A method for vacuum scattering and joining-up carbon-carbon composite material
A carbon composite material and vacuum diffusion technology, which is applied in the field of carbon/carbon composite material welding, can solve problems such as high connection temperature, poor joint performance, and large metal deformation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
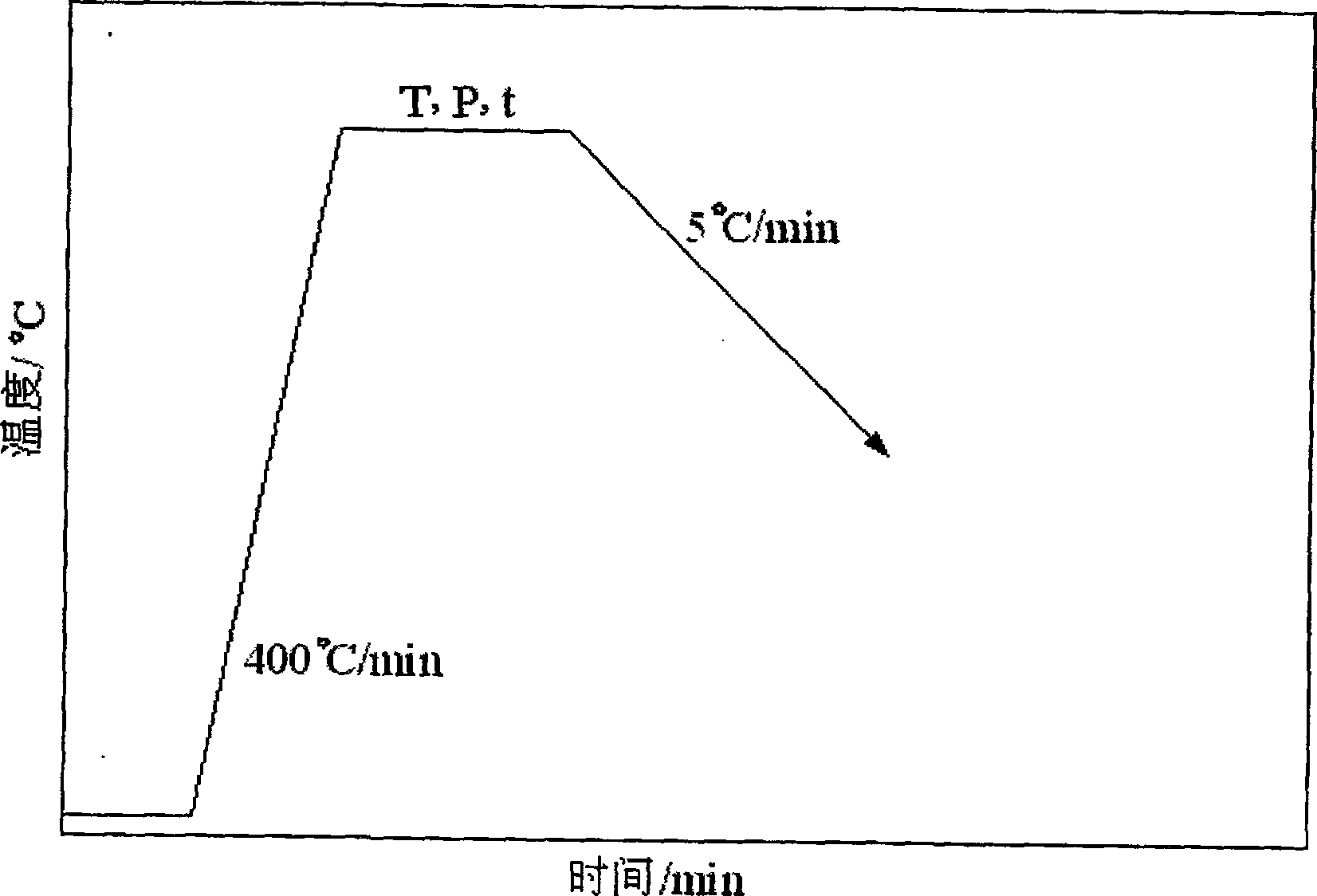
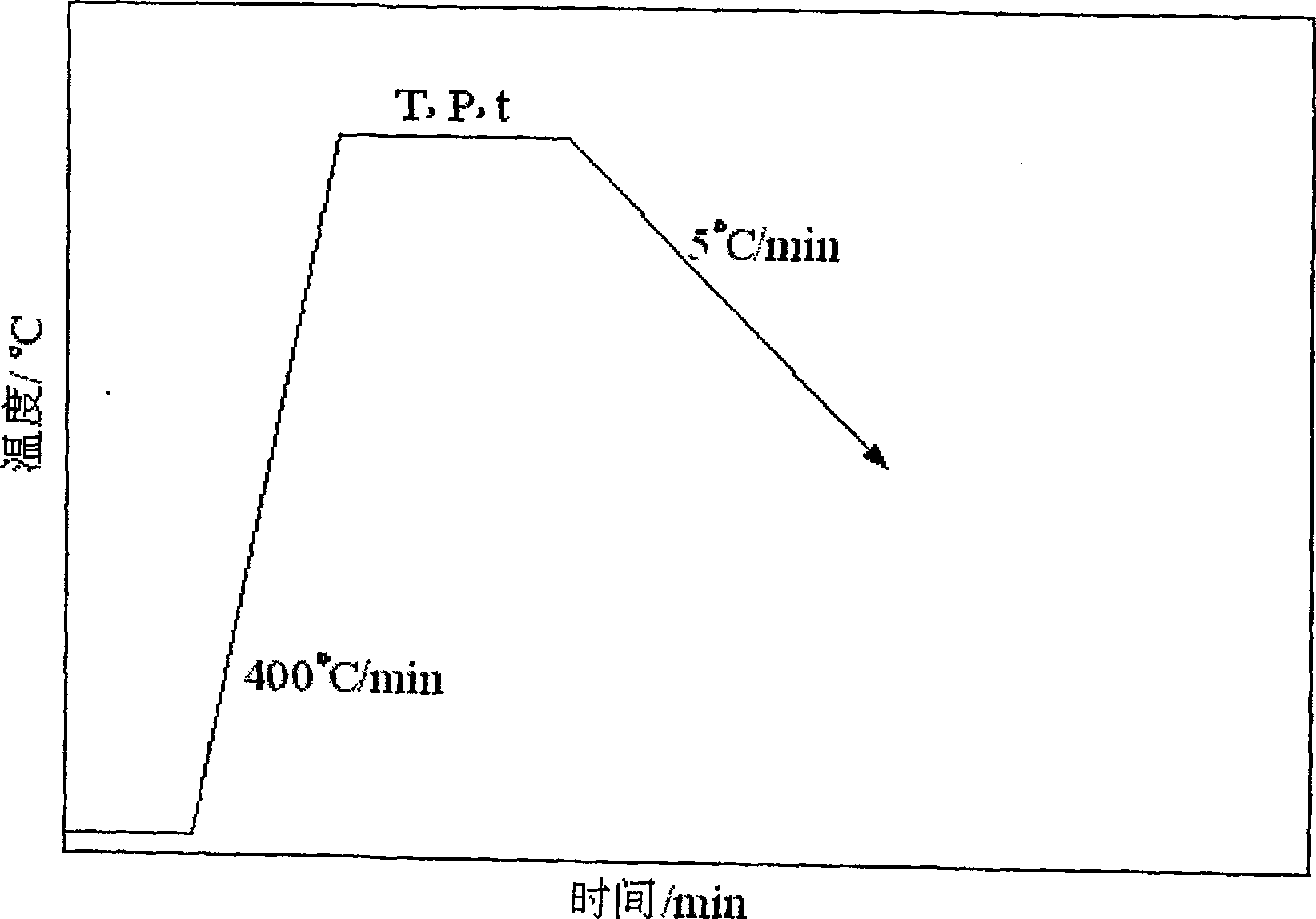
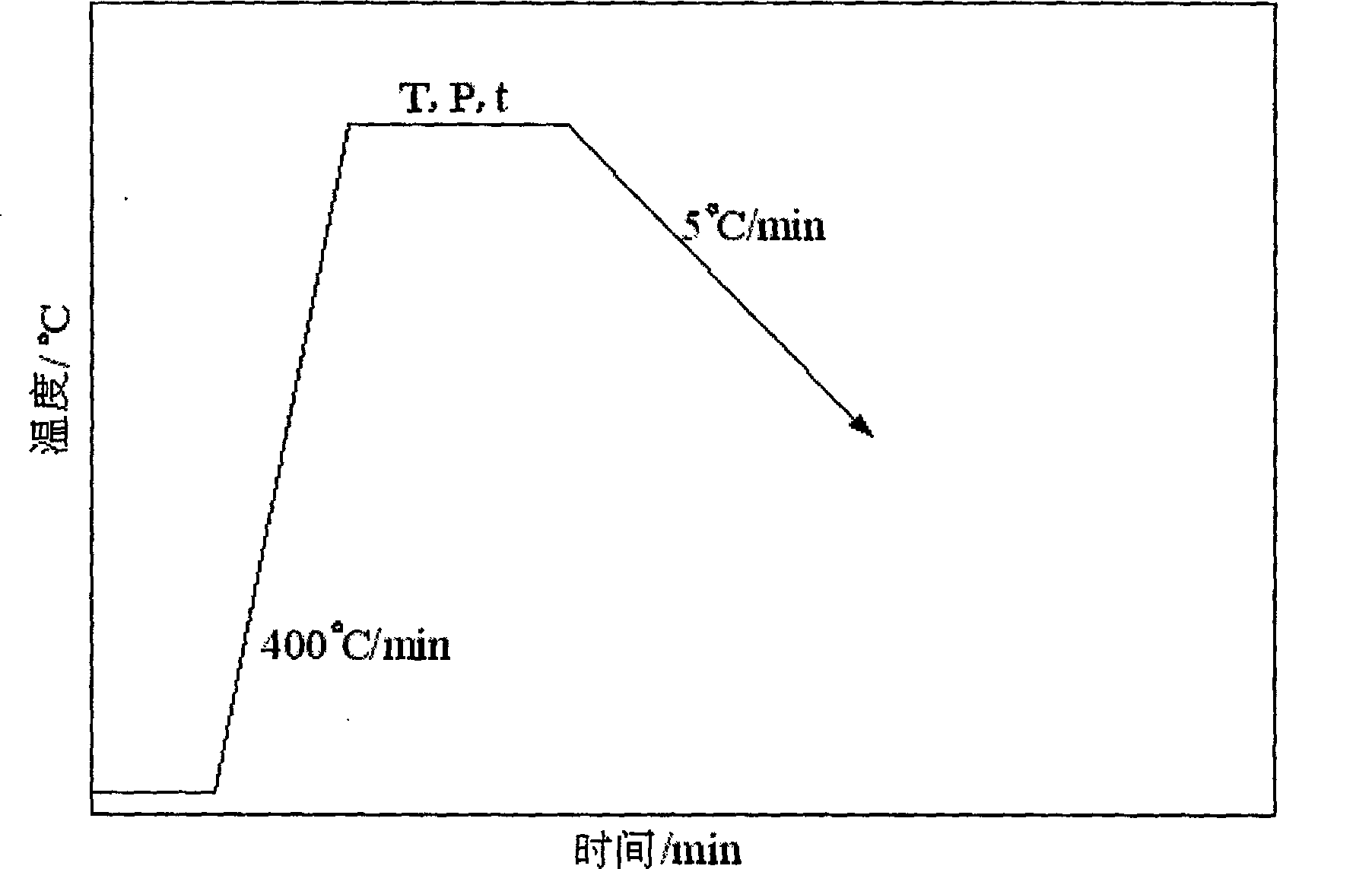
[0008] Specific embodiment 1: The method of vacuum diffusion bonding carbon / carbon composite material in this embodiment is implemented in the following steps: 1. The surface of the base material is cleaned before diffusion bonding; 2. The diffusion bonding intermediate layer is evenly placed to be welded The connecting surface of the base material; the diffusion bonding intermediate layer is hydrogenated titanium or titanium alloy foil, and the thickness of the diffusion bonding intermediate layer is 30-100μm; 3. The clamped weldment is placed in a vacuum diffusion welding machine for heating, The vacuum degree is 1.33×10 -3 ~4.0×10 -3 Diffusion bonding is carried out under Pa vacuum conditions; 4. After the welding is completed, the weldment is decompressed when the temperature is lowered to 100°C under the original vacuum condition, and the weldment is taken out when the temperature is lowered to room temperature.
[0009] In this implementation method, the diffusion bonding pr...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0010] Specific embodiment two: this embodiment is different from specific embodiment one in that in step one, the surface of the base material is cleaned by physical cleaning, chemical cleaning or first physical cleaning and then chemical cleaning; the physical cleaning is followed by 400 # , 500 # , 600 # , 800 # And 1000 # The metallographic sandpaper is polished step by step; the chemical cleaning is to prepare the corresponding corrosive liquid according to the difference of the base material to remove the adsorption layer, impurities or oxide film on the surface of the base material, and then wipe the surface of the base material to be welded with acetone or remove the base material. The material is cleaned by ultrasonic in the acetone solution. The other steps and parameters are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0011] Specific embodiment three: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the thickness of the diffusion bonding intermediate layer in step two is 30-80 μm. The other steps and parameters are the same as in the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com