Use of inorganic composite gelatinization material and using method
An inorganic composite and cementitious material technology, applied in the field of inorganic composite materials, can solve the problems of poor impact resistance, high cost, short service life, etc., and achieve the effects of safe and reliable fire resistance, fast construction, and long weather resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1 An inorganic composite gelling material, a colloidal material obtained by mixing the following raw materials (in parts by weight):
[0035] 100 parts of light burnt magnesium with active MgO content greater than 60%, 90 parts of brine with a specific gravity of 1.22, 50 parts of talcum powder with a fineness greater than 160 mesh, and 1.5 parts of ferrous sulfate. Brine is made from industrial magnesium chloride (MgCl 2 Content ≥ 45%) is prepared by adding appropriate amount of water.
[0036] The use of the above-mentioned inorganic composite gelling material is used to make the hardened layer on the surface of the insulation layer of insulation pipes, ventilation pipes, heating pipes, heat preservation containers, cold storage, building walls, etc.
[0037] A method for using an inorganic composite gelling material, comprising the following steps: (1) smoothing the surface of a pipe or container insulation layer and then cleaning it; (2) wrapping the ins...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2 An inorganic composite gelling material, a colloidal material obtained by mixing the following raw materials (in parts by weight):
[0042] 100 parts of lightly burned magnesium with an active MgO content greater than 60%, 80 parts of brine with a specific gravity of 1.20, 30 parts of talc powder with a fineness greater than 160 mesh, 2 parts of a mixture of ferrous sulfate and sodium phosphate, and expanded perlite powder with a fineness of 80 mesh 10 servings. Brine is made from industrial magnesium chloride (MgCl 2 Content ≥ 45%) is prepared by adding appropriate amount of water.
[0043] The purposes of this material are with embodiment 1.
[0044] A method for using an inorganic composite gelling material, comprising the following steps: (1) cleaning the surface of a pipeline or a container insulation layer after leveling; Wrap the insulation layer with glass fiber mesh; (3) coat the glass fiber mesh wrapping layer with thinner inorganic composite c...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Embodiment 3 An inorganic composite gelling material, a colloidal material obtained by mixing the following raw materials (in parts by weight):
[0049] 100 parts of light burnt magnesium with active MgO content greater than 60%, 95 parts of brine with a specific gravity of 1.24, 40 parts of talcum powder with a fineness greater than 160 mesh, 1.4 parts of ferrous sulfate, sodium phosphate and sodium polyphosphate mixture, 0.5 parts of red dye . Brine is made from industrial magnesium chloride (MgCl 2 Content ≥ 45%) is prepared by adding appropriate amount of water.
[0050] The material can be applied on the outermost surface of the thermal insulation hardened layer to enhance the sense of color and achieve the effect of beautifying decoration.
PUM
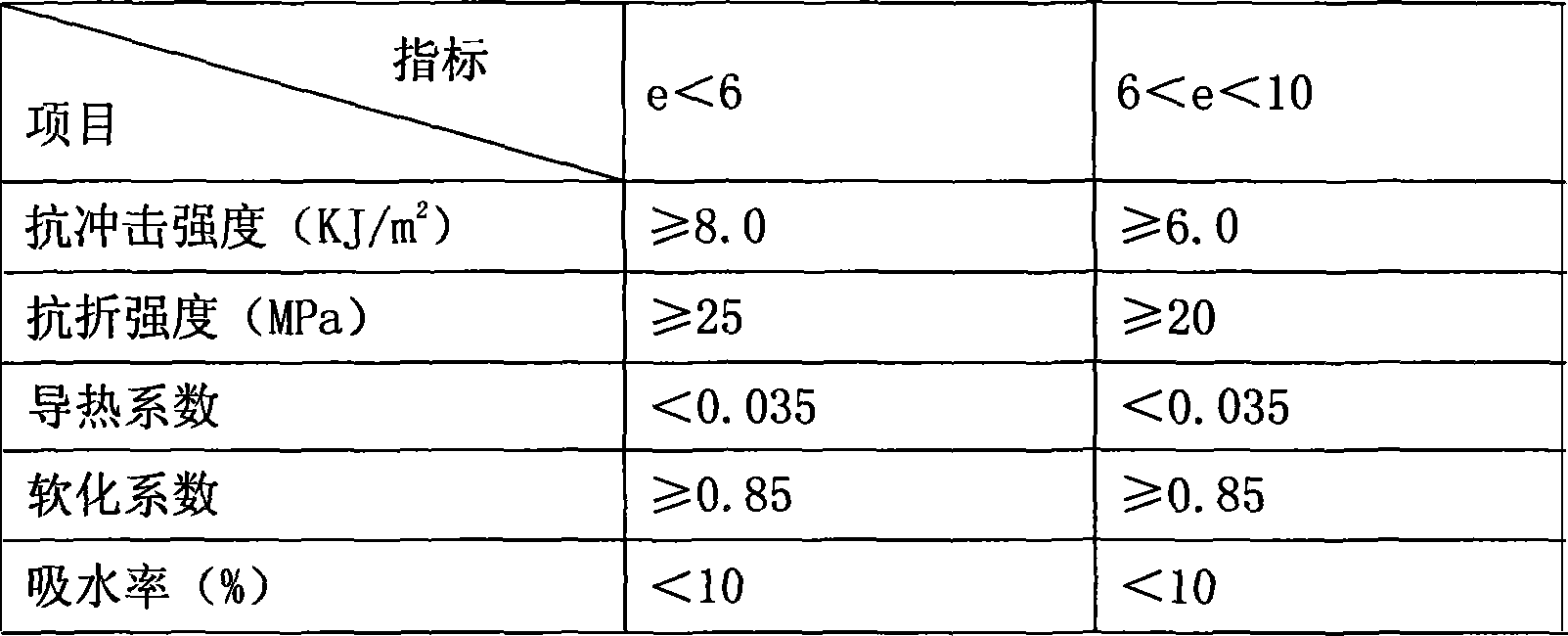
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| impact strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com