Process of preparing sodium chromate product without calcium
A preparation process, calcium sodium chromate technology, applied in chromate/dichromate and other directions, can solve the problems of high cost, large slag output, difficult to handle, etc., and achieves low production cost, low environmental pollution, and equipment. small investment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
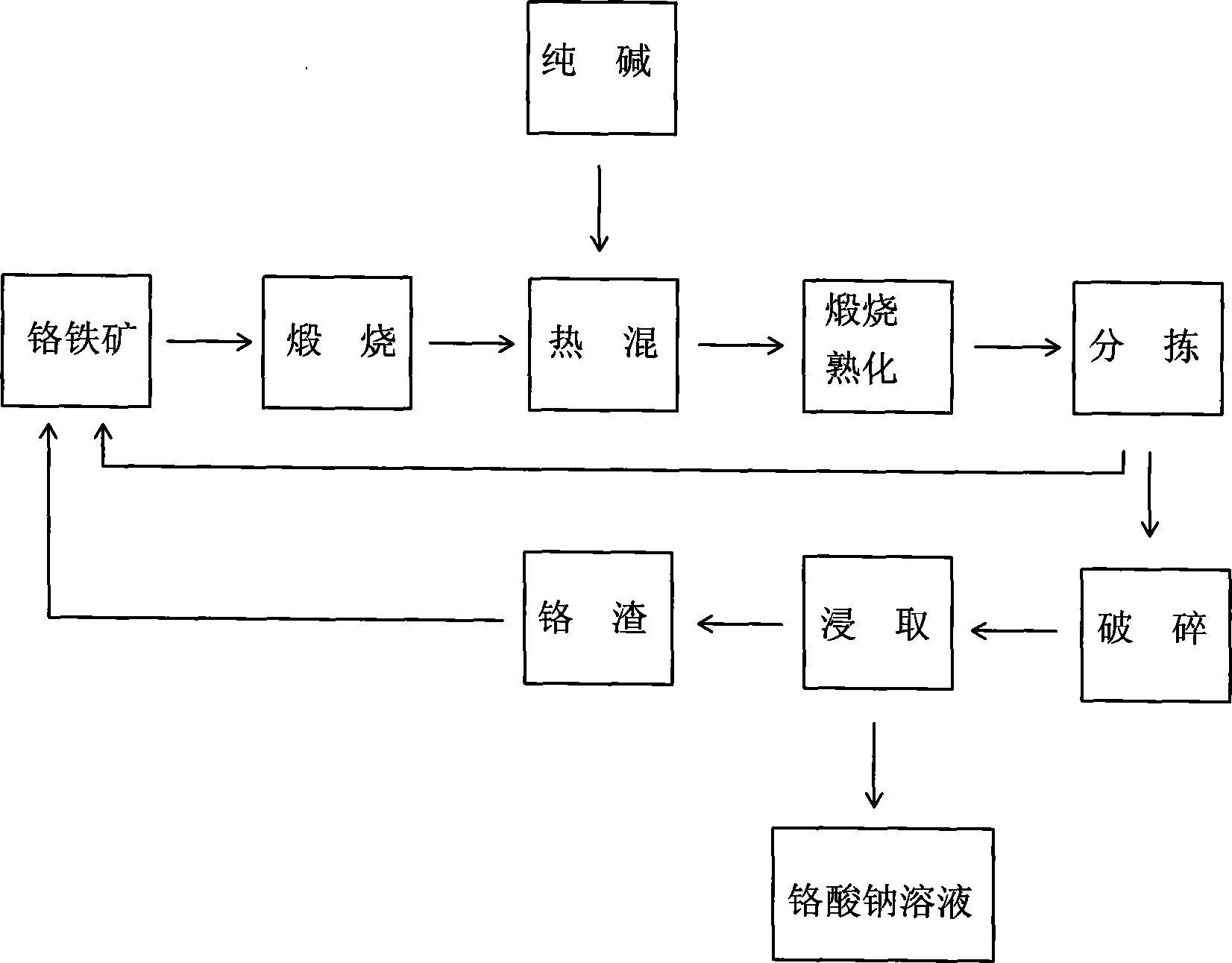
[0015] Send 1,000 kg of 150-mesh chromite powder into the rotary kiln and calcinate at 1250°C for 30 minutes; the calcined chromite powder is transferred out and mixed with 720 kg of soda ash; the mixed chromite and soda ash mixture is re- Send it to the rotary kiln for calcination and slaking; then sort out the unreacted materials in the mixture after calcination and slaking and mix them with chromite for repeated use; crush the slags of the slaking good materials into small particles of 3 meshes; The material is soaked in water, stirred, precipitated, and the slag is removed to obtain a sodium chromate solution; the chromium slag after the material is leached and precipitated can be mixed with chromite ore and reused.
Embodiment 2
[0017] Send 1,000 kg of 200-mesh chromite powder into the rotary kiln and calcinate at 1300°C for 90 minutes; transfer the calcined chromite powder and mix it with 800 kg of soda ash; mix the chromite and soda ash mixture again Send it to the rotary kiln for calcination and slaking; then sort out the unreacted materials in the mixture after calcination and slaking and mix them with chromite for reuse; crush the slags of the slags into 8-mesh small particles; The material is soaked in water, stirred, precipitated, and the slag is removed to obtain a sodium chromate solution; the chromium slag after the material is leached and precipitated can be mixed with chromite ore and reused.
Embodiment 3
[0019] Send 1,000 kg of 160-mesh chromite powder into the rotary kiln and calcinate at 1260°C for 40 minutes; transfer the calcined chromite powder and mix it with 750 kg of soda ash; mix the chromite and soda ash mixture again Send it to the rotary kiln for calcination and slaking; then sort out the unreacted materials in the mixture after calcination and slaking and mix them with chromite for repeated use; crush the slags of the slags into 5-mesh small particles; The material is soaked in water, stirred, precipitated, and the slag is removed to obtain a sodium chromate solution; the chromium slag after the material is leached and precipitated can be mixed with chromite ore and reused.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com