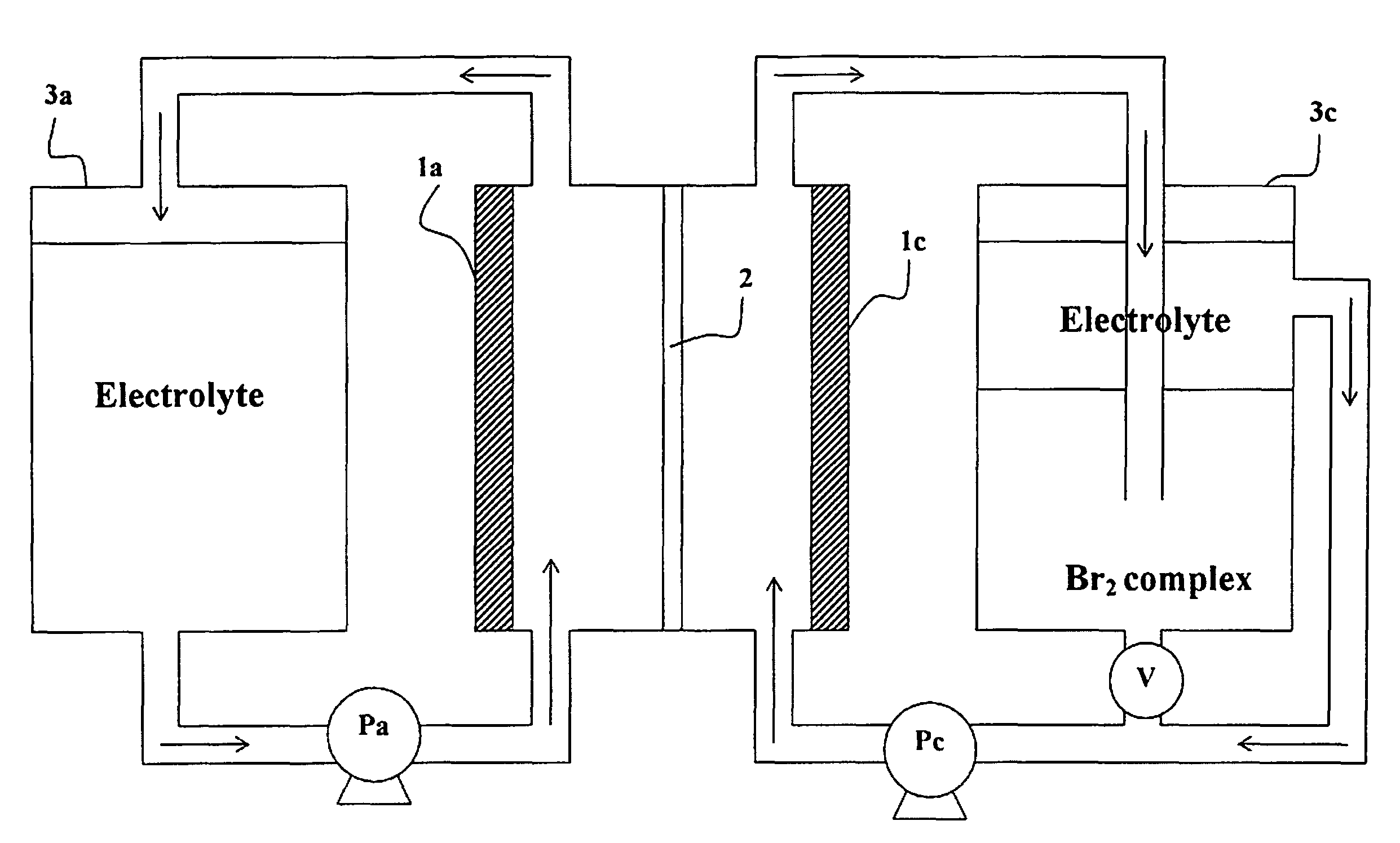
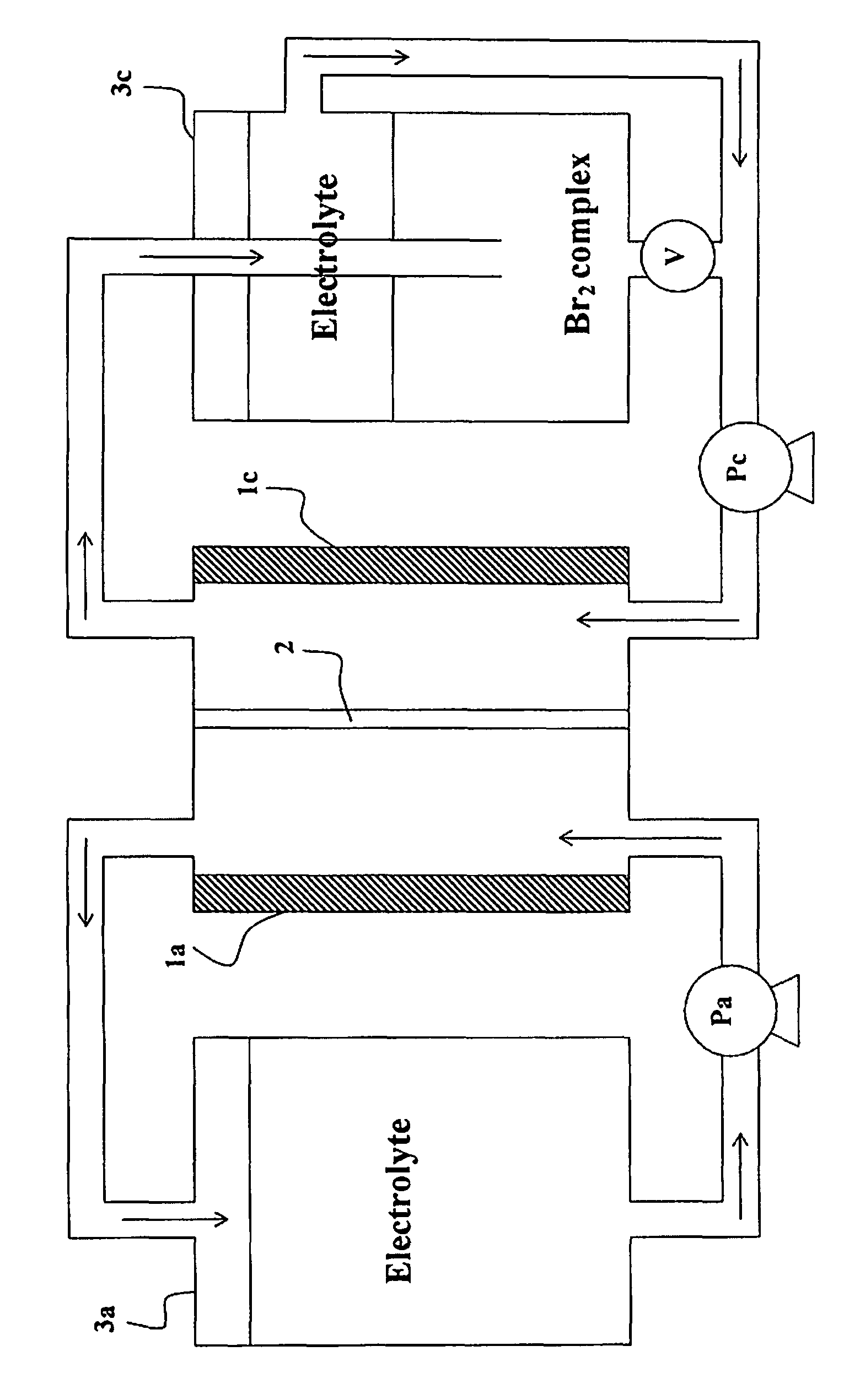
Method of operating metal-bromine cells
a technology of metal bromine and cell, applied in the direction of electrolysis components, electrical equipment, electrochemical generators, etc., can solve the problems of troublesome operation, troublesome operation, and easy volatile liquid of molecular bromine, and achieve the effect of convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation 1
[0028]An electrolyte solution was prepared by charging into an Erlenmeyer flask the following ingredients:[0029]1) Zinc bromide brine (672 g of 76% w / w aqueous ZnBr2 solution, commercially available from ICL-IP).[0030]2) Zinc chloride brine (74 g of 50% w / w aqueous ZnCl2 solution, commercially available from ICL-IP).[0031]3) MEP (commercially available from ICL-IP as 65% w / w aqueous solution); the concentration of the MEP in the electrolyte solution was 0.5M.[0032]4) MEM (commercially available from ICL-IP as 65% w / w aqueous solution); the concentration of the MEM in the electrolyte solution was 0.5M.[0033]4) An aqueous solution of hydrogen bromide (about 7-8 g of 48% w / w solution, commercially available from ICL-IP.[0034]5) Deionized water, up to 1000 g.
[0035]The procedure set forth above was repeated to produce electrolyte solutions which were used in the following examples. The pH values of the resultant electrolyte solutions were about 2.4 (±0.5).
example 1
Bromide source and acid: HBr
Oxidizer: H2O2
[0036]To 1000 g of an electrolyte solution containing ZnBr2, ZnCl2, HBr and MEP / MEM mixture in an Erlenmeyer flask, were added consecutively under stirring at 22° C. hydrobromic acid (20 g of an aqueous 48% HBr solution) and hydrogen peroxide (3.28 g of 52% H2O2 solution). The electrolyte solution was stirred in the closed flask at said temperature for 24 hours. The electrolyte solution was sampled in order to measure the bromine concentration at 2, 4, 18 and 24 hours after the beginning of the reaction. The concentration of bromine, which was measured in the electrolyte solution 24 hour after the beginning of the reaction, was about 0.8% (w / w). The measurements were carried out using either UV-vis absorption spectroscopy (against a calibration graph) or iodometric titration.
example 2
Bromide source and acid: HBr
Oxidizer: zinc peroxide (as ZnO2 / ZnO mixture)
[0037]To 1000 g of an electrolyte solution containing ZnBr2, ZnCl2, HBr and MEP / MEM in an Erlenmeyer flask, were added consecutively under stirring at 22° C. hydrobromic acid (7 g of an aqueous 48% HBr solution) and a 1:1 mixture of ZnO2 / ZnO (1.3 g). The electrolyte solution was stirred in the closed flask at said temperature for four hours. The electrolyte solution was sampled 1, 2, and 4 hours after the beginning of the reaction in order to measure the concentration of molecular bromine. The bromine content of the electrolyte solution after four hours was ˜0.1% (measured using the techniques set forth in Example 1).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water, soluble | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com