Device for reading an image having a common semiconductor layer
a semiconductor layer and image technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, radio frequency controlled devices, electrical devices, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to effectively take out the carriers generated in the semiconductor by light irradiation to the outside, the compactness and lightweight of the image reading device has been further required, and the effect of improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
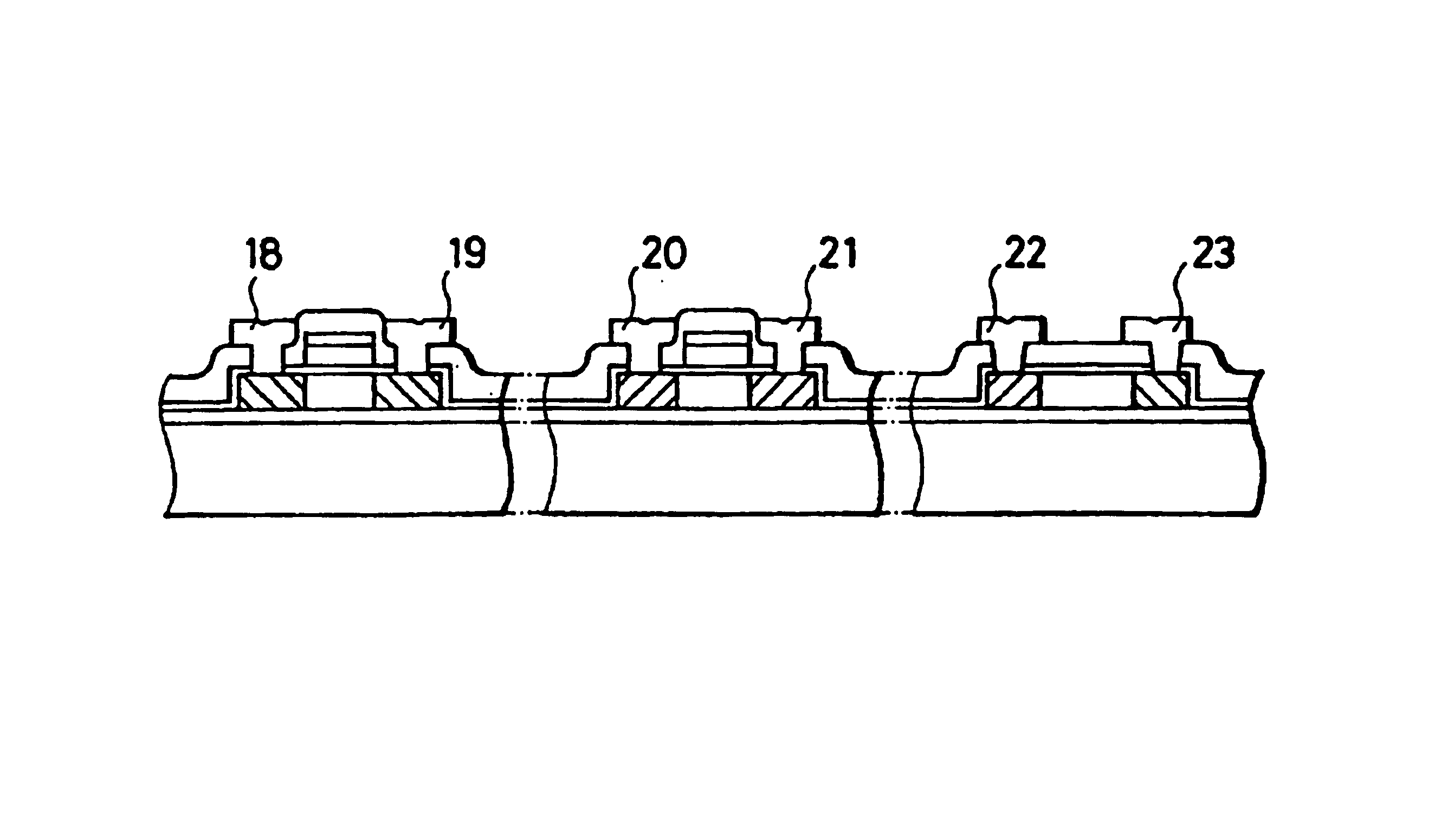
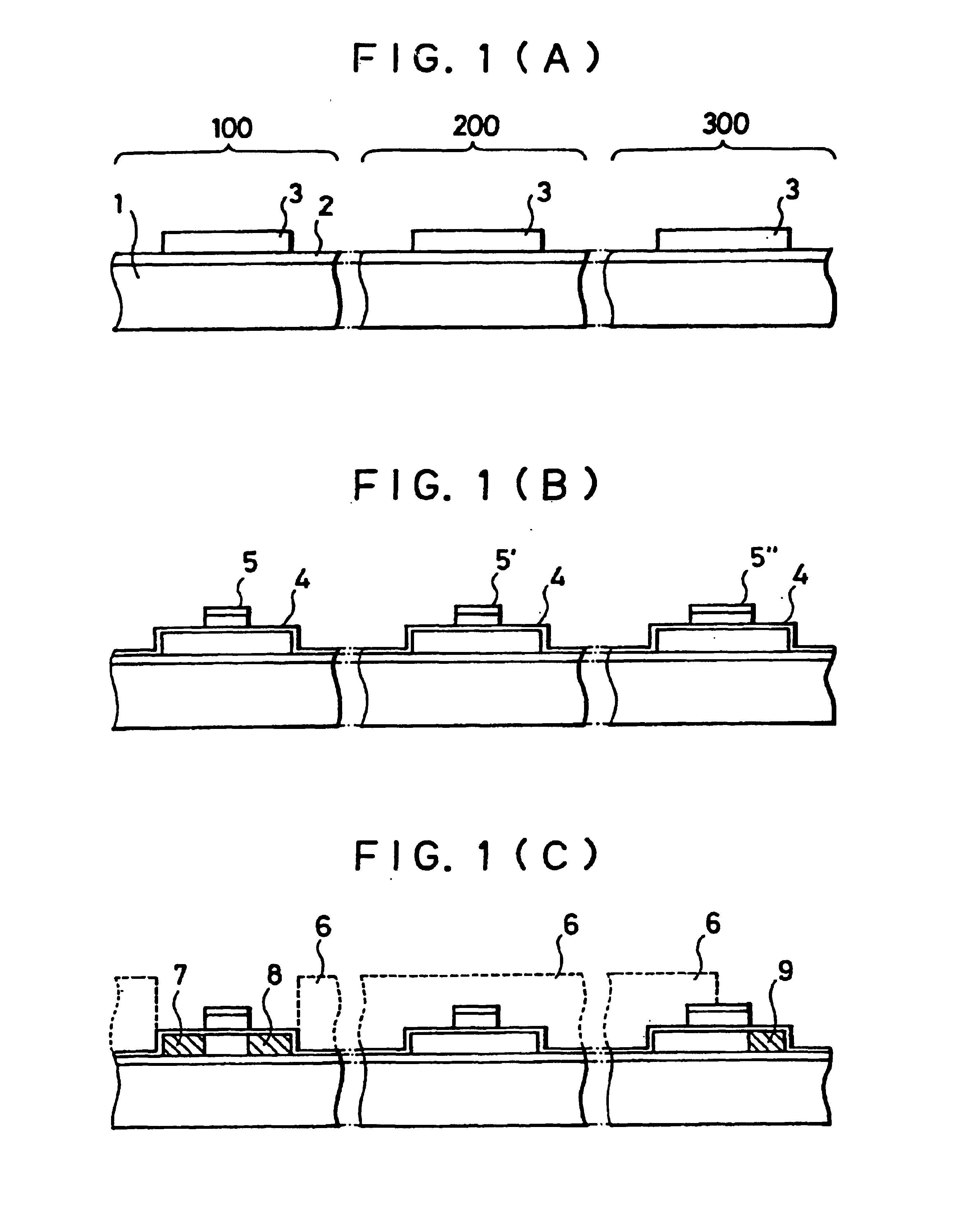
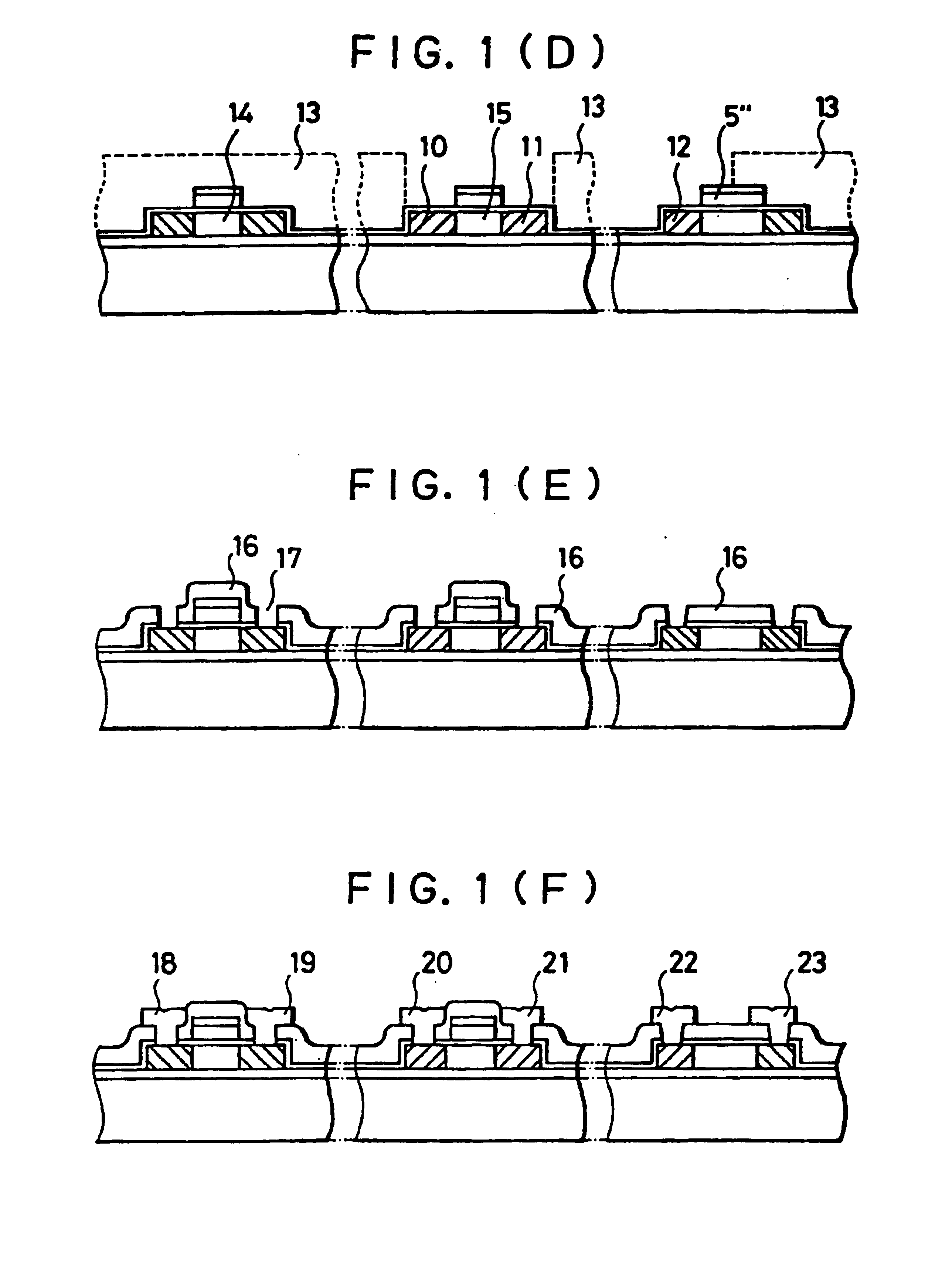
[0035]FIGS. 1(A) to 1(F) are longitudinal-sectional views showing a manufacturing process for an image reading device according to this invention, and in particular a manufacturing process for a photoelectric conversion device portion and P-type and N-type TFT portions.
[0036]In FIG. 1(A), a substrate 1 comprises a conductive or insulating substrate. For example, pottery, ceramic or glass material is used as a substrate in this embodiment. The reason for utilization of these materials resides in that these materials have low cost, high mechanical strength and heat-resistance for a film forming process.
[0037]In FIG. 1, reference numerals 100, 200 and 300 represent a P-channel TFT (P-type thin film transistor) portion, an N-channel TFT (N-type thin film transistor) portion and a photoelectric conversion device portion, respectively. The substrate 1 comprises glass material such as AN glass, Pyrex glass or the like which has a heat-resistance against a thermal process at a temperature o...
second embodiment
[0067]FIG. 2 shows another embodiment of the photoelectric conversion device portion of the image reading device, which has substantially the same structure as that of the first embodiment, except that an amorphous silicon semiconductor film 24 of 3000 Å in thickness is further formed on a light-irradiating surface side of the semiconductor film 3. The other film-forming processes are identical to those of the first embodiment.
[0068]The amorphous silicon semiconductor film 24 has a larger absorption coefficient than that of the semiconductor film 3. Accordingly, upon light-irradiation, a large amount of carriers are produced in the amorphous silicon semiconductor film 24, and then drift through the semiconductor film 3 and are outputted through the positive and negative electrodes to the outside.
[0069]At the same time, carriers are also produced in the semiconductor film 3. The photosensitivity of the semiconductor film 3 is dependent on the wavelength of the irradiated light. There...
third embodiment
[0072]The image reading device of this third embodiment has substantially the same construction as the first embodiment, except for the following point.
[0073]Only the N-type TFT includes the same semiconductor film as used for the photoelectric conversion device, and is formed simultaneously with the formation of the N-type impurity region of the photoelectric conversion device 300. At the time when the P-type impurity region is formed in the photoelectric conversion device portion 100, the TFT portion is masked by a photoresist, and thus no P-type impurity is doped. In this embodiment, unlike the complementary type of TFT, it is not necessary to coincide Vth between the P-type TFT and the N-type TFT. Accordingly, a permissible range for the manufacturing process is broadened.
[0074]In the embodiments as described above, the light is irradiated from an opposite side to the substrate. However, the light-irradiating direction is not limited to the above direction, and the light may be ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com