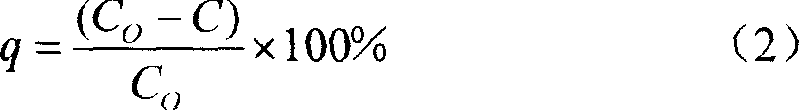Poly (m-phenylene diamine) used as mercury ion adsorbent
A technology of poly-m-phenylenediamine and mercury ions, which is applied in the direction of adsorption of water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc. It can solve the problem of dependence on import of monomers, high preparation costs, and cumbersome synthesis steps, etc. problems, to achieve the effects of shortened equilibrium adsorption time, high saturated adsorption capacity, and simple synthesis process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Embodiment 1: prepare polym-phenylenediamine
[0015] Dissolve 0.08mol (8.652g) of monomeric m-phenylenediamine in 200mL of distilled water, sonicate for 3 to 5 minutes to promote its full dissolution, then place the monomer solution in a water bath at 30°C and equilibrate for half an hour. 0.08 mol of oxidant ammonium persulfate (mass 18.256 g) was dissolved in 100 mL of distilled water, which was also maintained at 30°C. This ammonium persulfate solution was added to the above monomer solution. React for 24 hours, filter with suction, and wash the product in the funnel with distilled water until it is washed with BaCl 2 The solution was tested to be free of sulfate ions. After washing, it was sucked dry, and the product was dried at 50° C. for 3 days to obtain poly-m-phenylenediamine. Weighed and calculated yield was 74.3%.
[0016] The present invention adopts static adsorption method (or claims batch method) to utilize polym-phenylenediamine to adsorb mercury io...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Take 50 mg of poly-m-phenylenediamine and put it into 25 mL of mercuric nitrate solution at 30 °C with an initial concentration of 1.99 mmol / / L and stir and adsorb for 1 minute. After filtering through filter paper, titrate the content of mercury ions in the filtrate by Volhard method. Under this condition, the adsorption rate is 62.2%, and the adsorption capacity is 124.1 mg / g. Under the same conditions, changing the adsorption time to 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, and 30 minutes respectively, the obtained adsorption capacities were 164mg / g, 194.3mg / g, 197mg / g, 199mg / g, and the adsorption rates were 82.2%, 97.4%, 98.7%, 99.6%.
[0025] Thus, the equilibrium adsorption time when polym-phenylenediamine adsorbs mercury ions with an initial mercury ion concentration of 1.99mmol / / L is 10 minutes, and the adsorption kinetics simulation is carried out with the pseudo-second-order kinetic equation, and the simulated correlation coefficient is 0.9996, The standard deviati...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Take 50 mg of poly-m-phenylenediamine and put it into 25 mL of mercuric nitrate solution at 30 °C with an initial concentration of 4.00 mmol / / L and stir and adsorb for 1 minute. After filtering through filter paper, titrate the content of mercury ions in the filtrate by the Volhard method. The results show that, Under this condition, the adsorption rate is 66.05%, and the adsorption capacity is 265.0 mg / g. Under the same conditions, changing the adsorption time to 5 minutes, 15 minutes, 30 minutes, and 120 minutes respectively, the obtained adsorption capacities were 319mg / g, 373mg / g, 380mg / g, 380mg / g, and the adsorption rates were 79.5%, 93.1%, respectively. %, 94.6%, 94.6%.
[0028] Thus, the equilibrium adsorption time when polym-phenylenediamine adsorbs mercury ions with an initial mercury ion concentration of 4.00 mmol / / L is 20 minutes, and the adsorption kinetics simulation is carried out with the pseudo-second-order kinetic equation, and the simulated correlation...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com