Method for manufacturing stacked body used for COF substrate,
A manufacturing method and technology of laminates, which are applied in the processing of insulating substrates/layers, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, printed circuit manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to process micro-processing, uneven thickness, and good circuit linearity, etc. Achieve the effect of high adhesion and excellent electromigration resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
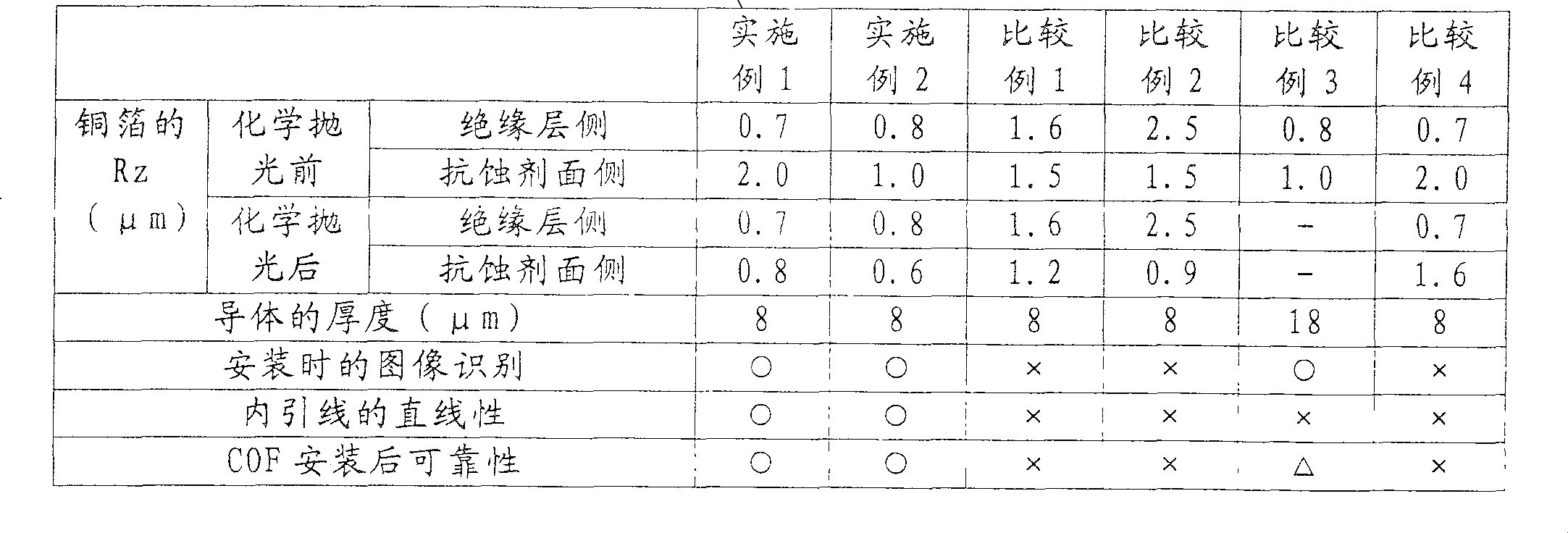
Examples
Synthetic example 1
[0036] Charge N-methylpyrrolidone in a reaction vessel equipped with a thermocouple and stirrer and capable of introducing nitrogen. After immersing the reaction container in the ice water put into the container, put pyromellitic anhydride (PMDA) into the reaction container, and then put 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether (DAPE) and 2'-methoxy - 4,4'-Diamino-N-benzoanilide (MABA). The total amount of monomers charged was 15 wt%, the molar ratio of each diamine (MABA:DAPE) was 60:40, and the molar ratio of acid anhydride and diamine was 0.98:1.0. Then, the stirring was continued, and when the temperature in the reaction container reached the range of room temperature ± 5°C, the reaction container was taken out from the ice water. Stirring was continued for 3 hours at room temperature, and the solution viscosity of the obtained polyamic acid was 15000 cps.
Synthetic example 2
[0038] Charge N-methylpyrrolidone in a reaction vessel equipped with a thermocouple and stirrer and capable of introducing nitrogen. After immersing the reaction container in the ice water put into the container, put PMDA / 3,3',4,4'-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BTDA) into the reaction container, and then put 4,4'-diamino Diphenyl ether (DAPE). The total amount of monomers charged was 15 wt%, and the molar ratio of acid anhydride and diamine was 1.03:1.0. Then, the stirring was continued, and when the temperature in the reaction container reached the range of room temperature ± 5°C, the reaction container was taken out from the ice water. Stirring was continued for 3 hours at room temperature, and the solution viscosity of the obtained polyamic acid was 3200 cps.
Synthetic example 3
[0040] Charge N-methylpyrrolidone in a reaction vessel equipped with a thermocouple and stirrer and capable of introducing nitrogen. After immersing the reaction container in the ice water put into the container, put 3,3',4,4'-diphenylsulfonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (DSDA) and PMDA into the reaction container, and then put 1,3-bis (4-Aminophenoxy)benzene (TPE-R). The total amount of monomers charged was 15 wt%, the molar ratio of each acid anhydride (DSDA:PMDA) was 90:10, and the molar ratio of acid anhydride and diamine was 1.03:1.0. Then, the stirring was continued, and when the temperature in the reaction container reached the range of room temperature ± 5°C, the reaction container was taken out from the ice water. Stirring was continued for 3 hours at room temperature, and the solution viscosity of the obtained polyamic acid was 3200 cps.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com