Drilling fluid additives and fracturing fluid additives containing cellulose nanofibers and/or nanocrystals
a technology of fracturing fluid and additives, which is applied in the field of nanocellulose, can solve the problems of fiber and particle damage, high energy consumption, and high energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
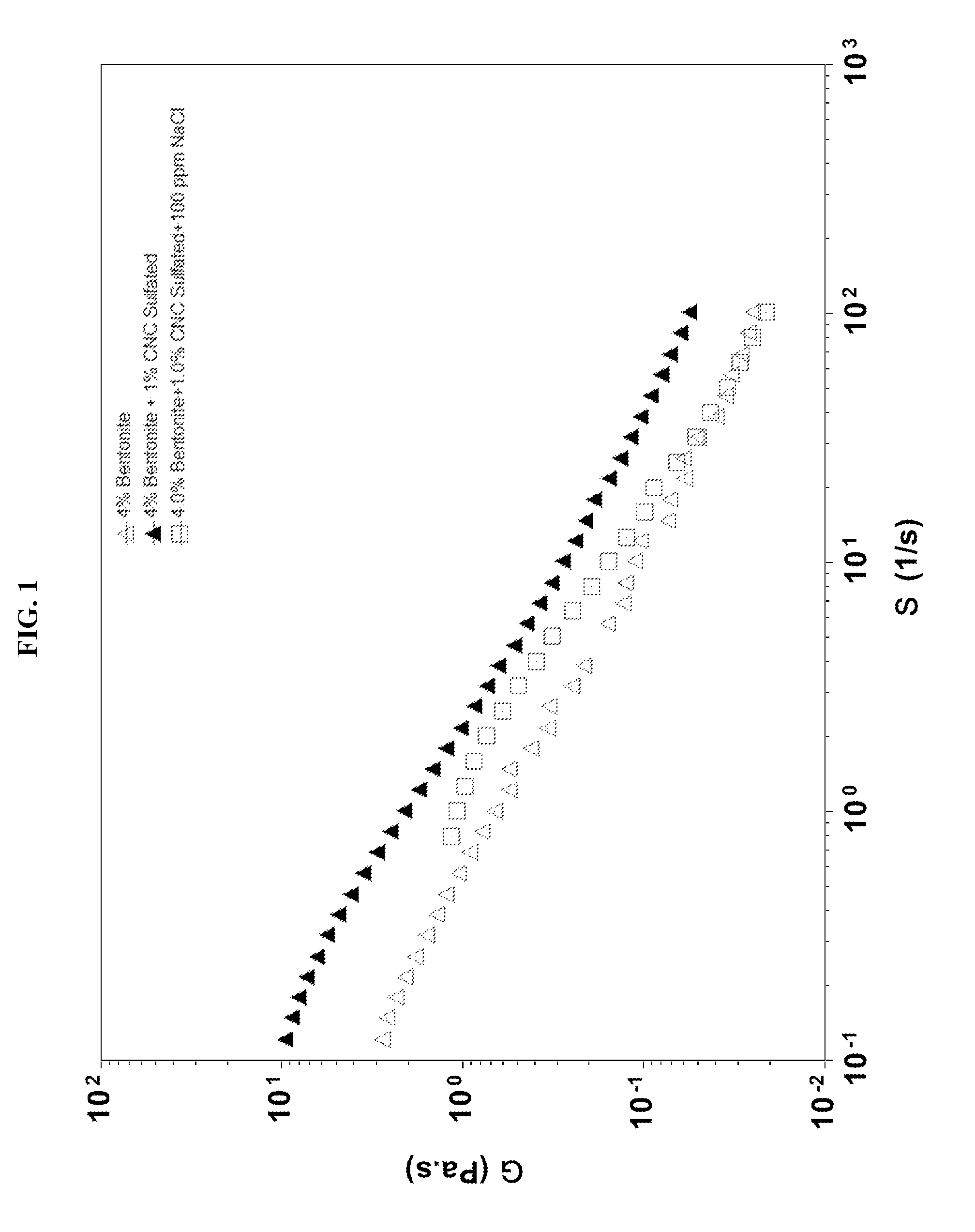
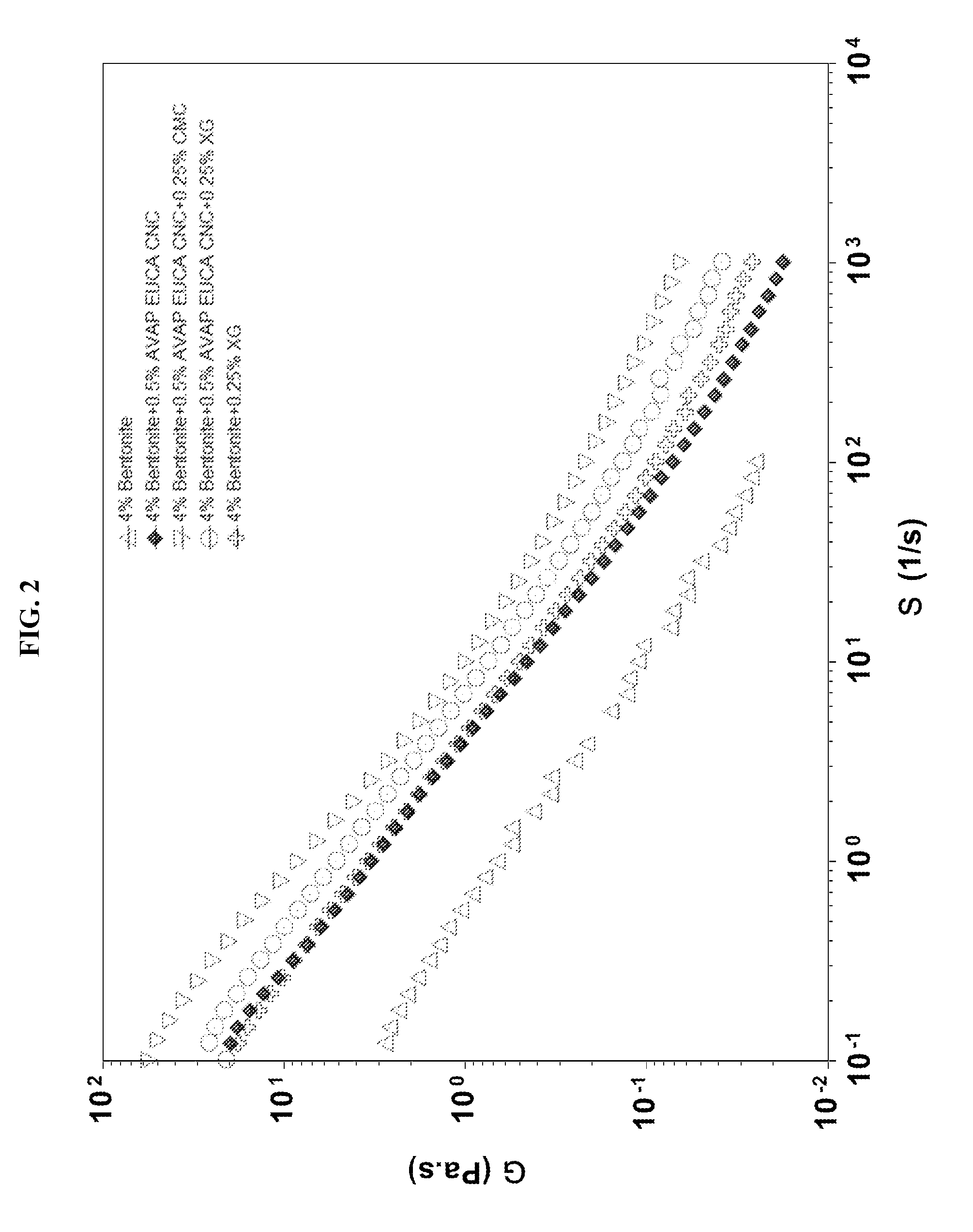
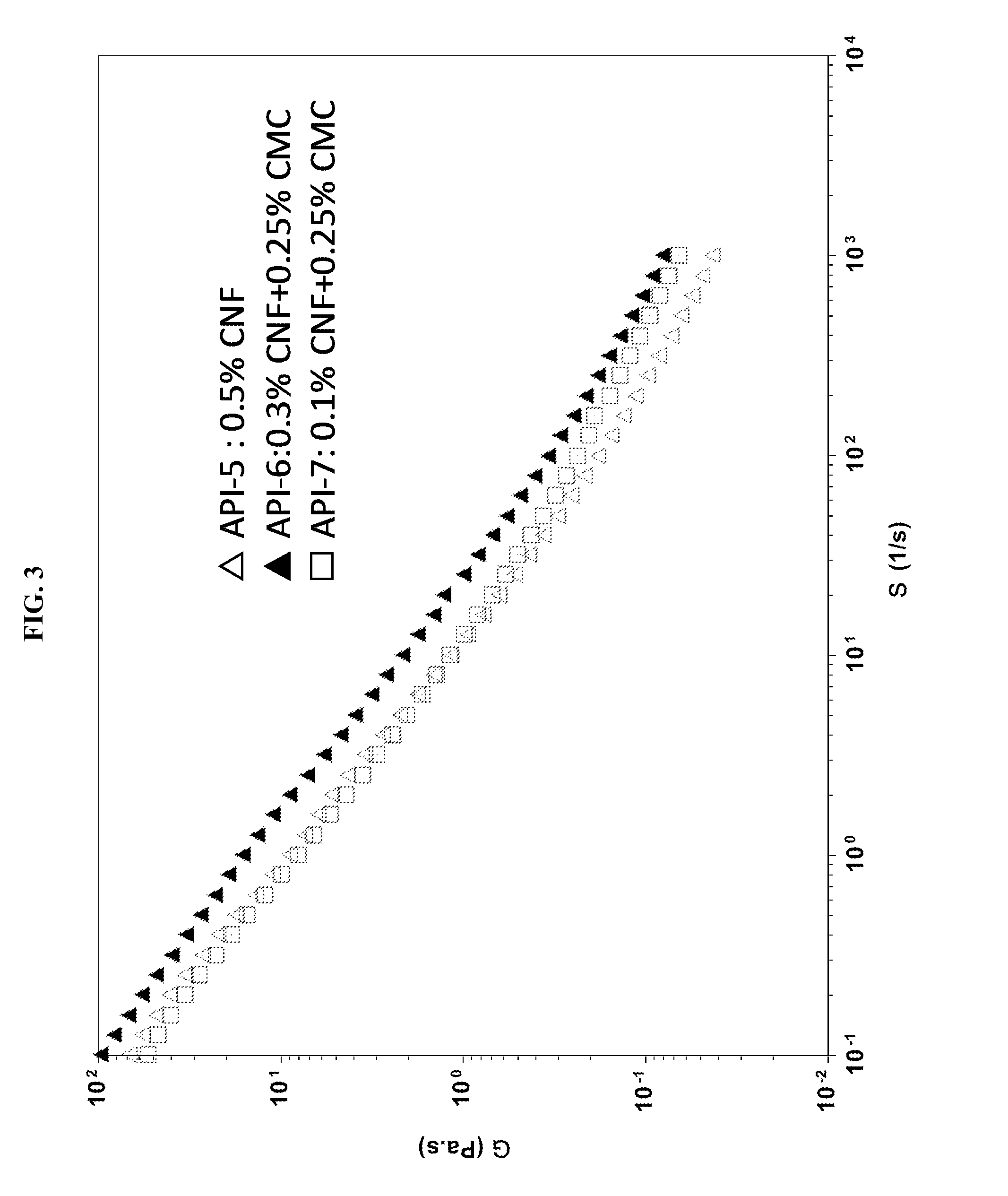
[0325]Colloidal suspensions are used in wide range of applications such as paints, coatings, cosmetics, ceramics, pharmaceutical formulations, food and household products. Addition of polymers to colloidal suspensions is a common practice to obtain the desired flow properties of such materials. Physical adsorption of polymers at the particle interface stabilizes or destabilizes colloidal suspensions. In addition, non-adsorbing polymers can also cause flocculation and / or phase separation. For the micron-size particles, polymer interactions have been studied extensively both experimentally and theoretically during the last three decades. While the nanoparticle-polymer mixtures are believed to start to play major roles in different fields, including drilling fluids and other oil field formulations, polymer-CNC and polymer-CNF interactions in aqueous solutions and their potential applications have not been exploited.
[0326]Drilling fluids have to meet multi-functional performance require...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com