Float glass for display substrate and method for producing it
a technology of substrate glass and floating glass, which is applied in the direction of glass rolling apparatus, glass making apparatus, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of unstable production, affecting the life span of production apparatuses, and asymmetrical substrate glass at anterior and posterior, so as to reduce the temperature of each step carried out for producing substrate glass, the effect of stable production and low viscosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Now, the present invention will be described in further detail with reference to Examples. However, the present invention is by no means restricted to such specific Examples.
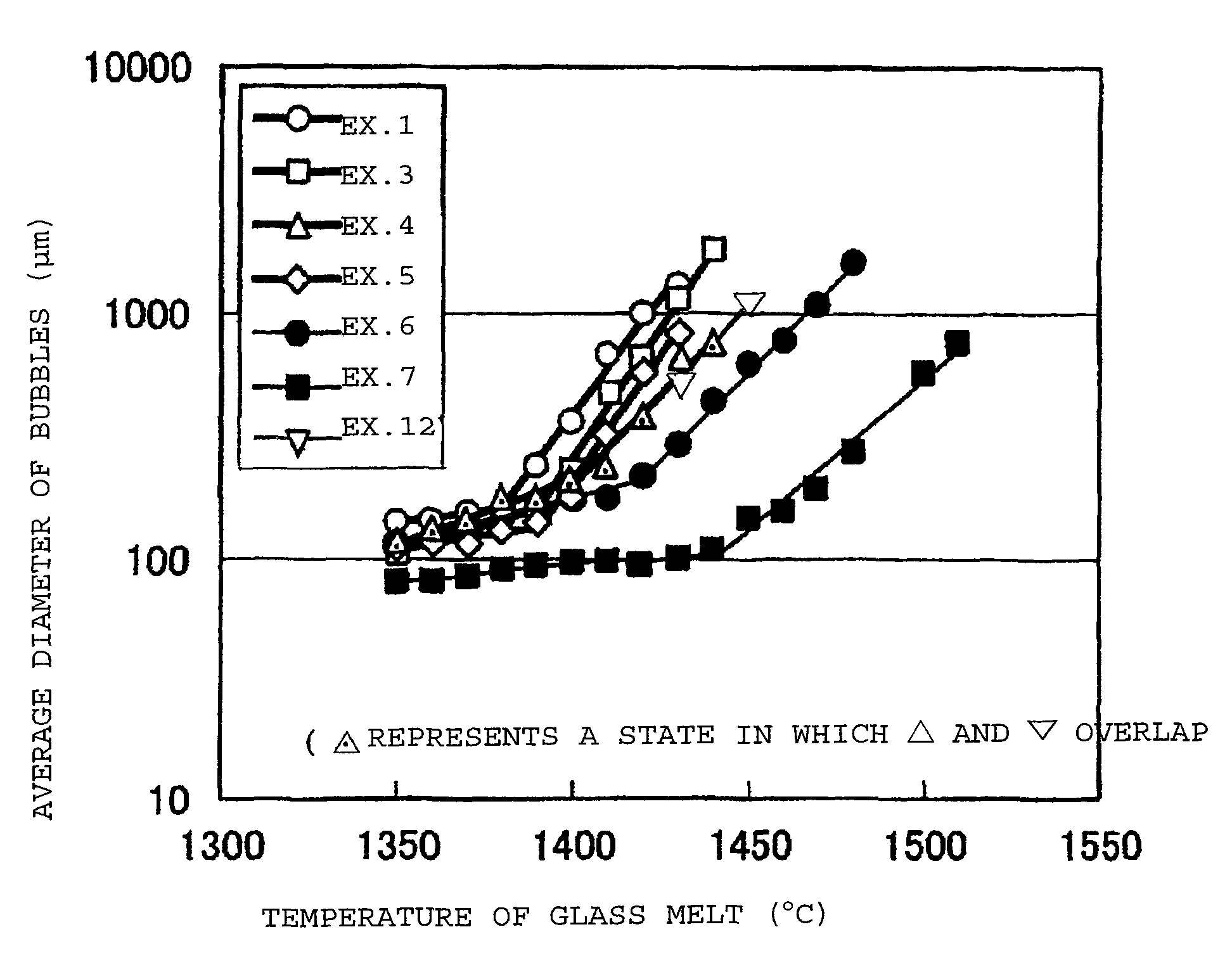
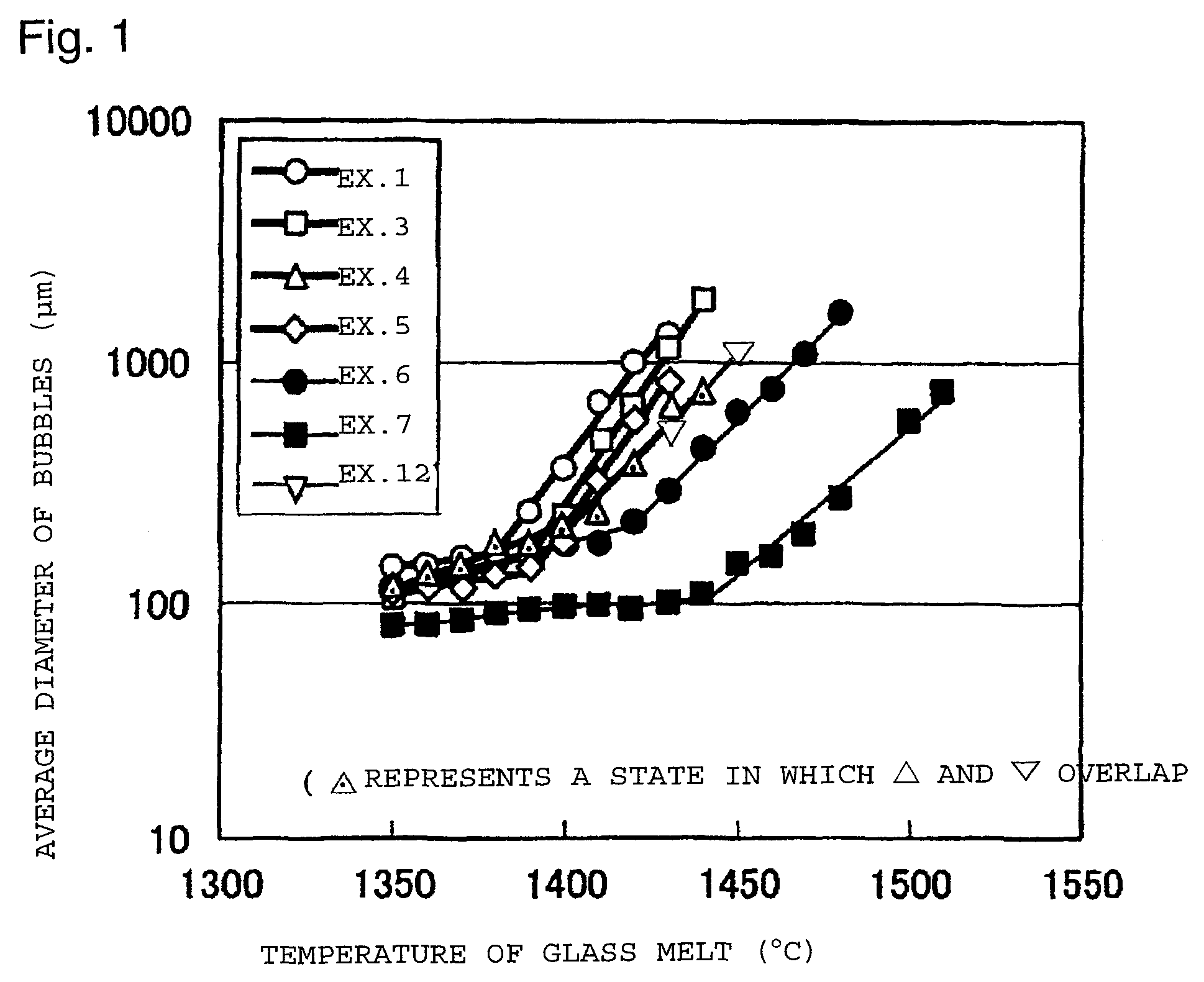
Table 1 shows glass compositions (mass %) of Examples 1 to 5 (Examples of the present invention), Table 2 shows glass compositions of Examples 6 to 11 (Comparative Examples), and Table 3 shows glass compositions of Examples 12 to 16 (Examples of the present invention).
Materials of respective components were prepared so as to be the desired composition, and heated and melted in a platinum crucible at a temperature of from 1,500 to 1,600° C. for 4 hours. At the time of melting the glass, a platinum stirrer was inserted, and the molten glass was stirred for 2 hours to homogenize the glass. Then, the glass melt was cast, annealed and then polished to obtain a glass plate having a thickness of 2.8 mm.
With respect to the glass thus obtained, the glass composition (unit: mass %), the thermal expansion coefficient (α, u...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com