Method for generating design constraints for modules in a hierarchical integrated circuit design system
a hierarchical integrated circuit and design system technology, applied in the direction of cad circuit design, program control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of system not being able to complete the implementation of some blocks according to their specifications, prohibitive execution time for designing or simulating the entire design, and the size of the design normally increases the execution time of ecad softwar
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
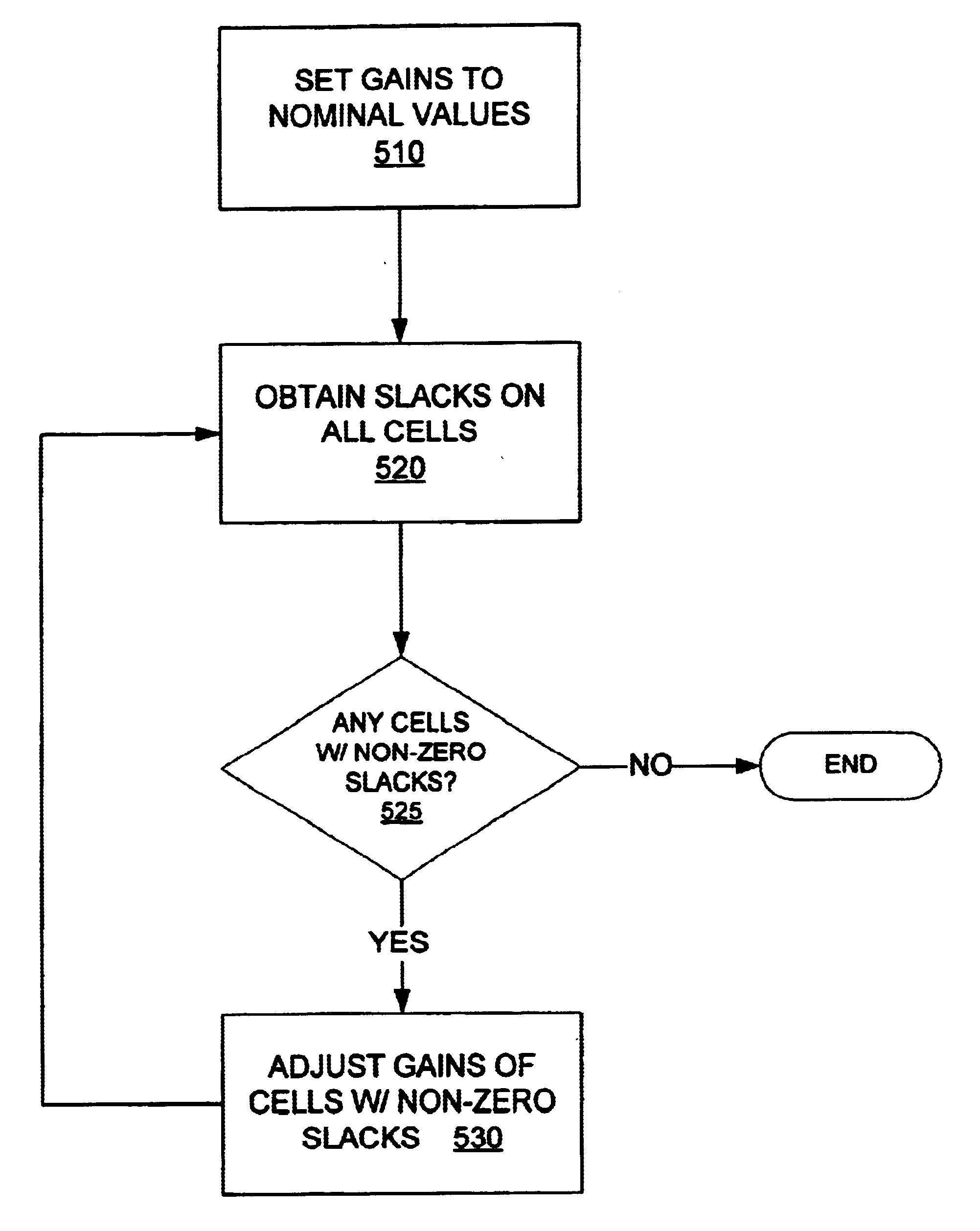
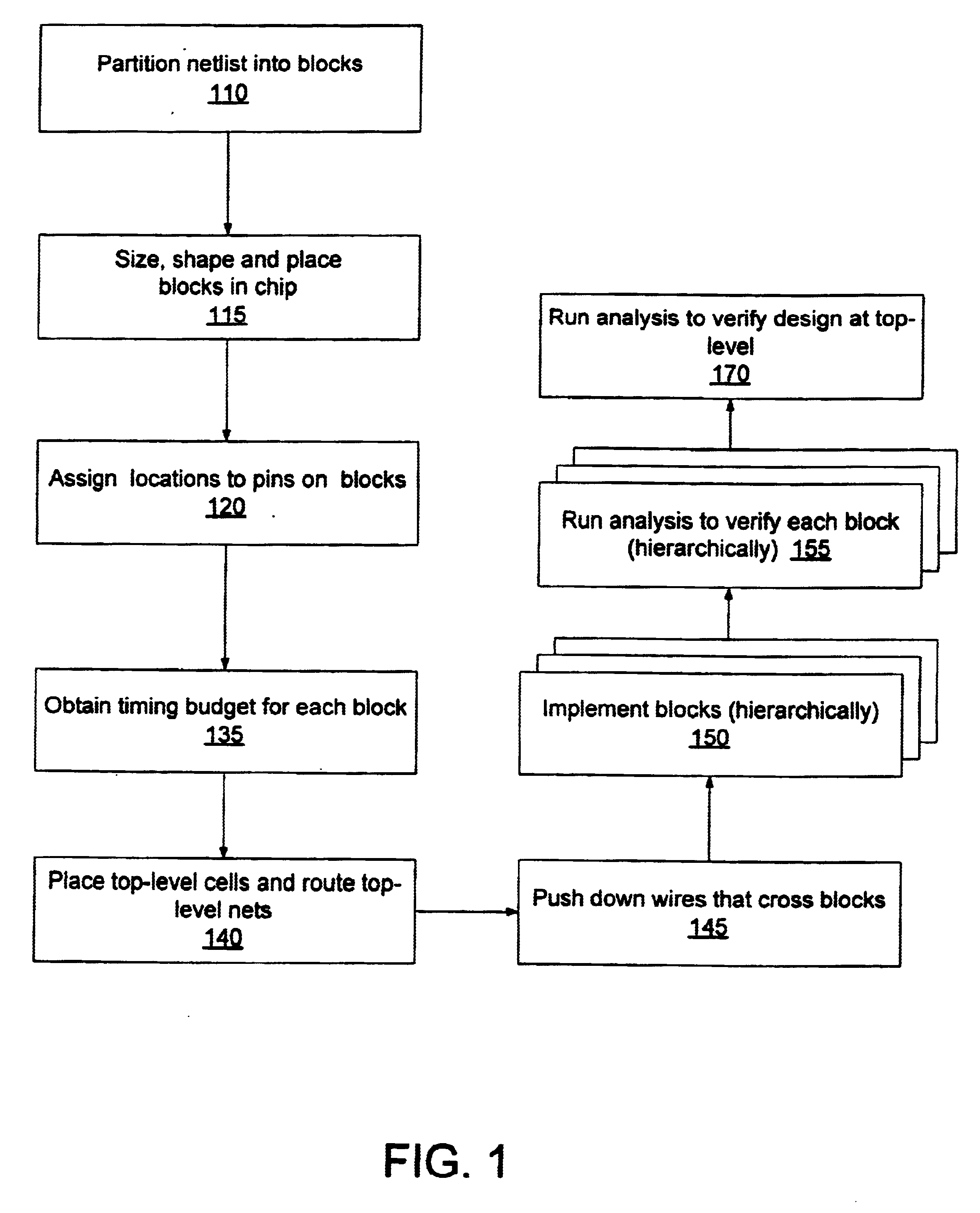
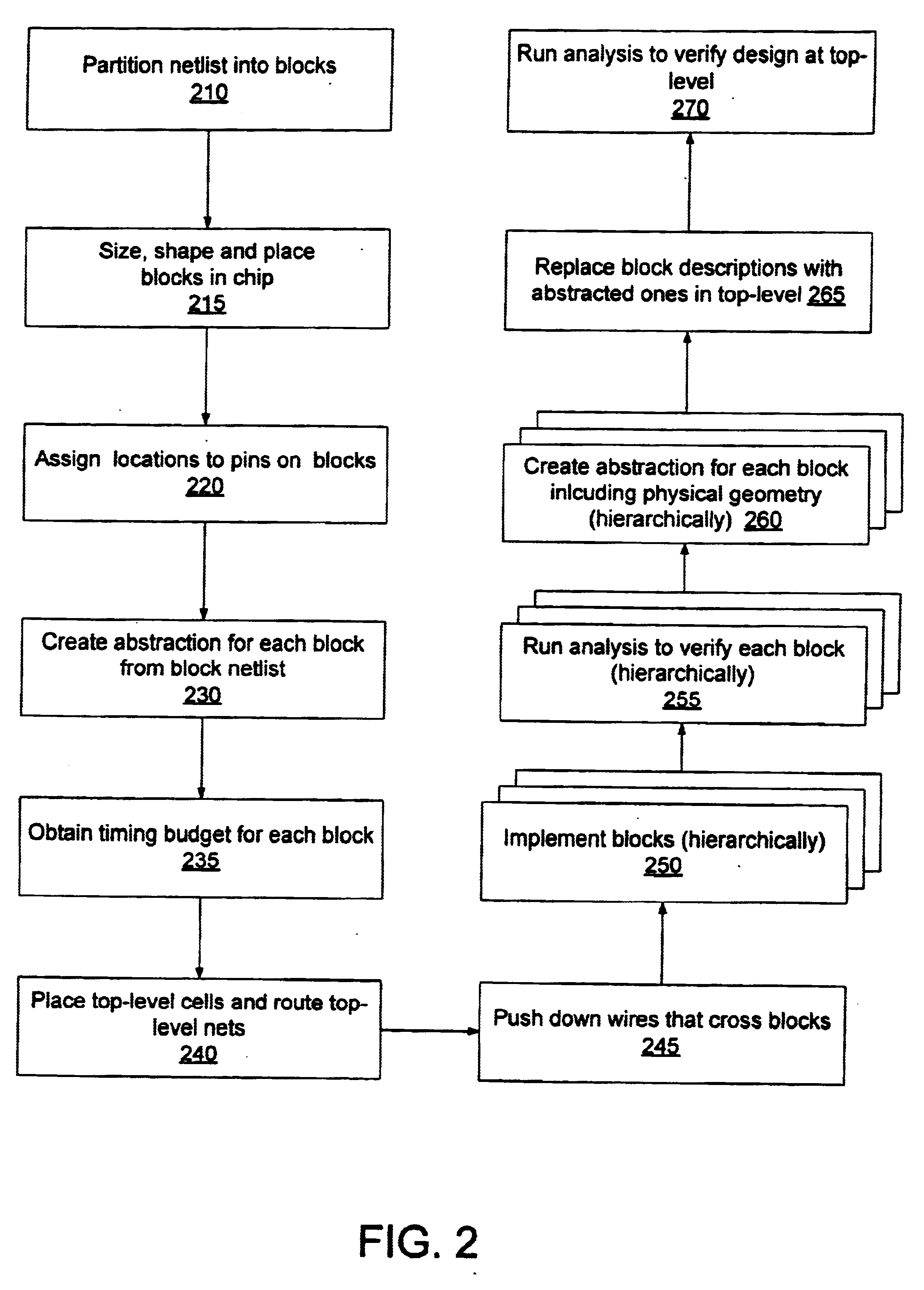
One way of implementing the top-down hierarchical design process is the hierarchical design flow shown and described in FIG. 2. The design flow shown in FIG. 2 is a refinement of the top-down flow shown in FIG. 1, with three additional steps, 230, 260, and 265. The refinement concerns a method for modeling a sub-block, in the context of its parent and sibling blocks, during the top-down budgeting and block implementation steps, as well as the bottom-up verification steps. These steps represent places in the flow at which the clean hierarchical boundaries are violated and there is a need for cross-boundary analysis. Without an effective technique for managing this cross-boundary analysis the primary advantage of the hierarchical design process—its ability to reduce the memory and runtime required to design a large integrated circuit-may be lost.
During the top-down budgeting step one objective is to analyze the combinational logic paths (combinational logic gates between registers (la...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com