Carbon monoxide releasing molecules and uses thereof
a carbon monoxide and releasing molecule technology, applied in the direction of biocide, organic chemistry, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective carbon monoxide delivery to therapeutic targets by inhalation, inability to achieve clinical application, and high dose requirements for delivering carbon monoxide to therapeutic targets in diseased tissues. likely to be associated with adverse effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Mo Complexes
Synthesis of Mo(CO)3(η6-C7H8)
[0232]The preparation of the molybdenum tri-CO complex Mo(CO)3(η6-C7H8) is described in the literature (see, e.g., W. A. Herrmann and A. Salzer, Synthetic Methods of Organometallic and Inorganic Chemistry, volume 1, Georg Thieme Verlag, New York, 1996, p 129; and Abel et al., J. Chem. Soc. (1958) 4559).
Preparation of Tricarbonyl[tris(isocyanoacetic acid)]Mo(0) (1-b)
[0233]
[0234]Preparation of tricarbonyl[tris(isocyanoacetic acid ethyl ester)]Mo(O) (1-a): Mo(CO)3(η6-C7H8) (2.1 g; 7.72 mmol; 272.1117 g / mol) was dissolved in 40 mL of MeOH to give a red, slightly turbid solution. CNCH2CO2Et (3 eq.; 2.53 mL; 23.15 mmol; 113.11 g / mol; 1.035 g / mL) was dissolved in 20 mL MeOH and added to the previous solution. The red solution immediately turned darker, greenish, and gradually became lighter. The solution was stirred at room temperature for 45 min, when a TLC analysis (hexane:ethyl acetate 1:3) showed that (Mo(CO)3(η6-C7H8)) had been c...
example 2
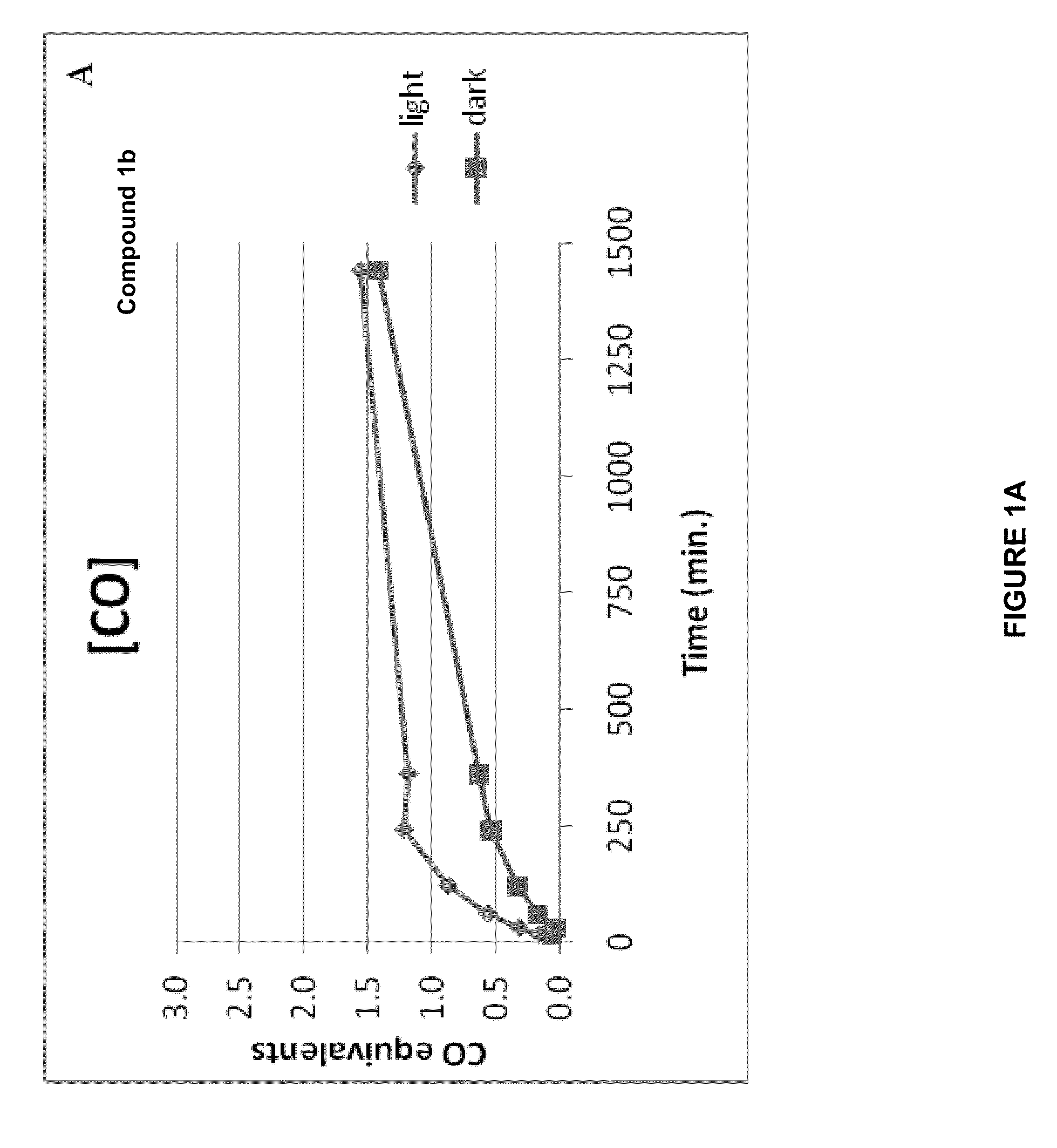
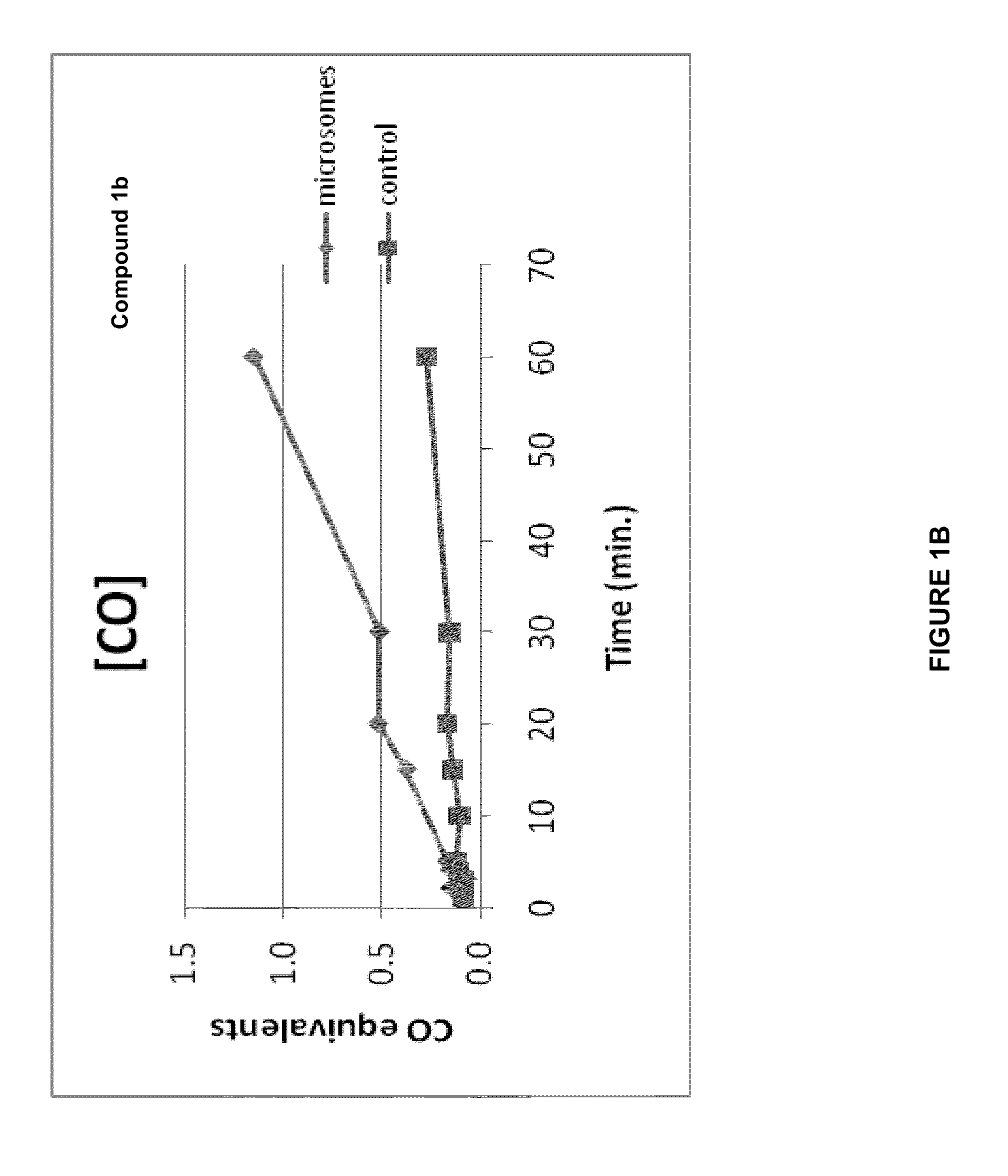
CO-Release Kinetics
[0275]The CO release kinetics of Compounds 1b, 2b, 3b, 4b, and 5b was performed in vitro in HEPES buffer (pH 7.4) or in phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) and in the presence of liver microsomes. The quantization of the released CO was performed according to Vreman et al. Anal. Biochem. (2005) 341: 280-289 using a Gas Chromatograph with a Reducing Compound Photometer detector (GC-RCP; Peak Laboratories, Mountain View, Calif.), which allows quantifying CO in gas mixtures at concentrations as low as 1-2 parts per billion (ppb).
General Method for the Determination of CO Release in HEPES Buffer
[0276]The CO release kinetics of all compounds was evaluated in 50 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.4) in a sealed 8-mL vial. Stock solutions (5 mM) of the compounds were prepared in PBS buffer (each compound was soluble in PBS after the addition of 3 equivalents of NaOH) and 10 μL were added to 990 μL of 50 mM HEPES buffer (final concentration in buffer was 50 μM). Since light activation can relea...
example 3
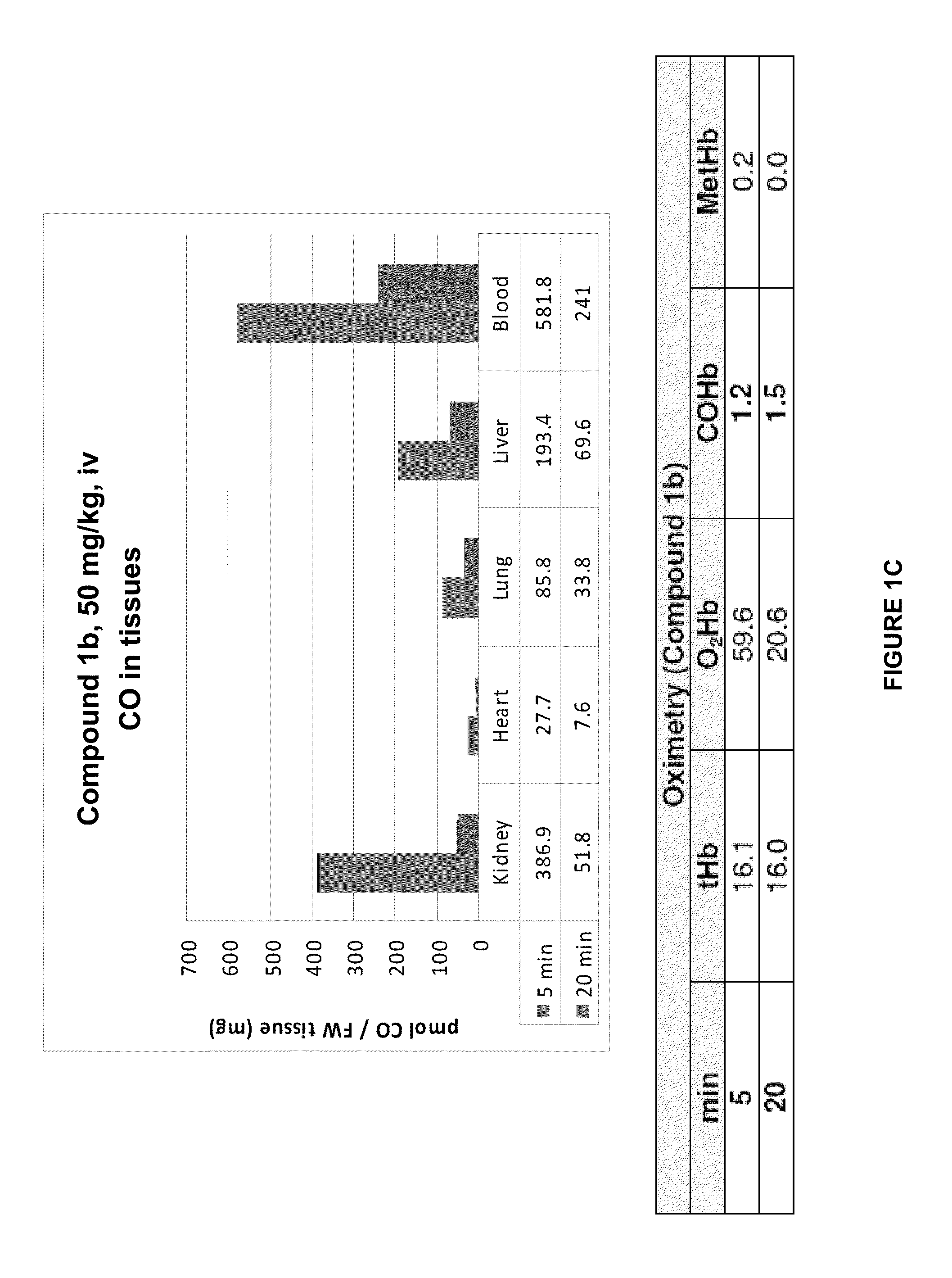
Accumulation of Carbon Monoxide (CO) in Tissues after Administration of Carbon-Monoxide Releasing Molecule
[0298]Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CO-RMs) are carriers of carbon monoxide (CO) and can release CO in vivo. CO can bind to hemoglobin in the blood and to various heme proteins in cells. Vreman et al. Anal Biochem 341:280-289 describes a method to release CO bound to tissues into the gas phase, and quantify it using GC-RCP chromatography. We applied this methodology to assay CO in various tissues of mice treated with CO-RMs (see Example 2, herein). However, since the CO release method of Vreman (in vitro incubation with sulfosalicylic acid) also releases CO from the CO-RM, the CO released from tissue samples represents CO bound to tissue proteins and CO from CO-RM compound accumulated in tissue. For CO-RM compounds with slow CO release rates in vivo, the CO measured at the earliest sampling point (5 min after CO-RM administration) may therefore mostly be a measure for the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com