Run to run control process for controlling critical dimensions
a control process and critical dimension technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, measurement devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as speed performance and power consumption of circuits, loss of linewidth control including the entire loss, contamination with airborne particles and air bubbles, etc., to achieve substantially improved control of critical dimension uniformity, improve manufacturability and control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
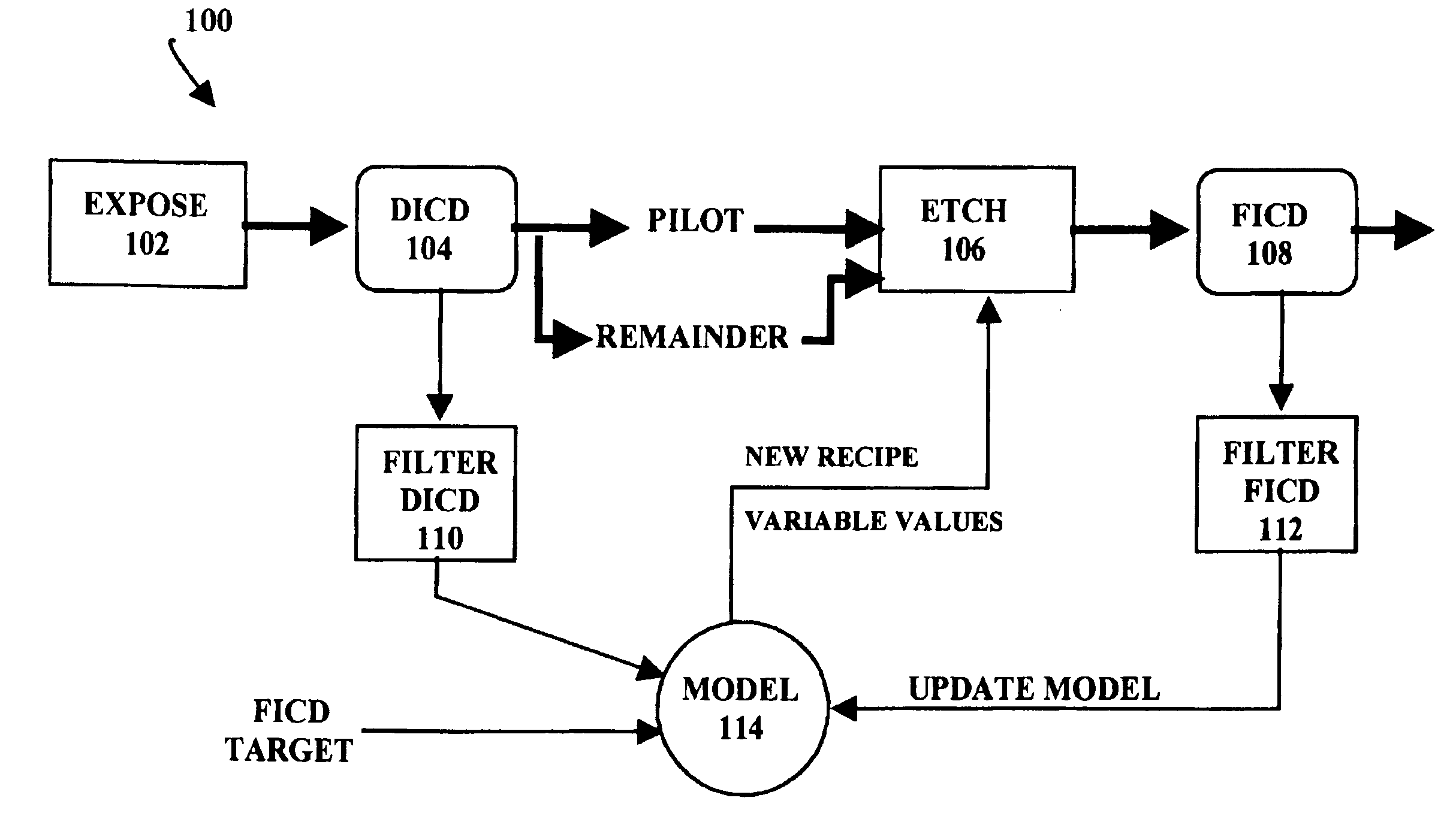
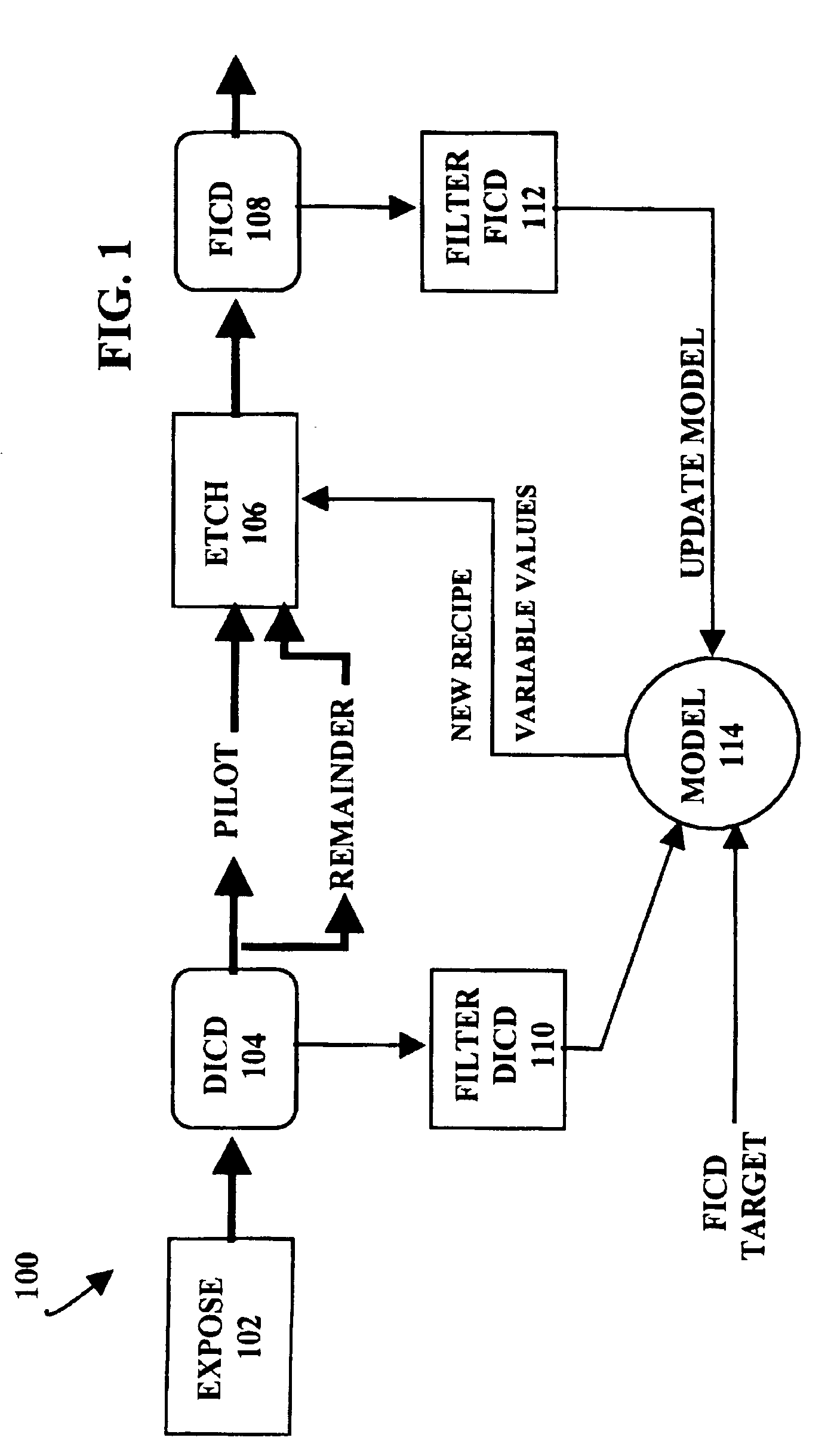
[0023]Referring to FIG. 1, a flow chart illustrates a control method for controlling critical dimensions in a semiconductor fabrication process 100 by adjusting the fabrication parameters or “recipe” for a photoresist etch step 106 previous to a polysilicon gate etch step in the fabrication process 100. In particular, the critical dimensions are controlled using photoresist etch time as a control variable to drive the critical dimensions to a target value.
[0024]In overview, the fabrication process 100 involves selection of one or more test wafers, called “pilot” wafers from an entire lot of wafers. The pilot wafers are tested to characterize the lot of wafers, processed through the photoresist etch step 106 using a nominal, average, or moving average processing recipe, and measured in a Final Inspection Critical Dimensions step 108. The results from the pilot lot tests are applied to update a process model 114 which is used to adjust the etch recipe for the remaining wafers in the l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com