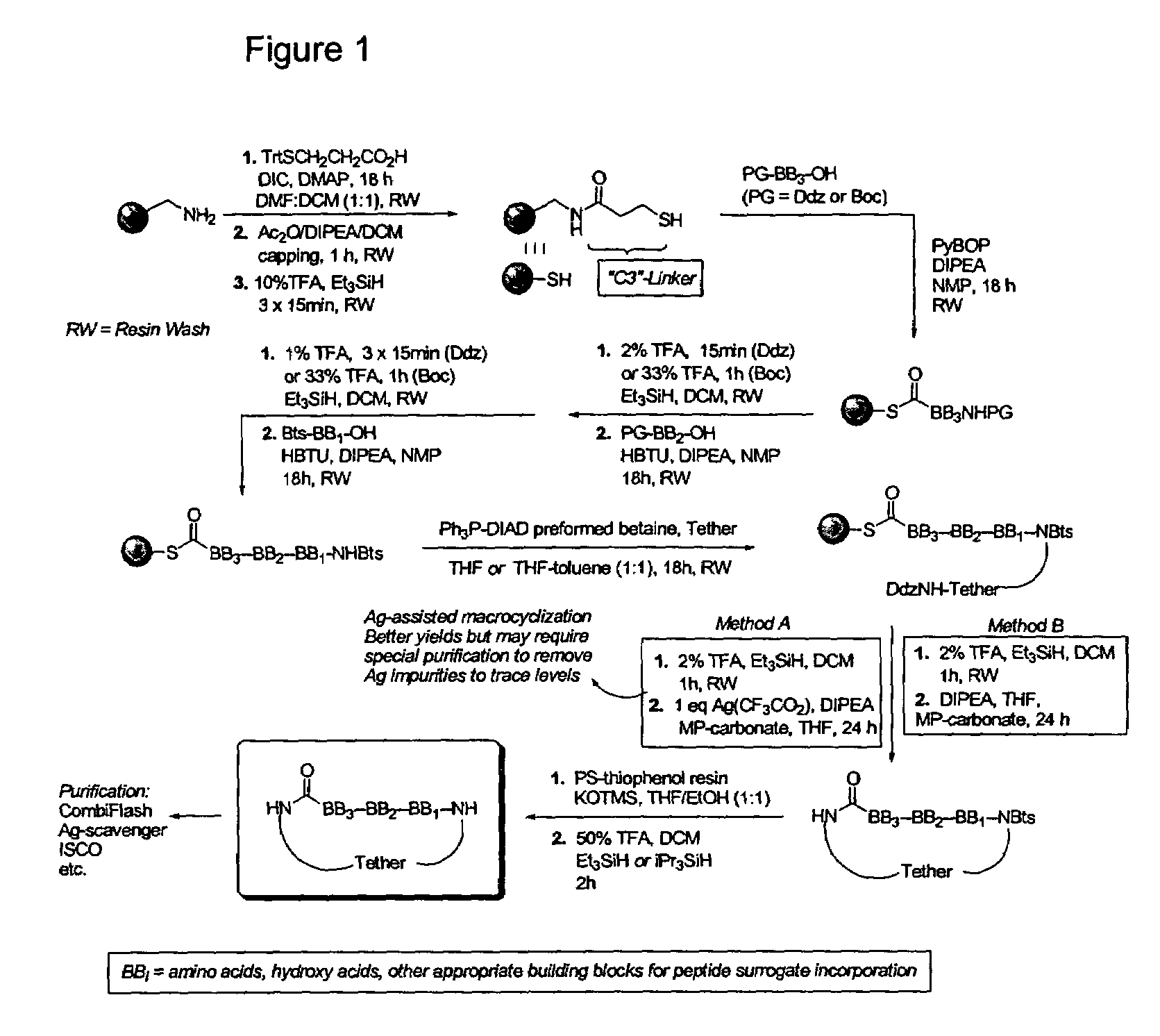
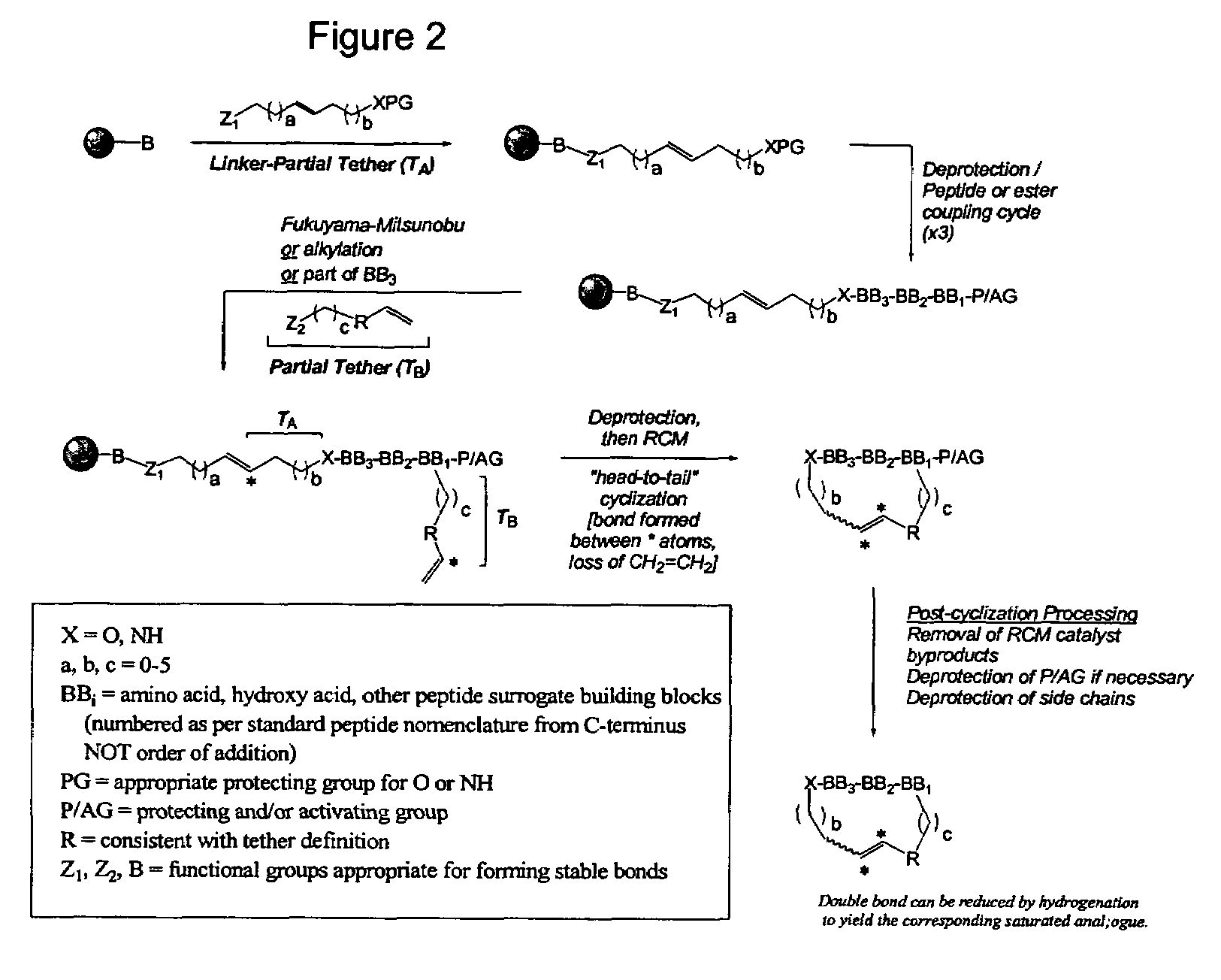
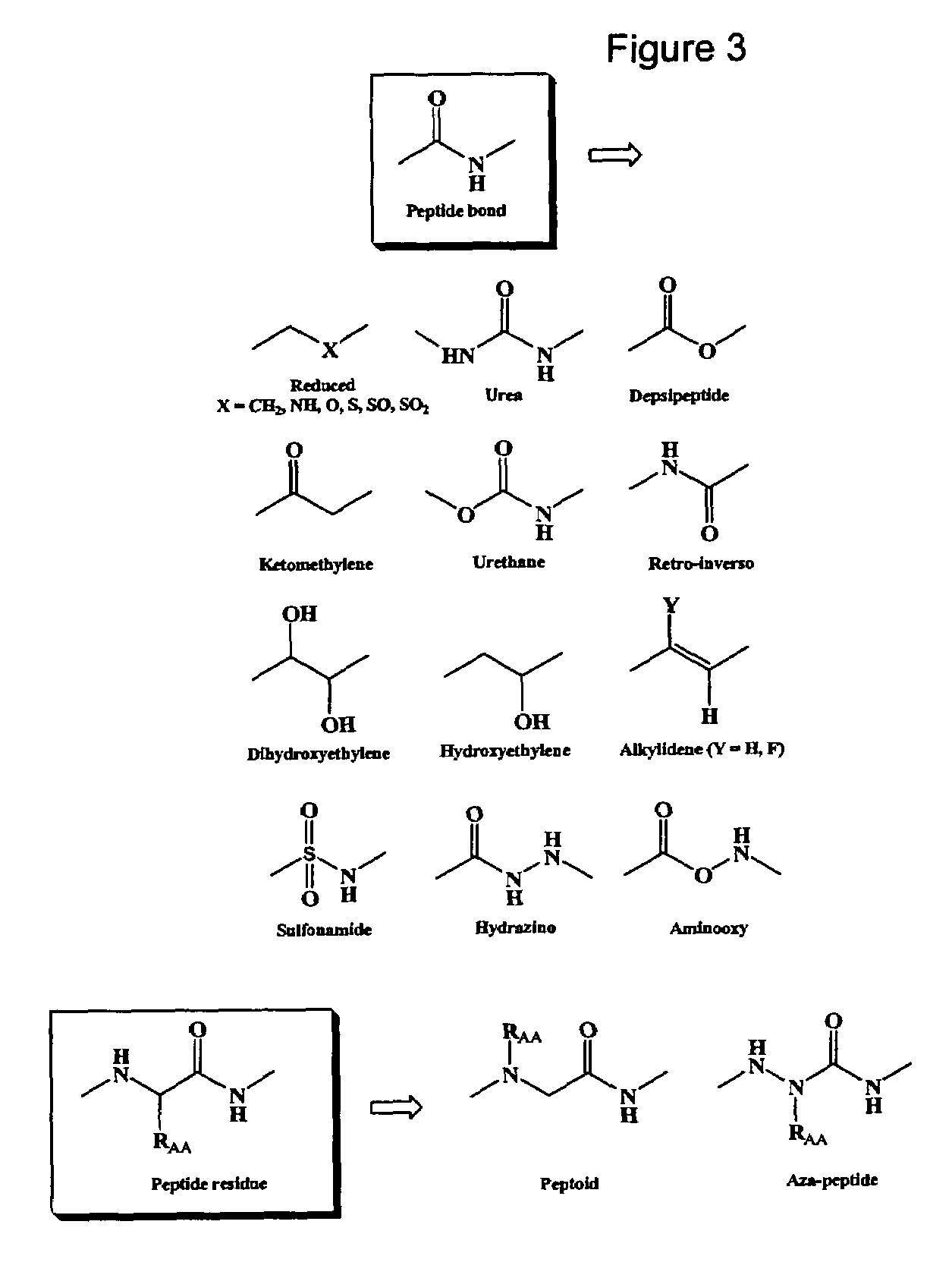
Spatially-defined macrocycles incorporating peptide bond surrogates
a macrocyclic compound and peptide technology, applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, drug compositions, metabolic disorders, etc., can solve the problems of long experimentation and long time required to control the conformation within a single cyclic molecule, and the usual limitations of direct use of peptides in new materials,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Representative Synthesis of Macrocyclic Compound of Formula I containing Peptide Surrogate S6
[0160]The synthetic scheme is presented as FIG. 4(a). Starting from polystyrene trityl resin containing the linker shown (1-0), initial standard Fmoc deprotection of the linker furnished 1-1. This was then coupled with Fmoc Nva-OH under standard conditions. Loading of the resin based upon quantitative analysis of a cleaved aliquot at this stage was 62%. After Fmoc cleavage using standard conditions followed by coupling with Fmoc-(D)Val-OH under standard condition, 1-2 was obtained. After Fmoc group deprotection, reductive alkylation with Fmoc-(D)Tyr(OtBu)-CHO 1-3 was carried out as described in Step 1-d.
Step 1-d: Reductive Amination for Introduction of First Building Block
[0161]The following stock solutions were prepared first.[0162]Solution A: 100 mL of 1% AcOH in TMOF (trimethylorthoformate).[0163]Solution B: 100 mL of 1% AcOH in DMF / TMOF / MeOH (1:1:1).
After deprotection of the Fmoc group o...
example 2
Representative Synthesis of Macrocyclic Compound of Formula I Containing Peptide Surrogate S6
[0171]The synthetic scheme is presented as FIG. 4(b). Anchoring of Fmoc-Nva-OH as well as subsequent Fmoc deprotection were performed following standard procedures. The aldehyde 2-2 from Fmoc-(D)Val-OH was prepared in 62% yield using standard methods. Reductive amination was performed as in step 1-d. Cbz protection of the resulting product under the conditions described in step 1-e (repeated 2×) furnished the desired product 2-3.
[0172]Fmoc deprotection, coupling with Bts-(D)Tyr(OtBu)-OH, and Mitsunobu reaction of the resin bound tripeptides surrogate with 2-4 were all carried out under standard conditions to give 2-5. Macrocyclization via RCM with Hoveyda-Grubbs catalyst following the standard procedure furnished the desired product, 2-6. CLND yield: 16.1 mg. Standard deprotection of the Bts group is preferentially performed prior to deprotection of the Cbz group, with simultaneous reduction...
example 4
Representative Synthesis of Macrocyclic Compound of Formula I containing Peptide Surrogate S3
[0185]This synthesis is presented in FIG. 6. The protocol highlights an alternative method to those previously reported for introduction of the peptoid moiety.
[0186]Step 4-a: In a 500 mL solid phase synthesis reactor was suspended 2-chlorotrityl chloride resin (16.5 g, loading 2.0 mmol / g) in DCM (350 mL). The resulting slurry was agitated for 30 min, filtered and washed with DCM (2×350 mL). Separately, a solution of Bts-Gly-OH (13.4 g, 1.5 eq) and DIPEA (17.2 mL, 3.0 eq) in DCM (350 mL) was prepared to form the Bts-Gly salt. This solution of the carboxylate salt was added to the resin mixture and agitated for an additional 2.5 h. The reaction mixture was filtered and the collected resin washed successively with DMF (3×350 mL), 2-propanol (3×350 mL) and DCM (3×350 mL). Finally, any remaining active sites on the resin were neutralized by treatment with a solution of 85 / 10 / 5 DCM / MeOH / DIPEA (350...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| v/v/v | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| v/v/v | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com