File system including non-volatile semiconductor memory device having a plurality of banks
a non-volatile semiconductor and memory device technology, applied in the field of file systems, can solve the problems of lowering operation speed, requiring large amount of time, and certain limits for erasures, and achieve the effect of high speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
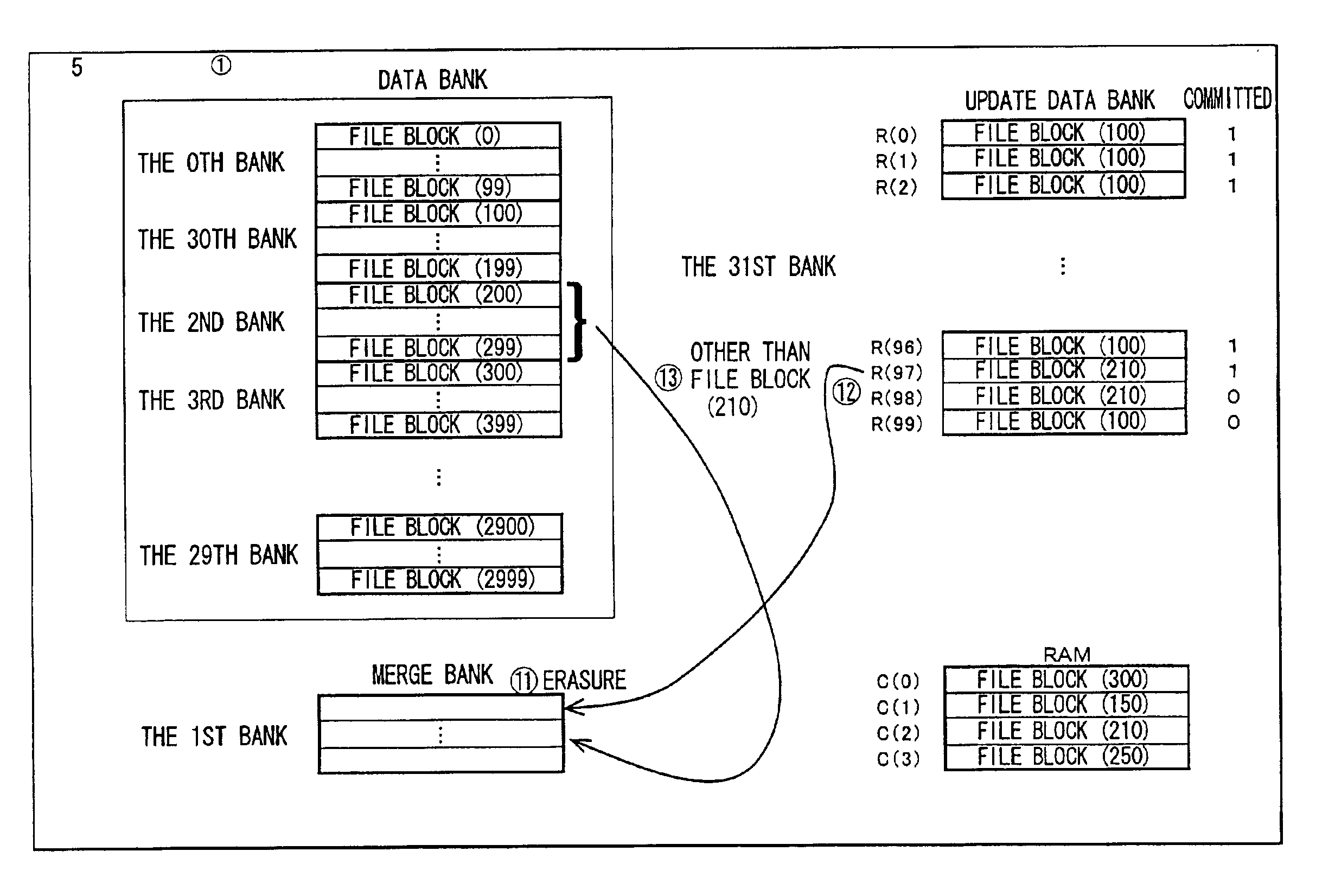
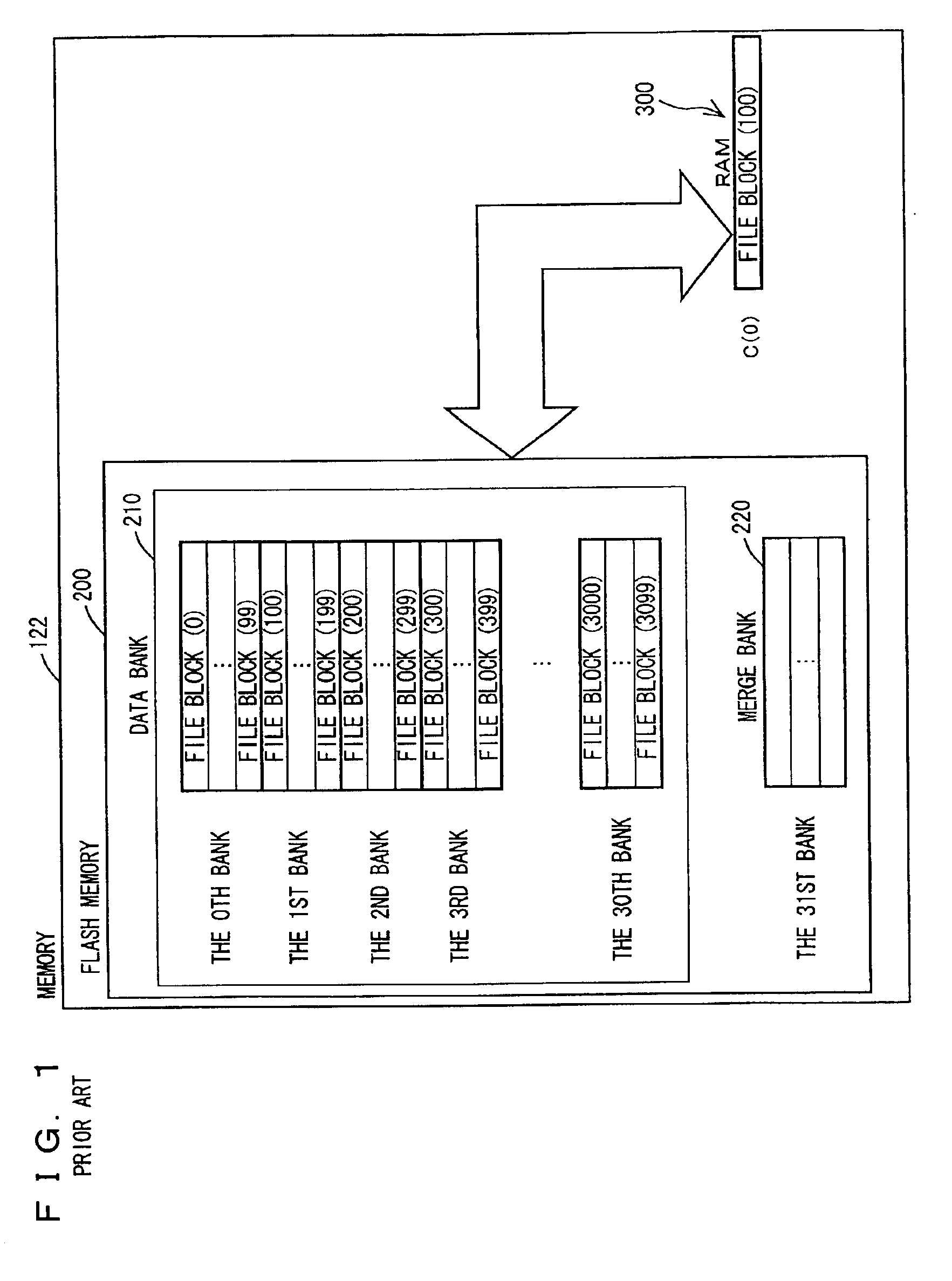
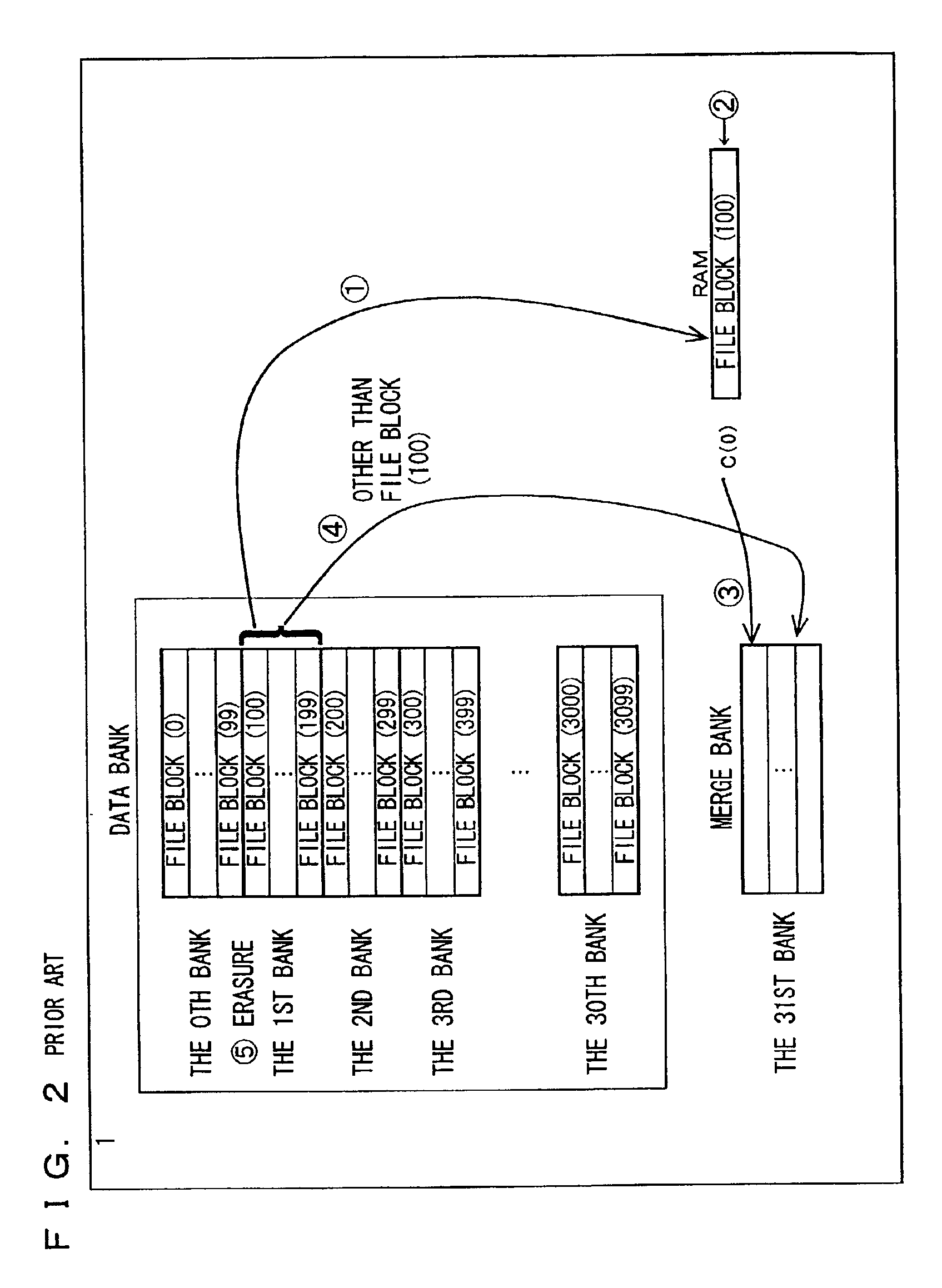
A file system according to the present embodiment involves file control of a non-volatile ROM (a flash memory) that is erasable bank by bank. The file system is used for, in particular, equipment in which a flash memory is mounted for the purpose of rewriting data more than once, e.g., portable equipment such as a mobile phone, a PDA and a digital still camera.
FIG. 7 shows the configuration of a portable equipment 1020 in the form of a block diagram. As shown in FIG. 7, portable equipment 1020 includes a CPU (Central Processing Unit) 1200, a memory 1220, an entry key 1100, and a liquid crystal monitor 1040 that are interconnected via a bus. A program for controlling the file system according to the present embodiment is pre-stored in a non-volatile memory portion (a flash memory) of memory 1220. The hardware itself in the portable equipment shown in FIG. 7 is a typical one. Thus, the essential part of the present invention is the file system implemented by a program stored in a stor...
second embodiment
The file system according to the present embodiment executes a writing process different from that in the first embodiment described above. The other parts of the hardware configuration and the flow charts except for the process steps described below are similar to those in the first embodiment described above. Therefore, detailed description thereof will not be repeated here.
Referring to FIGS. 26A and 26B, the control structure of the writing process executed in the file system according to the present embodiment is described. It is noted that the process steps in FIGS. 26A and 26B that are the same as the ones in FIGS. 12A and 12B are denoted by the same step numbers. The processes thereof are also the same. Therefore, detailed description thereof will not be repeated here.
At S2000, after initializing variable I, CPU 1200 resets a cache full flag. At S2002, if there is no free space in cache area 3100 of RAM 3000, CPU 1200 sets the cache full flag. Thereafter, the copy_cache_to_ba...
third embodiment
The file system according to the present embodiment is implemented using an SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) having a backup power-supply for update data bank 2300 in the first embodiment. Referring to FIG. 31, the internal structure of the memory in the file system according to the present embodiment is descried. As shown in FIG. 31, the memory in the file system according to the present embodiment includes a flash memory 2101 constituted by data bank 2100 and merge bank 2200, and an SRAM2301 constituted by an update data bank. The configuration of the other parts and the flow charts except for the process steps described below are the same as those in the first embodiment described earlier. Therefore, detailed description thereof will not be repeated here.
As the file system according to the present embodiment is implemented using the SRAM as an update data bank, there is no limit for data writing to the update data bank, compared to the case where a flash memory is used for the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com