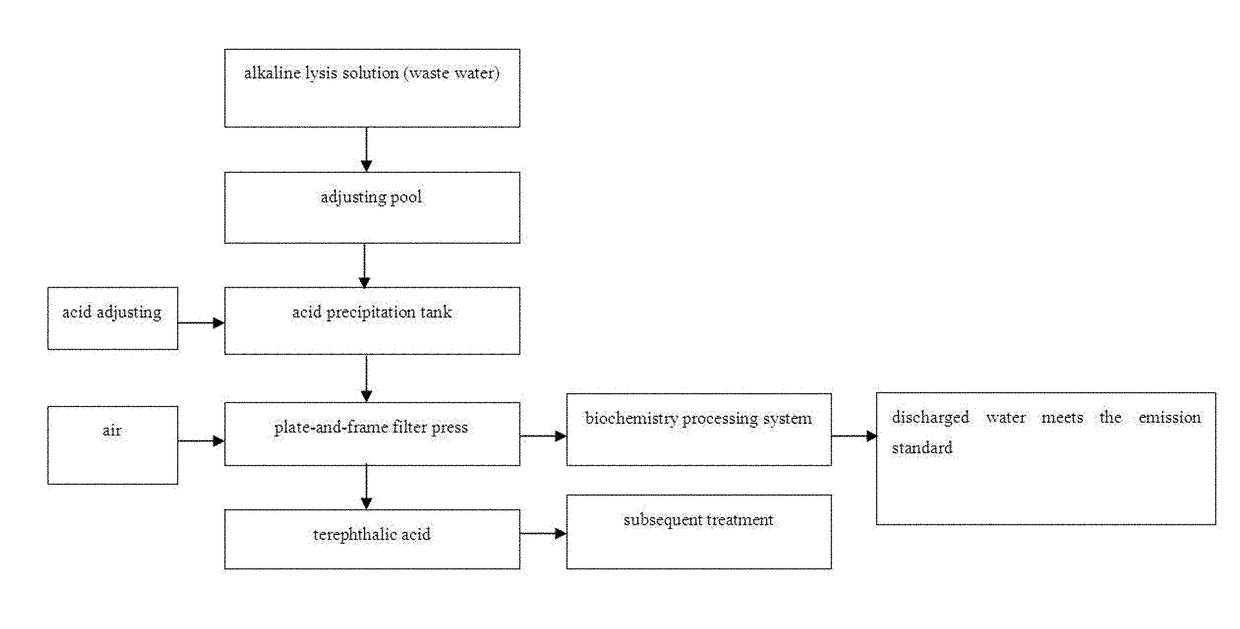
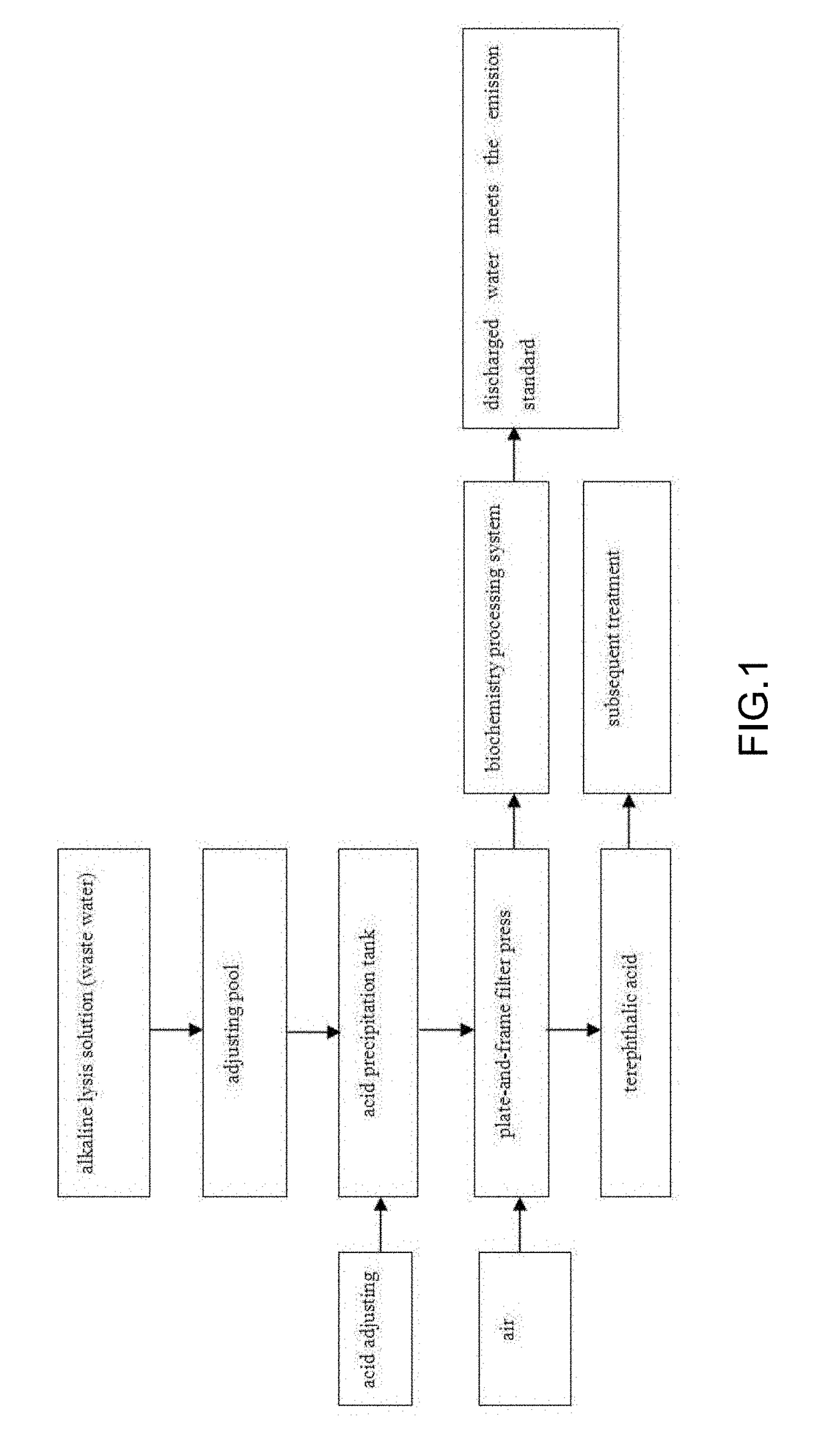
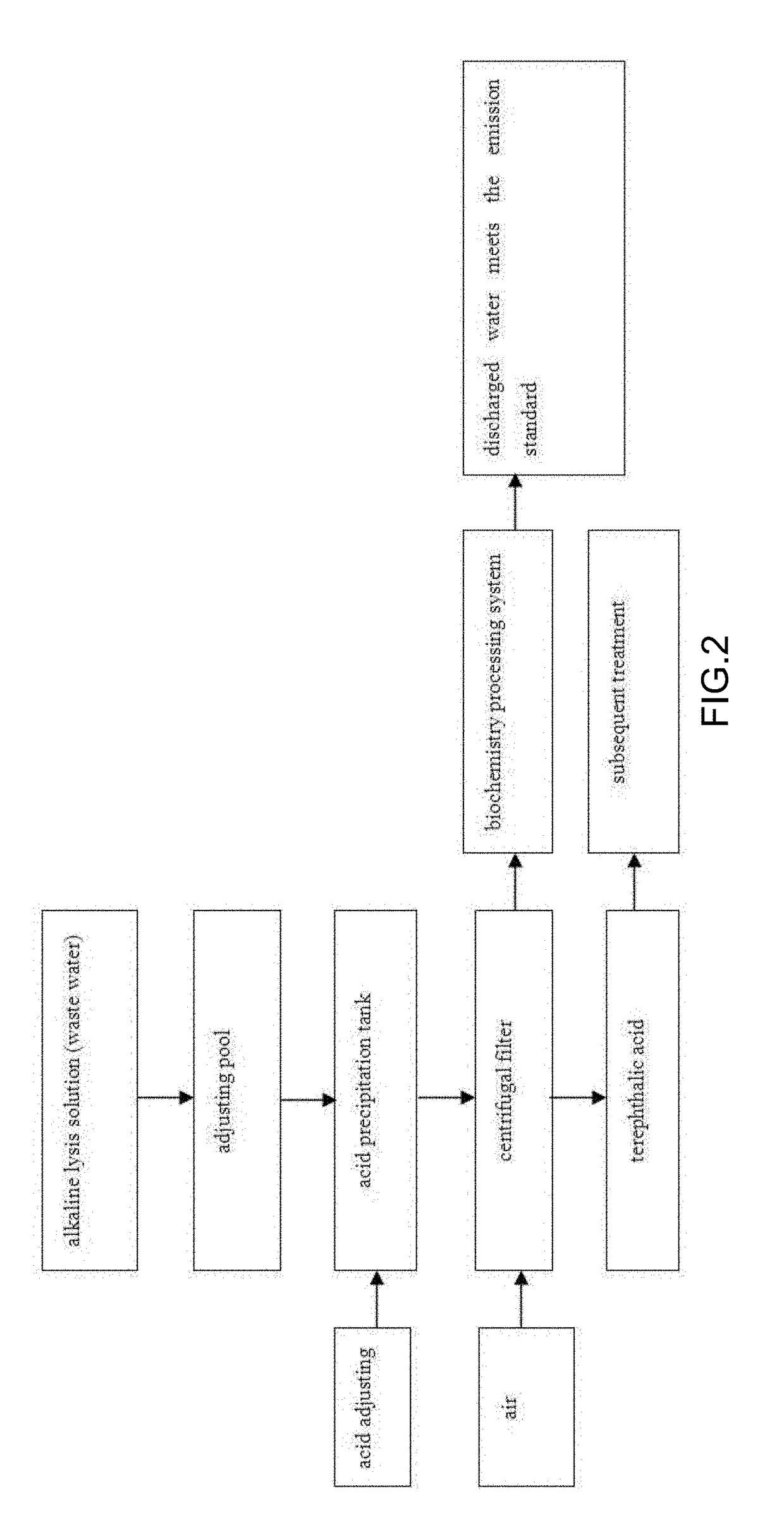
Method for Preparing Untwisted, Hollow, High-Count Textiles and Method for Recovering the Solute in an Alkaline Lysis Solution
a technology of alkali lysis and textiles, which is applied in the field of textiles, can solve the problems of difficult degradation, disadvantage for the environment, and high cost of pva fiber, and achieve the effects of easy alkaline soluble and degradabl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0030]The method for preparing untwisted textiles comprises the following steps:
[0031]a. preparing an alkaline degradable slice: during the polymerization of polyester raw materials, 5-sodium sulfonate-isophthalate polyethylene glycol ester containing totally 5 wt % of polymers and isophthalate containing totally 5 wt % of polymers were added, the obtained mixture was stirred and heated to 230° C., so as to form a slurry; the obtained mixture was transformed into a reactor, meanwhile adding polyethylene glycol containing 5 wt % of polymers, so as to dilute and cool the mixture to 210° C.; sequentially polyethylene glycol having molecular weight of 6000 was added into the reactor for the period of 50 min under stirring, wherein the amount of polyethylene glycol was 5% of the total weight of the polymers; under atmosphere, the mixture was heated up to 230° C. such that the mixed raw materials were polymerized under vacuum; finally, the polymerized alkaline degradable slice successivel...
example 2
[0037]The method for preparing hollow textiles comprises the following steps:
[0038]a. preparing an alkaline degradable slice: during the polymerization of polyester raw materials, 5-sodium sulfonate-isophthalate polyethylene glycol ester containing totally 4 wt % of polymers and isophthalate containing totally 3 wt % of polymers were added, the obtained mixture was stirred and heated to 230° C., so as to form a slurry; the obtained mixture was transformed into a reactor, meanwhile adding polyethylene glycol containing 5 wt % of polymers, so as to dilute and cool the mixture to 210° C.; sequentially polyethylene glycol having molecular weight of 6000 was added into the reactor for the period of 50 min under stirring, wherein the amount of polyethylene glycol was 3% of the total weight of the polymers; under atmosphere, the mixture was heated up to 230° C. such that the mixed raw materials were polymerized under vacuum; finally, the polymerized alkaline degradable slice successively w...
example 3
[0050]The method for preparing a high-count textiles comprises the following steps:
[0051]a. preparing an alkaline degradable slice: during the polymerization of polyester raw materials, 5-sodium sulfonate-isophthalate polyethylene glycol ester containing totally 3 wt % of polymers and isophthalate containing totally 4 wt % of polymers were added, the obtained mixture was stirred and heated to 230° C., so as to form a slurry; the obtained mixture was transformed into a reactor, meanwhile adding polyethylene glycol containing 3 wt % of polymers, so as to dilute and cool the mixture to 210° C.; sequentially polyethylene glycol having molecular weight of 6000 was added into the reactor for the period of 50 min under stirring, wherein the amount of polyethylene glycol was 2% of the total weight of the polymers; under atmosphere, the mixture was heated up to 230° C. such that the mixed raw materials were polymerized under vacuum; finally, the polymerized alkaline degradable slice successi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| break elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| break elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com