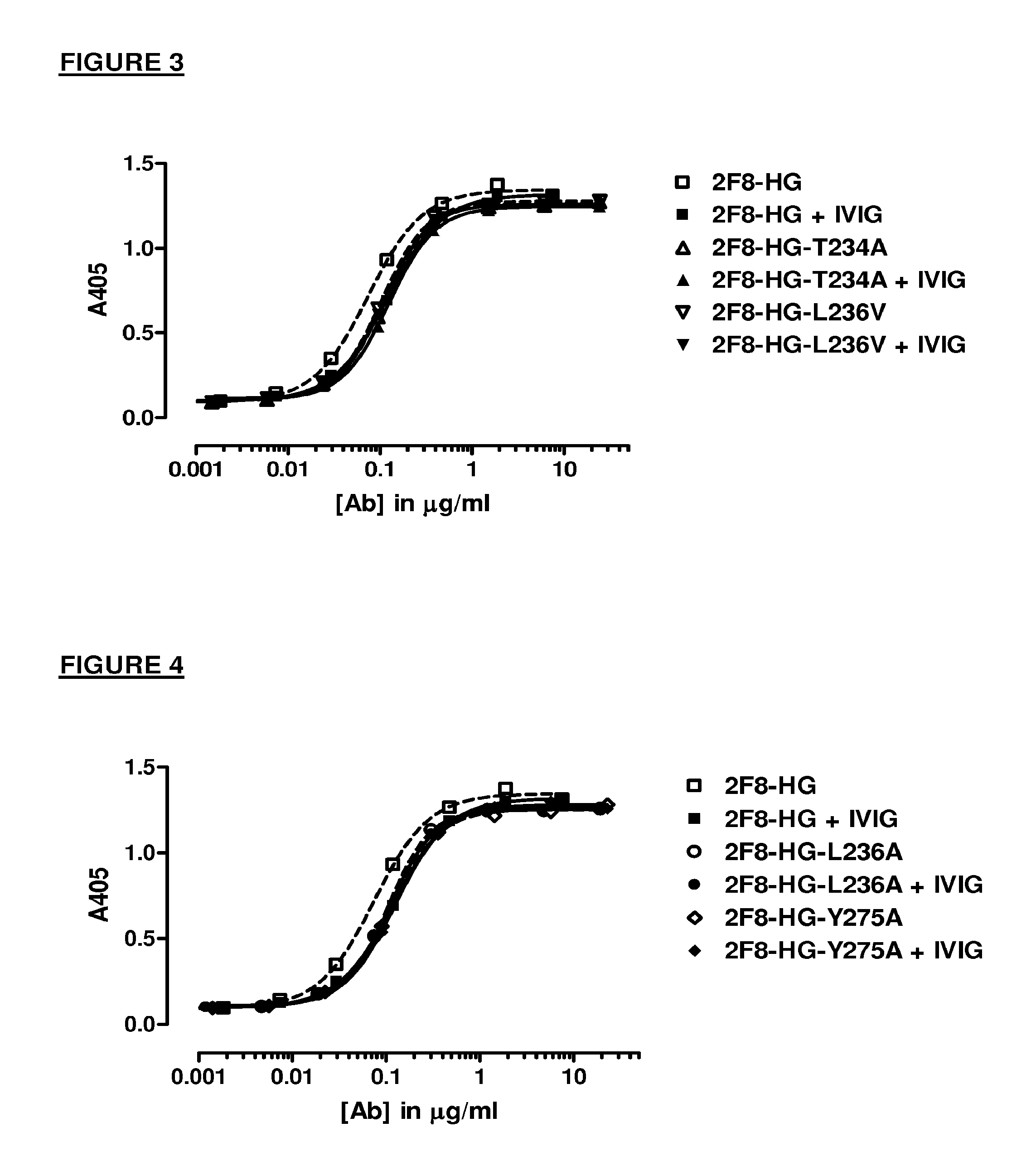
Antibody variants having modifications in the constant region
a constant region and antibody technology, applied in the field of modified antibodies, can solve the problems of inferior pharmacokinetics, dimerization may form undesirable immune complexes, and full-length antibodies may exhibit agonistic effects, and achieve the effect of preventing undeired fab arm exchang
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Structural Analysis of CH3-CH3 Interface
[0276]In human IgG1, the non-covalent interaction between the CH3 domains involves 16 residues located on four anti-parallel β-strands that make intermolecular contacts and burry 1090 Å2 from each surface (Deisenhofer, J.; Biochemistry, 1981. 20(9): p. 2361-70). Alanine scanning mutagenesis showed that stabilization of the IgG1 CH3-CH3 interaction was largely mediated by 6 of these residues, including K409 (Dall'Acqua, W., et al.; Biochemistry, 1998. 37(26): p. 9266-73). To get a better understanding of the role of K409 in the IgG1 CH3-CH3 interaction, the 1.65 Å 1 L6X crystal structure (Idusogie, E. E., et al.; J Immunol, 2000. 164(8): p. 4178-84) was studied in more detail using the Brugel modelling package (Delhaise, P., et al., J. Mol. Graph., 1984. 2(4): p. 103-106).
[0277]In order to propose mutations that should lead to a desired stabilization (or destabilization) of IgG4, a quantitative structure-based scoring methodology was employed (...
example 2
Water Hypothesis
[0278]In the IgG1 structure, K409 forms a hydrogen bond with D399′ on the opposite CH3 domain. Furthermore, K409 is part of a water-binding pocket together with S364 and T411 in the same CH3 domain and K370′ on the opposite CH3 domain. The presence of the water molecule prevents an electrostatic clash between K409 and K370′.
[0279]The K409R substitution (as in IgG4) was modelled in the 1 L6X structure by optimizing the side chain conformations of the arginine residue and its surrounding residues, using the FASTER algorithm (Desmet, J., et al.; Proteins, 2002. 48(1): p. 31-43). In this model, the guanidinium group of R409 takes up the position of the water molecule and causes an electrostatic clash with K370′. The side-chains of T411 and K370′ loose their interactions compared to the case with water present (as in IgG1), but D399 keeps its interaction with the side chain at position R409.
example 3
Destabilization of IgG4
[0280]The mutations in the Table below were made in order to destabilize the CH3-CH3 interaction of an IgG4.
[0281]KABAT indicates amino acid numbering according to Kabat (Kabat et al., Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th Ed. Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md. (1991). EU index indicates amino acid numbering according to EU index as outlined in Kabat et al., Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th Ed. Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md. (1991)).
Numbering of CH3 mutationsKABATEU index G4SEQ ID NO: 4370Y349R*Y217R*372L351N*L219N*372L351Q*L219Q*378E357AE225A378E357T*E225T*378E357V*E225V*378E357I*E225I*387S364R*S232R*387S364K*S232K*389T366AT234A389T366R*T234R*389T366K*T234K*389T366N*T234N*391L368AL236A391L368VL236V391L368E*L236E*391L368G*L236G*391L368S*L236S*391L368T*L236T*393K370AK238A393K370R*K238R*393K370TK238T427D399AD267A427D399T*D267T*427D399S*D267S*436F405AF273A436F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com